Microsoft Internet Explorer 11 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted web site, aka “Internet Explorer Memory Corruption Vulnerability,” a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-6072, CVE-2015-6073, CVE-2015-6075, CVE-2015-6077, CVE-2015-6079, CVE-2015-6080, and CVE-2015-6082.
Monthly Archives: November 2015
CVE-2015-6069
Microsoft Internet Explorer 8 through 11 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted web site, aka “Internet Explorer Memory Corruption Vulnerability,” a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-6081.
CVE-2015-6070
Microsoft Internet Explorer 7 through 11 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted web site, aka “Internet Explorer Memory Corruption Vulnerability,” a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-6066, CVE-2015-6071, CVE-2015-6074, CVE-2015-6076, and CVE-2015-6087.
Comcast resets 200,000 cleartext passwords that were up for sale online
Comcast resets customer account details after it found out that information was being sold on the dark web.
The post Comcast resets 200,000 cleartext passwords that were up for sale online appeared first on We Live Security.
![]()
Key Account: How Yahoo hopes to do away with passwords

For all we know about creating secure passwords, it’s still a pain that practically every service we use requires one – they’re easy to forget and, if we don’t change them often, a cybercriminal could possibly run amok with them.
So, there are some who believe that traditional text passwords are still necessary, while others think that the future of passwords rests in the hands of emoticons and selfies.
Meanwhile, Yahoo has proposed putting an end to passwords in general, by launching Key Account. As the company explains, this system was borne out of the need to simplify login procedures for users. In fact, with Key Account, it’s now as easy as pushing a button.
The service is already available for Yahoo Mail and allows the user to access the account via their smartphone. All they need to do is click on a button in Key Account and they’ll receive a notification on their smartphone.
This will serve as validation to enter the email account, as it will indicate if the access attempt is legitimate or, on the other hand, if it is suspicious and we suspect that someone is trying to access the account.
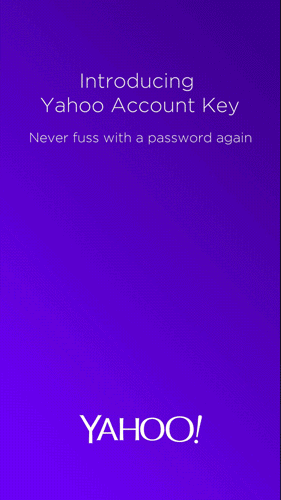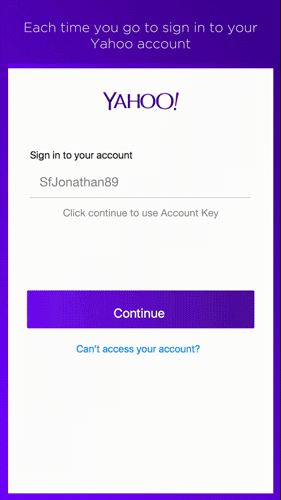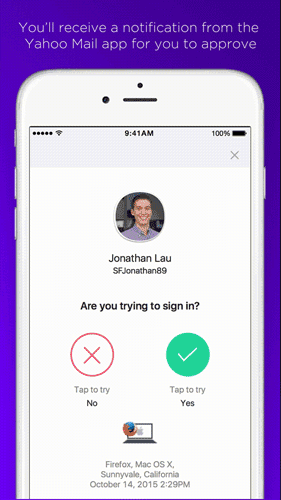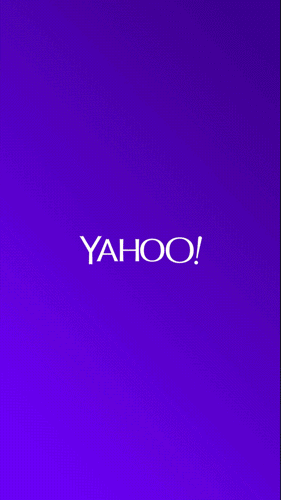
“It’s safer than a traditional password because once Key Account is activated, even if someone gets hold of the account information, only the user can access it”, explained a spokesperson for the company. So, just like that, the screen of your smartphone has turned itself into a password, and has the ability to block unwarranted access to your account.
Once the smartphone and Key Account are linked there is only one problem and that is if your device is stolen. In this case, Yahoo has established a system that will allow you to verify your identity via email or an SMS that is sent to a different number.
For now, this new method of access is only available on Yahoo’s email platform (from which you can also access Outlook, Hotmail, and AOL) and it’s hoped that by the end of the year Key Account can be used on other services, such as Tumblr.
This is the second attempt that the company has made at making passwords obsolete. In March they created a system of “low demand” and temporary passwords that the user didn’t have to memorize – all they had to do was request it and Yahoo sent it to their phone via SMS. However, it seems that the company has decided to bet on a system that is safer than a text message.
So it seems that traditional passwords are on the way out. With any luck, it won’t be long before we can forget them forever, without compromising our security.
The post Key Account: How Yahoo hopes to do away with passwords appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.
RHBA-2015:1992-1: kernel bug fix update
Red Hat Enterprise Linux: Updated kernel packages that fix several bugs are now available for Red Hat
Enterprise Linux 6.
RHEA-2015:2022-1: new package: Windows Azure Linux Agent (WALinuxAgent)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux: A new Windows Azure Linux Agent package is now available for Red Hat Enterprise
Linux 7 Extras.
RHEA-2015:2021-1: new package: Windows Azure Linux Agent (WALinuxAgent)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux: A new Windows Azure Linux Agent package is now available for Red Hat Enterprise
Linux 6 Extras.
USN-2808-1: wpa_supplicant and hostapd vulnerabilities
Ubuntu Security Notice USN-2808-1
10th November, 2015
wpa vulnerabilities
A security issue affects these releases of Ubuntu and its
derivatives:
- Ubuntu 15.10
- Ubuntu 15.04
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
Summary
Several security issues were fixed in wpa_supplicant and hostapd.
Software description
- wpa
– client support for WPA and WPA2
Details
It was discovered that wpa_supplicant incorrectly handled WMM Sleep Mode
Response frame processing. A remote attacker could use this issue to
perform broadcast/multicast packet injections, or cause a denial of
service. (CVE-2015-5310)
It was discovered that wpa_supplicant and hostapd incorrectly handled
certain EAP-pwd messages. A remote attacker could use this issue to cause a
denial of service. (CVE-2015-5314, CVE-2015-5315)
It was discovered that wpa_supplicant incorrectly handled certain EAP-pwd
Confirm messages. A remote attacker could use this issue to cause a
denial of service. This issue only applied to Ubuntu 15.10. (CVE-2015-5316)
Update instructions
The problem can be corrected by updating your system to the following
package version:
- Ubuntu 15.10:
-
hostapd
2.4-0ubuntu3.2
-
wpasupplicant
2.4-0ubuntu3.2
- Ubuntu 15.04:
-
hostapd
2.1-0ubuntu7.3
-
wpasupplicant
2.1-0ubuntu7.3
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS:
-
hostapd
2.1-0ubuntu1.4
-
wpasupplicant
2.1-0ubuntu1.4
To update your system, please follow these instructions:
https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Security/Upgrades.
After a standard system update you need to reboot your computer to make
all the necessary changes.
References
USN-2807-1: Linux kernel (Wily HWE) vulnerability
Ubuntu Security Notice USN-2807-1
10th November, 2015
linux-lts-wily vulnerability
A security issue affects these releases of Ubuntu and its
derivatives:
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
Summary
The system could be made to crash under certain conditions.
Software description
- linux-lts-wily
– Linux hardware enablement kernel from Wily
Details
Ben Serebrin discovered that the KVM hypervisor implementation in the Linux
kernel did not properly catch Alignment Check exceptions. An attacker in a
guest virtual machine could use this to cause a denial of service (system
crash) in the host OS.
Update instructions
The problem can be corrected by updating your system to the following
package version:
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS:
-
linux-image-4.2.0-18-lowlatency
4.2.0-18.22~14.04.1
-
linux-image-4.2.0-18-generic-lpae
4.2.0-18.22~14.04.1
-
linux-image-4.2.0-18-powerpc64-emb
4.2.0-18.22~14.04.1
-
linux-image-4.2.0-18-generic
4.2.0-18.22~14.04.1
-
linux-image-4.2.0-18-powerpc-e500mc
4.2.0-18.22~14.04.1
-
linux-image-4.2.0-18-powerpc64-smp
4.2.0-18.22~14.04.1
-
linux-image-4.2.0-18-powerpc-smp
4.2.0-18.22~14.04.1
To update your system, please follow these instructions:
https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Security/Upgrades.
After a standard system update you need to reboot your computer to make
all the necessary changes.
ATTENTION: Due to an unavoidable ABI change the kernel updates have
been given a new version number, which requires you to recompile and
reinstall all third party kernel modules you might have installed. If
you use linux-restricted-modules, you have to update that package as
well to get modules which work with the new kernel version. Unless you
manually uninstalled the standard kernel metapackages (e.g. linux-generic,
linux-server, linux-powerpc), a standard system upgrade will automatically
perform this as well.