LizardSquad DDoS Stresser suffers from cross site scripting and session tampering vulnerabilities.
Monthly Archives: January 2015
RedaxScript 2.1.0 Privilege Escalation
RedaxScript version 2.1.0 suffers from a privilege escalation vulnerability.
Bugtraq: ESA-2015-004: EMC M&R (Watch4Net) Multiple Vulnerabilities
ESA-2015-004: EMC M&R (Watch4Net) Multiple Vulnerabilities
Bugtraq: [SECURITY] [DSA 3133-1] privoxy security update
[SECURITY] [DSA 3133-1] privoxy security update
Bugtraq: [SECURITY] [DSA 3134-1] sympa security update
[SECURITY] [DSA 3134-1] sympa security update
Bugtraq: [security bulletin] HPSBUX03235 SSRT101750 rev.1 – HP-UX Running BIND, Remote Denial of Service (DoS)
[security bulletin] HPSBUX03235 SSRT101750 rev.1 – HP-UX Running BIND, Remote Denial of Service (DoS)
Terror on the streets leads to terror in cyberspace
Earlier this January, the Charlie Hebdo attacks in Paris shocked millions across the globe. News channels brought us almost 24 hour coverage of events and are still analyzing the effects, some weeks later.
However, there’s more to the aftermath than first meets the eye. France has received a massive spike in detected cyber-attacks, reporting over 19,000 attacks since events unfolded in the capital.
This cyber-terrorism represents an often ‘hidden’ side to politically motivated conflict and are neither new nor unique.
For many years, we have witnessed a close correlation between tensions in the middle-east and the number of cyber-attacks detected in conflict zones.
Political conflicts between Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt and Palestine regularly trigger waves of cyber-attacks such as website defacements and Denial of Service attacks (DDoS).
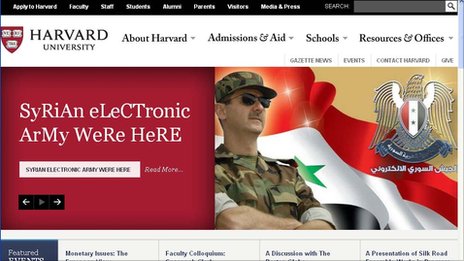
Here are just a few examples of this cyber-terrorism:
- Harvard website hacked by Syria protesters
- Turks hack Israeli Facebook accounts over Gaza blockade incident
- With Gaza Conflict, Cyberattacks Come Too
- Syrian Electronic Army attacked most major Qatar websites
Just as street-level conflict can be a way to express opinion and get your voice heard; for others, cyber-attacks are the most powerful protest tool available.
“these attacks are usually unsophisticated and are not motivated by theft of data or money”.
In my experience, these attacks are usually unsophisticated and are not motivated by theft of data or money. Instead, they are brought about simply by an individual or group’s need to voice their opinions.
So as Europe experiences a wave of terror attacks, what can it learn from the middle-east and its longstanding tensions?
For one, there is a very real correlation between civil conflicts and attacks in cyberspace, although thankfully not visa-versa.
Second, consumers and businesses should make sure they protect themselves in cyberspace once terror or political conflicts hit the streets.
Visit our AVG Academy on YouTube for helpful tips on protecting yourself online.
CESA-2015:0067 Critical CentOS 7java-1.7.0-openjdk Security Update
CentOS Errata and Security Advisory 2015:0067 Critical Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2015-0067.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) x86_64: 07dd8d83088ca16e50b7b588cdfcc2b818347385581f26829eb4302e037045dd java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.75-2.5.4.2.el7_0.x86_64.rpm be71bbff840faed621bae1246be3553c6119aeae9c3d66dbd1df0909f9d3aa3f java-1.7.0-openjdk-accessibility-1.7.0.75-2.5.4.2.el7_0.x86_64.rpm 980d1b9c1150b2d4ee1170fdb1b8446d3ac3b26a931c6a1cdc7679fea454db4e java-1.7.0-openjdk-demo-1.7.0.75-2.5.4.2.el7_0.x86_64.rpm 734982d0d1c631cd6463009d39956240cb744ab9da1e10ee3a9672782d6fa5a6 java-1.7.0-openjdk-devel-1.7.0.75-2.5.4.2.el7_0.x86_64.rpm 4513b70adcd367a8ba0541834c2407133e2c83159e54366aca7354d595a6c801 java-1.7.0-openjdk-headless-1.7.0.75-2.5.4.2.el7_0.x86_64.rpm 95ccbe3e0c9128042724bead079ec667b64469e989d9405681a3ba8dcb2b575d java-1.7.0-openjdk-javadoc-1.7.0.75-2.5.4.2.el7_0.noarch.rpm 78edf2de19914d18148159aa213565aabedd0609face4c533bfdb14a5e8657ce java-1.7.0-openjdk-src-1.7.0.75-2.5.4.2.el7_0.x86_64.rpm Source: 30e0061f31a4c3d43ccc7e6c509d160c68d81f702aa95685da4a4202efa607ef java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.75-2.5.4.2.el7_0.src.rpm
RHSA-2015:0068-1: Important: java-1.7.0-openjdk security update
Red Hat Enterprise Linux: Updated java-1.7.0-openjdk packages that fix multiple security issues are
now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.
Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having Important security
impact. Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base scores, which give
detailed severity ratings, are available for each vulnerability from the
CVE links in the References section.
CVE-2014-3566, CVE-2014-6585, CVE-2014-6587, CVE-2014-6591, CVE-2014-6593, CVE-2014-6601, CVE-2015-0383, CVE-2015-0395, CVE-2015-0407, CVE-2015-0408, CVE-2015-0410, CVE-2015-0412
RHSA-2015:0067-1: Critical: java-1.7.0-openjdk security update
Red Hat Enterprise Linux: Updated java-1.7.0-openjdk packages that fix multiple security issues are
now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and 7.
Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having Critical security
impact. Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base scores, which give
detailed severity ratings, are available for each vulnerability from the
CVE links in the References section.
CVE-2014-3566, CVE-2014-6585, CVE-2014-6587, CVE-2014-6591, CVE-2014-6593, CVE-2014-6601, CVE-2015-0383, CVE-2015-0395, CVE-2015-0407, CVE-2015-0408, CVE-2015-0410, CVE-2015-0412