One small Android application shows lots of determination and persistence. Too bad it’s evil.
The year 2014 was significant with a huge rise in mobile malware. One of the families impacting our users was malware Fobus, also known as Podec. This malware poses as a more or less useful application, but for sure it won’t be what the user expects. This malware usually has two language versions, English and Russian, and applications seem to be generated automatically.
All that, and a bag of chips
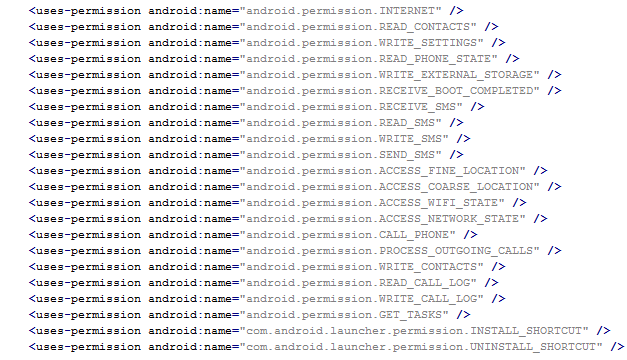
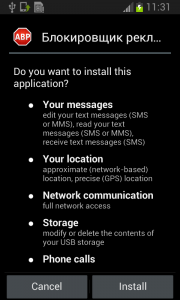
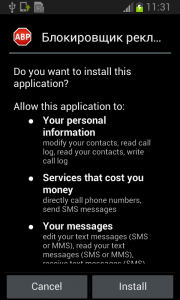
From the permissions in the manifest, we can see that once Fobus is installed on the victim’s device it cannot only send SMS and call premium numbers, which may cost a lot of money, but it also works as Spyware and can steal personal data from the infected device. That’s a lot of bad stuff packed into one small application.
Next up is a bit more technical stuff. If you are really eager, skip to Me thinks that something is amiss section to see how it works.
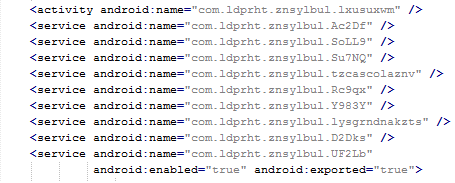
Inspecting the manifest file provides the clues of the automatic modification of the application files. As you can see in the following picture, service names are randomly generated. Going through samples in our database we were able to identify some similarities, which helped us categorize this malware as the Fobus family.
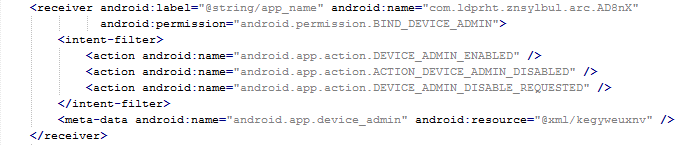
The manifest also includes several receivers which are indicators that the malware is able to spy on the device. It can also protect itself against uninstallation.
This receiver provides persistence of Fobus.
These receivers are able to check the outgoing calls and received SMS.


The receiver pictured here helps to protect the malware against removal.
Me thinks that something is amiss
During installation, the Fobus permissions already show that something might not be in order. But, we all know, that most people fly through this step without much thought.
The Great Pretender
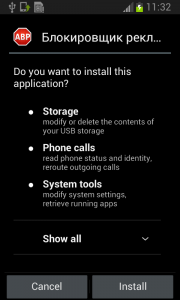
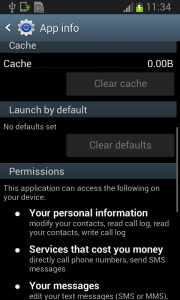
Fobus pretends to be an Ad Block but permissions to make phone calls, send messages, system tools, and services that cost money should not really be needed for an Ad Block application, nor for most legitimate applications. That is, unless you hope it will block unsolicited calls and marketing SMSs. Our advice: The user should always take great care when an application requires these types of permissions and try to link them to the expected app functionality. Inadequate permission requirements are often the first indicator of something fishy.
When the user accepts all these permissions nevertheless, Fobus installs as any other application would.
Here comes trouble!
The real trouble, however, begins when the user runs this application and grants Fobus device administrator privileges.
Once the user activates the device administrator, the application icon disappears from the device.
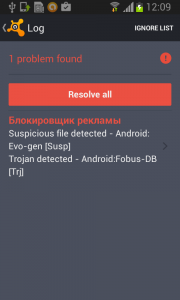
But in fact, Fobus is still in the device and starts doing what it was build for – SPYING on the device! The user is not able to Stop or Uninstall this application by standard means. Why? Because they gave permission for the app to do all these things in the previously accepted device administrator policy!
Well, just deactivate the device administrator and uninstall this application… That shouldn’t be so hard, right? But it is! The application is easily visible in the device administrator along with the deactivation button. So what is the problem?
Blink and you’ll miss it…
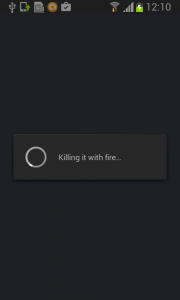
The sneaky Fobus has a receiver which checks for calls on device_admin_disable_request. The moment the user tries to deactivate the device administrator, this receiver catches the request and forces the device to lock the screen with a call to the Lock Now function. This function prevents the user from confirming the deactivation.
Afterwards, the application attempts to relock the screen with any unlock attempt. The confirmation box is visible for just a moment before the application forces the lock screen, however the user will never be able to confirm it in time because the device is not able to capture the user click on screen. The screen locking usually lasts for a while until the confirmation box simply disappears. Sometimes users are required to push one of the hardware buttons on their device to activate the screen. When they finally manage to unlock the device the application is still there and happily running. By now, the person who installed this sneaky little thief, is not a happy camper.
Empty threats
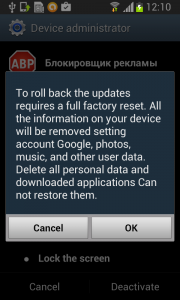
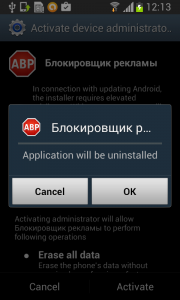
Should the user have lightening-fast reflexes and be able to get past the locking screen mechanism, the authors have another trick up their sleeves. This time, they try to scare the users from disabling the device administrator privilege by threatening to perform a full factory reset.
Fobus shows the user a fake warning about a full factory reset during which the user will lose all data stored on their device. “Heavens, NO!”, most users will say, as they choose the cancel button. But when user is brave and pushes the OK button, the device administrator privilege will be successfully removed and theuser will also able to uninstall the malicious application from the mobile device.
This is a pretty strong uninstall prevention, isn’t it?
It can be very difficult to circumvent this type of protection, especially, since the application cannot be uninstalled by any other means, like ADB or the safe-mode. In ADB, the uninstalling operation finishes as failure and even though the safe-mode disables user-installed applications, in this case the malicious application is still protected by the device administrator privileges and therefore cannot be uninstalled.
How to remove this persistent malware
Affected victims can use third party software to remove this malicious application from their mobile device or actually perform the suggested factory reset.
The removal itself is a two-phase process.
First, you need to deactivate the device administrator privilege.
Then, uninstall Fobus itself.
The little malware that could…
What makes the Fobus so special is not that it can spy on victims devices, send SMSs, or call on premium numbers; there are loads of malicious apps that can do that. Just like The Little Engine That Could, Fobus never gives up. Usually users are able to remove bad apps from their devices easily by themselves by simply uninstalling them. Fobus, though, doesn’t give up so easily, it’s strong removal protection can frustrate even the most experienced users.
Acknowledgement
Thanks to my colleague, Ondřej David, for cooperation on this analysis.
The Litttle Engine That Could image is from Hero Wikia.
Source
Here is a sample connected with the analysis
011a379b3f81dbfb4f6fb4f5c80b5ba4cf9f0677f0ee30c3a8d41711ade2d226