Researchers with Google and a handful of universities believe security practitioners need to focus on evaluating how cybercriminals adapt to interventions instead of trying to protect users.
Monthly Archives: September 2015
Why parents must teach their children about internet security
Children as young as five are surfing the web on a daily basis, but are parents doing enough to educate them on the dangers of the online world? We investigate.
The post Why parents must teach their children about internet security appeared first on We Live Security.
![]()
If Google sends you an SMS warning you that someone has accessed your account… be careful!

With the Smartphone revolution and the wide choice of free messaging services available, receiving an SMS is definitely an unusual occurrence. Instead of being a way for friends and family to communicate, it has now become the preferred way for businesses to get in contact with you. However, you need to be vigilant of exactly what it is that these messages are trying to tell you as it could put your security at risk.
As was uncovered in a recent report published by the University of Toronto, SMS messages are being used by a group of cybercriminals to rob Gmail account passwords with the aim of accessing the victim’s account.
This attack doesn’t just avoid the two-step verification process offered by Google as a security measure, but also manages to work in a way that the victim won’t suspect a thing.

It all starts with an SMS being sent to the victim’s mobile. It appears to be from Google advising the user that someone has tried to access their email account.

The purpose of this message is to alarm the victim. Ten minutes later the victim will then receive an email which appears to be from Google warning them of an “unexpected login”. The email contains a link that, supposedly, will lead the victim to a website where they can change the password in order to reinforce the safety of their account. However, this couldn’t be further from the truth.
What really happens is that the user is brought to a phishing tool which permits the cybercriminal to obtain their password. What’s more, this false webpage will ask for the user’s verification code which is sent to the user’s mobile phone by SMS.
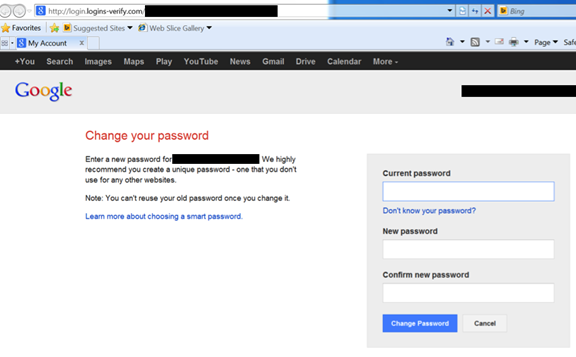
This way, in just two steps, they are able to steal your Gmail information and bypass the two-step verification process that Google has in place.
However, this isn’t the only attack that the investigators uncovered. Cybercriminals are also trying to steal password information by a phishing system which begins with what seems to be a phone call pertaining to a business proposal.
This is of course a trick and the false proposal was sent to the victim’s email account via a link that is held in a Google Drive document. Of course, to access this document the user must enter their Google password which allows the cybercriminals to get a hold of this private information.
So far what is known about these attacks is that they have originated from a group of cybercriminals based in Iran that have gone after political dissidents in their country. However, all Gmail users should take precautions and be alert to any possible scam, as anybody could become a victim of identity fraud.
To help protect yourself, and to be safe against any form of password theft, we recommend that you always create secure passwords and change them frequently.
The post If Google sends you an SMS warning you that someone has accessed your account… be careful! appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.
FortiManager 5.2.2 Cross Site Scripting
FortiManager version 5.2.2 suffers from multiple cross site scripting vulnerabilities.
Gentoo Linux Security Advisory 201509-03
Gentoo Linux Security Advisory 201509-3 – Multiple vulnerabilities have been found in Cacti, the worst of which could lead to arbitrary code execution. Versions less than 0.8.8d are affected.
Gentoo Linux Security Advisory 201509-04
Gentoo Linux Security Advisory 201509-4 – Multiple vulnerabilities have been found in libtasn1, the worst of which could lead to arbitrary code execution. Versions less than 1.4.5 are affected.
Gentoo Linux Security Advisory 201509-05
Gentoo Linux Security Advisory 201509-5 – Improper handling of Router Advertisements in NetworkManager could cause a Denial of Service condition in IPv6 network stacks. Versions less than 1.0.2 are affected.
Gentoo Linux Security Advisory 201509-06
Gentoo Linux Security Advisory 201509-6 – An attacker could execute arbitrary commands via Git repositories in a case-insensitive or case-normalizing filesystem. Versions less than 2.0.5 are affected.
Ubuntu Security Notice USN-2745-1
Ubuntu Security Notice 2745-1 – Lian Yihan discovered that QEMU incorrectly handled certain payload messages in the VNC display driver. A malicious guest could use this issue to cause the QEMU process to hang, resulting in a denial of service. This issue only affected Ubuntu 12.04 LTS and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS. Qinghao Tang discovered that QEMU incorrectly handled receiving certain packets in the NE2000 network driver. A malicious guest could use this issue to cause the QEMU process to hang, resulting in a denial of service. Various other issues were also addressed.
Red Hat Security Advisory 2015-1834-02
Red Hat Security Advisory 2015-1834-02 – Mozilla Firefox is an open source web browser. XULRunner provides the XUL Runtime environment for Mozilla Firefox. Several flaws were found in the processing of malformed web content. A web page containing malicious content could cause Firefox to crash or, potentially, execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the user running Firefox. Two information leak flaws were found in the processing of malformed web content. A web page containing malicious content could cause Firefox to disclose sensitive information or, in certain cases, crash.
