CentOS Errata and Security Advisory 2015:0771 Important Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2015-0771.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) i386: b923092c5411b96e3732b1a9a3491a43fa9ded362b2dfb91a8280447ac7c899d thunderbird-31.6.0-1.el5.centos.i386.rpm x86_64: bc45f9ffc81cdee944d9616d921277f73841be88edc06ddb336cf93473ad0a69 thunderbird-31.6.0-1.el5.centos.x86_64.rpm Source: b77452b4fdd245dcc599fba4b0624a3ce8ab1dc4c8ea41544079cb9b8768b06b thunderbird-31.6.0-1.el5.centos.src.rpm
Monthly Archives: April 2015
USN-2553-1: LibTIFF vulnerabilities
Ubuntu Security Notice USN-2553-1
31st March, 2015
tiff vulnerabilities
A security issue affects these releases of Ubuntu and its
derivatives:
- Ubuntu 14.10
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 10.04 LTS
Summary
LibTIFF could be made to crash or run programs as your login if it opened a
specially crafted file.
Software description
- tiff
– Tag Image File Format (TIFF) library
Details
William Robinet discovered that LibTIFF incorrectly handled certain
malformed images. If a user or automated system were tricked into opening a
specially crafted image, a remote attacker could crash the application,
leading to a denial of service, or possibly execute arbitrary code with
user privileges. (CVE-2014-8127, CVE-2014-8128, CVE-2014-8129,
CVE-2014-8130)
Paris Zoumpouloglou discovered that LibTIFF incorrectly handled certain
malformed BMP images. If a user or automated system were tricked into
opening a specially crafted BMP image, a remote attacker could crash the
application, leading to a denial of service. (CVE-2014-9330)
Michal Zalewski discovered that LibTIFF incorrectly handled certain
malformed images. If a user or automated system were tricked into opening a
specially crafted image, a remote attacker could crash the application,
leading to a denial of service, or possibly execute arbitrary code with
user privileges. (CVE-2014-9655)
Update instructions
The problem can be corrected by updating your system to the following
package version:
- Ubuntu 14.10:
-
libtiff5
4.0.3-10ubuntu0.1
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS:
-
libtiff5
4.0.3-7ubuntu0.2
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS:
-
libtiff4
3.9.5-2ubuntu1.7
- Ubuntu 10.04 LTS:
-
libtiff4
3.9.2-2ubuntu0.15
To update your system, please follow these instructions:
https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Security/Upgrades.
In general, a standard system update will make all the necessary changes.
References
USN-2554-1: GnuPG vulnerabilities
Ubuntu Security Notice USN-2554-1
1st April, 2015
gnupg, gnupg2 vulnerabilities
A security issue affects these releases of Ubuntu and its
derivatives:
- Ubuntu 14.10
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 10.04 LTS
Summary
Several security issues were fixed in GnuPG.
Software description
- gnupg
– GNU privacy guard – a free PGP replacement - gnupg2
– GNU privacy guard – a free PGP replacement
Details
Daniel Genkin, Lev Pachmanov, Itamar Pipman, and Eran Tromer discovered
that GnuPG was susceptible to an attack via physical side channels. A local
attacker could use this attack to possibly recover private keys.
(CVE-2014-3591)
Daniel Genkin, Adi Shamir, and Eran Tromer discovered that GnuPG was
susceptible to an attack via physical side channels. A local attacker could
use this attack to possibly recover private keys. (CVE-2015-0837)
Hanno Böck discovered that GnuPG incorrectly handled certain malformed
keyrings. If a user or automated system were tricked into opening a
malformed keyring, a remote attacker could use this issue to cause GnuPG to
crash, resulting in a denial of service, or possibly execute arbitrary
code. (CVE-2015-1606, CVE-2015-1607)
In addition, this update improves GnuPG security by validating that the
keys returned by keyservers match those requested.
Update instructions
The problem can be corrected by updating your system to the following
package version:
- Ubuntu 14.10:
-
gnupg2
2.0.24-1ubuntu2.2
-
gnupg
1.4.16-1.2ubuntu1.2
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS:
-
gnupg2
2.0.22-3ubuntu1.3
-
gnupg
1.4.16-1ubuntu2.3
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS:
-
gnupg2
2.0.17-2ubuntu2.12.04.6
-
gnupg
1.4.11-3ubuntu2.9
- Ubuntu 10.04 LTS:
-
gnupg
1.4.10-2ubuntu1.8
To update your system, please follow these instructions:
https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Security/Upgrades.
In general, a standard system update will make all the necessary changes.
References
USN-2555-1: Libgcrypt vulnerabilities
Ubuntu Security Notice USN-2555-1
1st April, 2015
libgcrypt11, libgcrypt20 vulnerabilities
A security issue affects these releases of Ubuntu and its
derivatives:
- Ubuntu 14.10
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 10.04 LTS
Summary
Several security issues were fixed in Libgcrypt.
Software description
- libgcrypt11
– LGPL Crypto library - libgcrypt20
– LGPL Crypto library
Details
Daniel Genkin, Lev Pachmanov, Itamar Pipman, and Eran Tromer discovered
that Libgcrypt was susceptible to an attack via physical side channels. A
local attacker could use this attack to possibly recover private keys.
(CVE-2014-3591)
Daniel Genkin, Adi Shamir, and Eran Tromer discovered that Libgcrypt was
susceptible to an attack via physical side channels. A local attacker could
use this attack to possibly recover private keys. (CVE-2015-0837)
Update instructions
The problem can be corrected by updating your system to the following
package version:
- Ubuntu 14.10:
-
libgcrypt20
1.6.1-2ubuntu1.14.10.1
-
libgcrypt11
1.5.4-2ubuntu1.1
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS:
-
libgcrypt11
1.5.3-2ubuntu4.2
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS:
-
libgcrypt11
1.5.0-3ubuntu0.4
- Ubuntu 10.04 LTS:
-
libgcrypt11
1.4.4-5ubuntu2.4
To update your system, please follow these instructions:
https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Security/Upgrades.
In general, a standard system update will make all the necessary changes.
References
USN-2550-1: Firefox vulnerabilities
Ubuntu Security Notice USN-2550-1
1st April, 2015
firefox vulnerabilities
A security issue affects these releases of Ubuntu and its
derivatives:
- Ubuntu 14.10
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS
Summary
Firefox could be made to crash or run programs as your login if it
opened a malicious website.
Software description
- firefox
– Mozilla Open Source web browser
Details
Olli Pettay and Boris Zbarsky discovered an issue during anchor
navigations in some circumstances. If a user were tricked in to opening
a specially crafted website, an attacker could potentially exploit this
to bypass same-origin policy restrictions. (CVE-2015-0801)
Bobby Holley discovered that windows created to hold privileged UI content
retained access to privileged internal methods if navigated to
unprivileged content. An attacker could potentially exploit this in
combination with another flaw, in order to execute arbitrary script in a
privileged context. (CVE-2015-0802)
Several type confusion issues were discovered in Firefox. If a user were
tricked in to opening a specially crafted website, an attacker could
potentially exploit these to cause a denial of service via application
crash, or execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the user invoking
Firefox. (CVE-2015-0803, CVE-2015-0804)
Abhishek Arya discovered memory corruption issues during 2D graphics
rendering. If a user were tricked in to opening a specially crafted
website, an attacker could potentially exploit these to cause a denial of
service via application crash, or execute arbitrary code with the
privileges of the user invoking Firefox. (CVE-2015-0805, CVE-2015-0806)
Christoph Kerschbaumer discovered that CORS requests from
navigator.sendBeacon() followed 30x redirections after preflight. If a
user were tricked in to opening a specially crafted website, an attacker
could potentially exploit this to conduct cross-site request forgery
(XSRF) attacks. (CVE-2015-0807)
Mitchell Harper discovered an issue with memory management of simple-type
arrays in WebRTC. An attacker could potentially exploit this to cause
undefined behaviour. (CVE-2015-0808)
Felix Gröbert discovered an out-of-bounds read in the QCMS colour
management library. If a user were tricked in to opening a specially
crafted website, an attacker could potentially exploit this to obtain
sensitive information. (CVE-2015-0811)
Armin Razmdjou discovered that lightweight themes could be installed
in Firefox without a user approval message, from Mozilla subdomains
over HTTP without SSL. A remote attacker could potentially exploit this by
conducting a Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attack to install themes without
user approval. (CVE-2015-0812)
Aki Helin discovered a use-after-free when playing MP3 audio files using
the Fluendo MP3 GStreamer plugin in certain circumstances. If a user were
tricked in to opening a specially crafted website, an attacker could
potentially exploit this to cause a denial of service via application
crash, or execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the user invoking
Firefox. (CVE-2015-0813)
Christian Holler, Andrew McCreight, Gary Kwong, Karl Tomlinson, Randell
Jesup, Shu-yu Guo, Steve Fink, Tooru Fujisawa, and Byron Campen discovered
multiple memory safety issues in Firefox. If a user were tricked in to
opening a specially crafted website, an attacker could potentially exploit
these to cause a denial of service via application crash, or execute
arbitrary code with the privileges of the user invoking Firefox.
(CVE-2015-0814, CVE-2015-0815)
Mariusz Mlynski discovered that documents loaded via resource: URLs (such
as PDF.js) could load privileged chrome pages. If a user were tricked in
to opening a specially crafted website, an attacker could potentially
exploit this in combination with another flaw, in order to execute
arbitrary script in a privileged context. (CVE-2015-0816)
Update instructions
The problem can be corrected by updating your system to the following
package version:
- Ubuntu 14.10:
-
firefox
37.0+build2-0ubuntu0.14.10.1
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS:
-
firefox
37.0+build2-0ubuntu0.14.04.1
- Ubuntu 12.04 LTS:
-
firefox
37.0+build2-0ubuntu0.12.04.1
To update your system, please follow these instructions:
https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Security/Upgrades.
After a standard system update you need to restart Firefox to make
all the necessary changes.
References
Verizon Allows Opt Out of UIDH Mobile Supercookie
Verizon Wireless has made a change that now allows customers to opt out of the ad-targeting program that relies on the so-called supercookie identifier that was inserted into Web requests users send. The use of the identifier, known as a UIDH, drew the ire of privacy advocates and users when it was exposed last year. […]
User Import – Moderately Critical – Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) – SA-CONTRIB-2015-093
- Advisory ID: DRUPAL-SA-CONTRIB-2015-093
- Project: User Import (third-party module)
- Version: 6.x, 7.x
- Date: 2015-April-01
- Security risk: 13/25 ( Moderately Critical) AC:Basic/A:None/CI:None/II:Some/E:Theoretical/TD:All
- Vulnerability: Cross Site Request Forgery
Description
This module enables the import of users into Drupal, or the update of existing users, with data from a CSV file (comma separated file).
Some management URLs were not properly protected. A malicious user could trick an administrator into continuing or deleting an ongoing import by getting them to request certain URLs, thereby leading to a Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) vulnerability.
CVE identifier(s) issued
- A CVE identifier will be requested, and added upon issuance, in accordance with Drupal Security Team processes.
Versions affected
- User Import 6.x-4.x versions prior to 6.x-4.4
- User Import 7.x-2.x versions prior to 7.x-2.3
Drupal core is not affected. If you do not use the contributed User Import module, there is nothing you need to do.
Solution
Install the latest version:
- If you use the User Import module for Drupal 6.x, upgrade to User Import 6.x-4.4
- If you use the User Import module for Drupal 7.x, upgrade to User Import 7.x-2.3
Also see the User Import project page.
Reported by
- Pere Orga of the Drupal Security Team
Fixed by
- Robert Castelo module maintainer and member of the Drupal Security Team
Coordinated by
- Pere Orga of the Drupal Security Team
Contact and More Information
The Drupal security team can be reached at security at drupal.org or via the contact form at https://www.drupal.org/contact.
Learn more about the Drupal Security team and their policies, writing secure code for Drupal, and securing your site.
Follow the Drupal Security Team on Twitter at https://twitter.com/drupalsecurity
Help others with their computer issues using Avast Remote Assistance
Avast Remote Assistance gives you access to any other computer with Avast installed.
Do your friends and family always call you when they run into a problem with their computer? Forget driving across town to help them out – if they are also Avast users, you can remotely access their computer.

Avast Remote Assistance makes it a lot easier on the family IT person.
How to use Avast Remote Assistance
If you are the IT expert, the person in need of help has to request assistance from you. Instruct them to open the Avast user interface. The easiest way to find it, is to go to one of the four tiles on the Overview screen, and click on the small menu icon in the top right corner. A drop-down selection will open. Choose Remote Assistance.
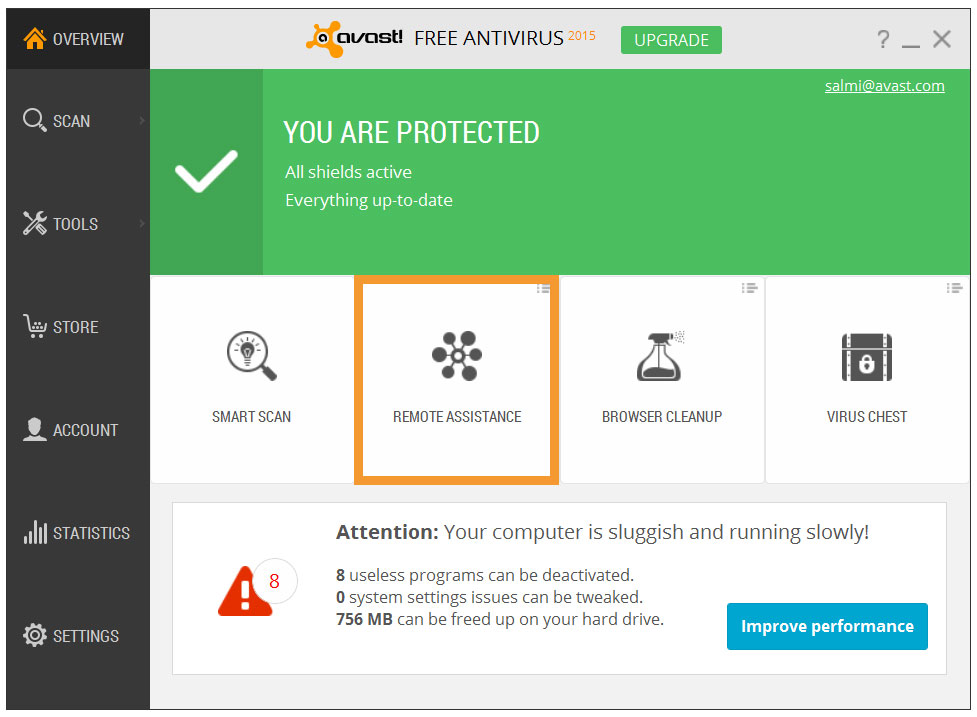
Customize your Avast Overview screen for fast access.
Next, tell them to click the blue Get Assistance button. Avast will generate a code that they need to provide to you. They can transfer the code to you by telephone, email, or chat. Make sure they understand that by sending the code they are granting you remote access to their computer. After you take control, this dialog disappears automatically.
When you receive the code, you will copy it into the box on your Avast’s Remote Assistance screen. Follow the directions to connect. When the connection is established, this dialog disappears and the remote desktop window appears.
To close the connection, press the Alt+Shift+End shortcut.
CESA-2015:0771 Important CentOS 7 thunderbirdSecurity Update
CentOS Errata and Security Advisory 2015:0771 Important Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2015-0771.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) x86_64: 7ebfced7a86fc0807143f90dbf4ca28fdd63b38d2cfe442fffbc8ca3d9395394 thunderbird-31.6.0-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm Source: 61228bdaf11280dbf4a5f9360fc668b3460f5f9cc8ec981a3efb808384207d86 thunderbird-31.6.0-1.el7.centos.src.rpm
Open Graph Importer – Moderately Critical – Access bypass – Unsupported – SA-CONTRIB-2015-092
- Advisory ID: DRUPAL-SA-CONTRIB-2015-092
- Project: Open Graph Importer (third-party module)
- Version: 7.x
- Date: 2015-April-01
- Security risk: 10/25 ( Moderately Critical) AC:Basic/A:User/CI:None/II:Some/E:Theoretical/TD:Default
- Vulnerability: Access bypass
Description
This module enables you to import content from a web page by scraping its Open Graph data.
The module doesn’t sufficiently check for “create” permission to the content type that is configured as the destination for imported content, thus allowing a user with the “import og_tag_importer” permission to create content regardless of other permissions.
CVE identifier(s) issued
- A CVE identifier will be requested, and added upon issuance, in accordance
with Drupal Security Team processes.
Versions affected
- og_tag_importer 7.x-1.x versions.
Drupal core is not affected. If you do not use the contributed Open Graph Importer module,
there is nothing you need to do.
Solution
Disable the module. There is no safe version of the module to use.
Also see the Open Graph Importer project page.
Reported by
- Chang Xiao the module maintainer
- Cameron Eagans of the Drupal Security Team
Fixed by
Not applicable.
Coordinated by
- David Stoline of the Drupal Security Team
- Damien McKenna of the Drupal Security Team (provisional)
Contact and More Information
The Drupal security team can be reached at security at drupal.org or via the contact form at https://www.drupal.org/contact.
Learn more about the Drupal Security team and their policies, writing secure code for Drupal, and securing your site.
Follow the Drupal Security Team on Twitter at https://twitter.com/drupalsecurity
