Cisco Security Advisory – A vulnerability in the installation procedure of the Cisco Mobility Services Engine (MSE) appliance could allow an authenticated, local attacker to escalate to the root level. The vulnerability is due to incorrect installation and permissions settings on binary files during the MSE physical or virtual appliance install procedure. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by logging into the device and escalating their privileges. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to acquire root-level privileges and take full control of the device. Cisco has released software updates that address this vulnerability. There are no workarounds that mitigate this vulnerability.
Monthly Archives: November 2015
Cisco Security Advisory 20151104-aos
Cisco Security Advisory – A vulnerability in the network stack of Cisco AsyncOS for Cisco Email Security Appliance (ESA), Cisco Content Security Management Appliance (SMA) and Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA) could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to exhaust all available memory, preventing the affected device from accepting new TCP connections. The vulnerability is due to improper handling of TCP packets sent at a high rate. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted TCP packets to the affected system. Note: A full device reload is needed to recover the system to an operational state.
Cisco Security Advisory 20151104-wsa1
Cisco Security Advisory – A vulnerability in the proxy cache functionality of Cisco AsyncOS for Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA) could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition because the device runs out of system memory. The vulnerability is due to improper memory operations by the affected software. The software fails to free a memory object when it retrieves data from the proxy server cache to terminate a TCP connection. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by opening many proxy connections through the WSA. An exploit could allow the attacker to cause the WSA to stop passing traffic when enough memory is leaked. Cisco has released software updates that address this vulnerability. A workaround that mitigates this vulnerability is also available.
Cisco Security Advisory 20151104-wsa2
Cisco Security Advisory – A vulnerability in the file-range request functionality of Cisco AsyncOS for Cisco Web Security Appliance (WSA) could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to cause a denial of service (DoS) condition on an appliance because the appliance runs out of system memory. The vulnerability is due to a failure to free memory when a file range is requested through the Cisco WSA. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by opening multiple connections that request file ranges through the WSA. A successful exploit could allow the attacker to cause the WSA to stop passing traffic when enough memory is used and not freed. Cisco has released software updates that address this vulnerability. A workaround that mitigates this vulnerability is also available.
HP Security Bulletin HPSBGN03519 1
HP Security Bulletin HPSBGN03519 1 – A potential security vulnerability has been identified in HP Project and Portfolio Management Center. This is the TLS vulnerability using US export-grade 512-bit keys in Diffie-Hellman key exchange known as ” Logjam ” which could be exploited remotely resulting in disclosure of information. Note: This vulnerability is in the TLS protocol and not specific to HP Project and Portfolio Management Center. Revision 1 of this advisory.
Debian Security Advisory 3393-1
Debian Linux Security Advisory 3393-1 – Multiple security issues have been found in Iceweasel, Debian’s version integer overflows, buffer overflows and other implementation errors may lead to the execution of arbitrary code, information disclosure or denial of service.
CEBA-2015:1988 CentOS 7 screen FASTTRACK BugFixUpdate
CentOS Errata and Bugfix Advisory 2015:1988 Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHBA-2015-1988.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) x86_64: 92057de1fcc98976f307be19cf298640a1fb6975d526ea947d42d2cef3100f22 screen-4.1.0-0.22.20120314git3c2946.el7.x86_64.rpm Source: de2b9e8d133cd88512293cbf63962f44797d8d8433766edcb3945758c133ed6f screen-4.1.0-0.22.20120314git3c2946.el7.src.rpm
SEC Consult SA-20151105-0 :: Insecure default configuration in Ubiquiti Networks products
Posted by SEC Consult Vulnerability Lab on Nov 05
SEC Consult Vulnerability Lab Security Advisory < 20151105-0 >
=======================================================================
title: Insecure default configuration
product: various Ubiquiti Networks products
vulnerable version: see Vulnerable / tested versions
fixed version: none available
impact: High
homepage: https://www.ubnt.com/
found: 2015-08-17…
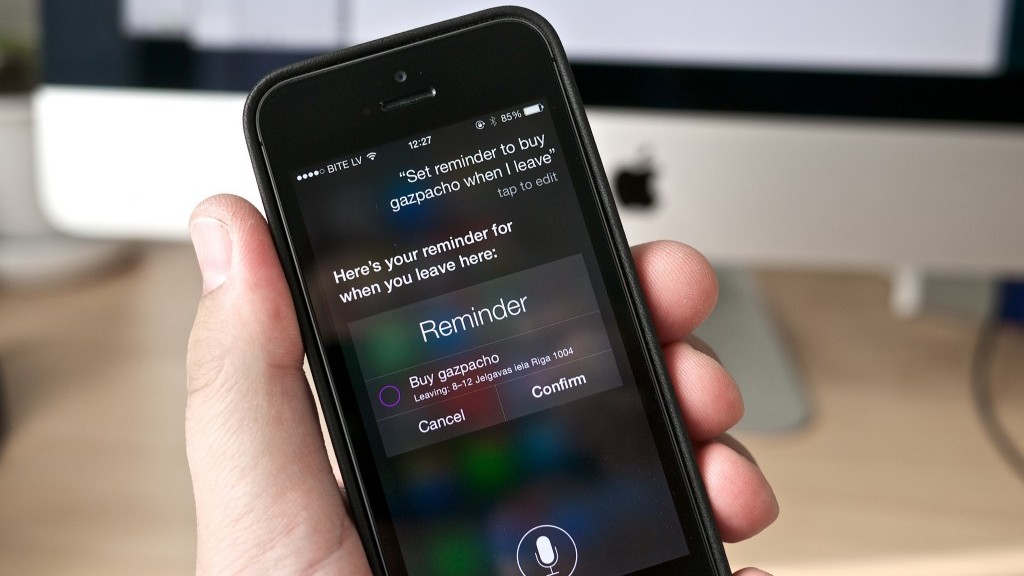
Voice assistants like Siri and Google Now could be vulnerable to attack

Virtual voice assistants such as Siri and Google Now detect key words when you ask them questions so as to understand and be able to offer you the service that you require. They also have access to the majority of tools built into your phone. For example, Siri is able to search your contact list and tell you where each of your friends is at any given moment. Both Siri and Google Now allow for calls or messages to be sent with a simple and direct command.
But what might happen if it’s not only you that could give the command, and if someone else were able to send orders remotely without even uttering a word?
A group of investigators from the National Agency for Computer Security in France (ANSSI) have discovered that these voice assistants could be tapped into by outside sources. They’re unearthed a method in which it is possible to send them commands from a distance of up to 10 meters.
To complete these tests, the team of investigators used radios waves to communicate with these voice tools without making any sounds. The only things needed are headphones with an in-built microphone.
For short distances (around two meters), the tools needed are even simpler – the group used an open-key program called GNU radio, a USRP radio, an antenna, and a signal amplifier.
The headphones serve as an antenna (for cellphones with a radio you need to connect them in order to listen) and the cable allows the cybercriminals to convert the electromagnetic waves into electric ones.
Once the message is translated and understood, it acts as an audio coming from the microphone: the operating system would recognize it as such and would transmit the instructions to Siri or Google Now.
This way, the cybercriminals are able to make them perform calls, send text messages, or even mark their own number so as the devices become listening tools. What’s more, they could even send the web browser to a page filled with malware and send spam messages or carry out phishing attacks via the email, Facebook, or Twitter accounts.

“The likelihood of sending signals to devices that accept voice commands could provoke an increase in attacks”, stated the authors of the study, which was published on the digital site IEEE.
Everything that a user can do by using voice commands is an opening for cybercriminals, who could have the chance to communicate with various devices at once. In public spaces such as airports, the attacks could be immense.
This strategy, however, isn’t without limitations. Many Android telephones don’t have Google Now available on a blocked screen, or are configured to only respond to one type of voice. Even though Siri can be accessed via a blocked screen, the latest version (on iPhone 6) is also configurable to only recognize one voice – that of the user.
The post Voice assistants like Siri and Google Now could be vulnerable to attack appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.
WordPress Neuvoo-Jobroll 2.0 Cross Site Scripting
WordPress plugin Neuvoo-Jobroll version 2.0 suffers from a reflective cross site scripting vulnerability.