Resolved Bugs
1236296 – icecast-2.4.2 is available
1210198 – CVE-2015-3026 icecast: NULL pointer dereference in stream_auth handler leading to DoS
1210199 – CVE-2015-3026 icecast: NULL pointer dereference in stream_auth handler leading to DoS [fedora-all]
1210200 – CVE-2015-3026 icecast: NULL pointer dereference in stream_auth handler leading to DoS [epel-all]<br
* update to 2.4.2
* fix CVE-2015-3026
Monthly Archives: August 2015
Fedora EPEL 7 Security Update: icecast-2.4.2-1.el7
Resolved Bugs
1236296 – icecast-2.4.2 is available
1210198 – CVE-2015-3026 icecast: NULL pointer dereference in stream_auth handler leading to DoS
1210199 – CVE-2015-3026 icecast: NULL pointer dereference in stream_auth handler leading to DoS [fedora-all]
1210200 – CVE-2015-3026 icecast: NULL pointer dereference in stream_auth handler leading to DoS [epel-all]<br
* update to 2.4.2
* fix CVE-2015-3026
Mandos Encrypted File System Unattended Reboot Utility 1.7.0
The Mandos system allows computers to have encrypted root file systems and at the same time be capable of remote or unattended reboots. The computers run a small client program in the initial RAM disk environment which will communicate with a server over a network. All network communication is encrypted using TLS. The clients are identified by the server using an OpenPGP key that is unique to each client. The server sends the clients an encrypted password. The encrypted password is decrypted by the clients using the same OpenPGP key, and the password is then used to unlock the root file system.
QNAP Crypto Key Disclosure
QNAP devices running the QNAP modified 3.12.6 kernel with firmware older than 4.1.4 Build 0804 log crypto keys on an unencrypted disk partition in world accessible files.
Debian Security Advisory 3330-1
Debian Linux Security Advisory 3330-1 – It was discovered that the Apache ActiveMQ message broker is susceptible to denial of service through an undocumented, remote shutdown command.
Slackware Security Advisory – mozilla-nss Updates
Slackware Security Advisory – New mozilla-nss packages are available for Slackware 14.0, 14.1, and -current to fix security issues.
Slackware Security Advisory – mozilla-firefox Updates
Slackware Security Advisory – New mozilla-firefox packages are available for Slackware 14.1 and -current to fix security issues.
DSA-3332 wordpress – security update
Several vulnerabilities have been fixed in WordPress, the popular
blogging engine.
Vuln: SSL/TLS RC4 CVE-2015-2808 Information Disclosure Weakness
SSL/TLS RC4 CVE-2015-2808 Information Disclosure Weakness
How to scan and remove viruses when your computer is offline
Some sophisticated viruses hide when you turn on your computer (also known as booting up your computer), and even antivirus software like Avast, with its boot-time scan feature, can be prevented from seeing it. If you believe your computer is infected with a virus, the first step you should take is to download and install Avast Free Antivirus and run an entire system scan. If for some reason you are unable to do that, and you have exhausted all other alternatives, like asking our support team for help by submitting a request online at http://www.avast.com/support, then you can create an Avast Rescue Disk that will scan, detect, and remove most malware. This bootable version of Avast attacks a virus from outside of your computer system, catching it before it hides or camouflages itself.
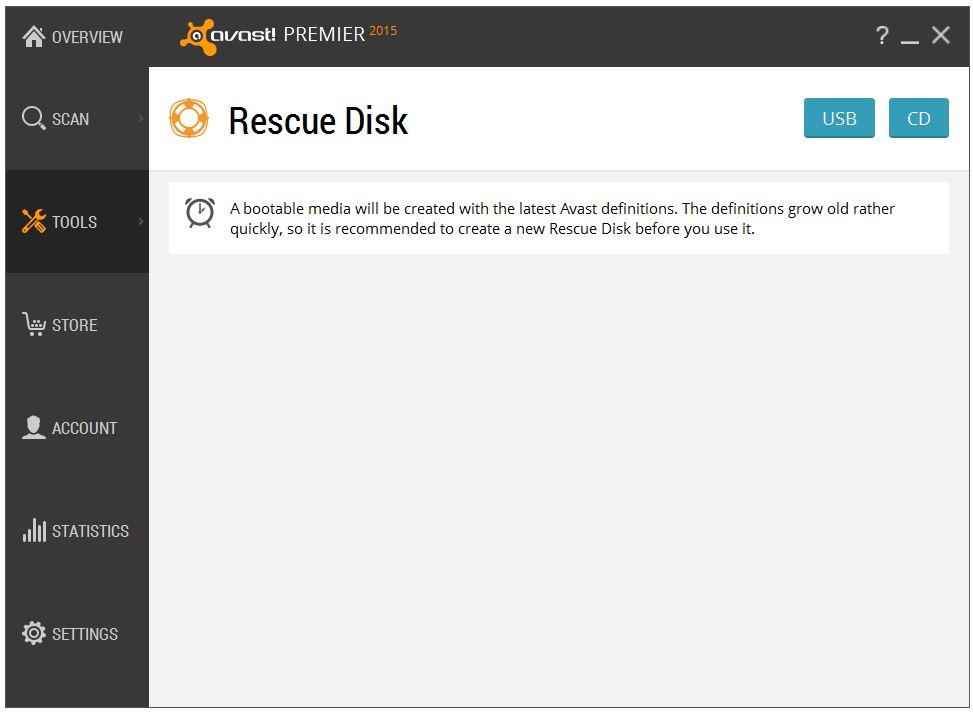
To run a virus scan when offline, create an Avast Rescue Disk.
You can create the Avast Rescue Disk from any Avast product. All you need is an uninfected computer with Avast Antivirus 2015 installed and an empty USB flash drive (make sure it is fairly new so that it supports booting) or a blank recordable CD/DVD.
Follow these easy steps:
- Open the Avast user interface.
- From the menu selection on the left, select Tools, then click Rescue Disk.
- Choose the media type that you want to use; an empty USB flash drive or a recordable CD/DVD.
- Follow the directions. Creating the rescue disk only takes a few minutes, depending on the speed of your computer and internet connection.
For detailed instructions with screenshots please visit our FAQ: Create Avast Rescue Disk as a bootable USB flash drive or CD.
Once you have created the Rescue Disk, plug it into your infected computer and reboot. There are a variety of ways to boot into the so-called Recovery mode; the ESC, F11 or F12 keys are the most common way to enter the boot menu. Our FAQ: Start up your computer from external bootable media with Avast Rescue Disk explains in more detail how to boot up your infected computer using the USB flash drive or CD/DVD that you created.
The Avast Rescue Disk wizard will walk you through the steps to scan for malware on your infected computer. You can choose to scan your entire computer or you can select specific folders or disks.
When the scan has finished the wizard will show you an overall results page and you will receive a scan log report listing the threats that were found. From there you may decide to repair or delete the infected files.
There are two options when a threat is found:
- Avast can remove the malicious code automatically. If it fails to repair the files, they will be automatically deleted.
- You may choose to work with the files manually. You have the choice to repair selected files or delete selected files. After you’re done, just to be on the safe side, you may want to start another scan.
Once you are done and your computer has been restarted, you can remove Avast Rescue Disk. You can also safely use Avast Rescue Disk to scan and disinfect other Windows PCs, but since virus definitions are always being added, it’s better to create a fresh Rescue Disk when needed.
Avast evangelist, Bob G. made a video about Avast Rescue Disk when it was introduced. It still works the same way, even though the Avast program interface looks a little different. Thank you, Bob, for making informative, helpful videos.
![]()
