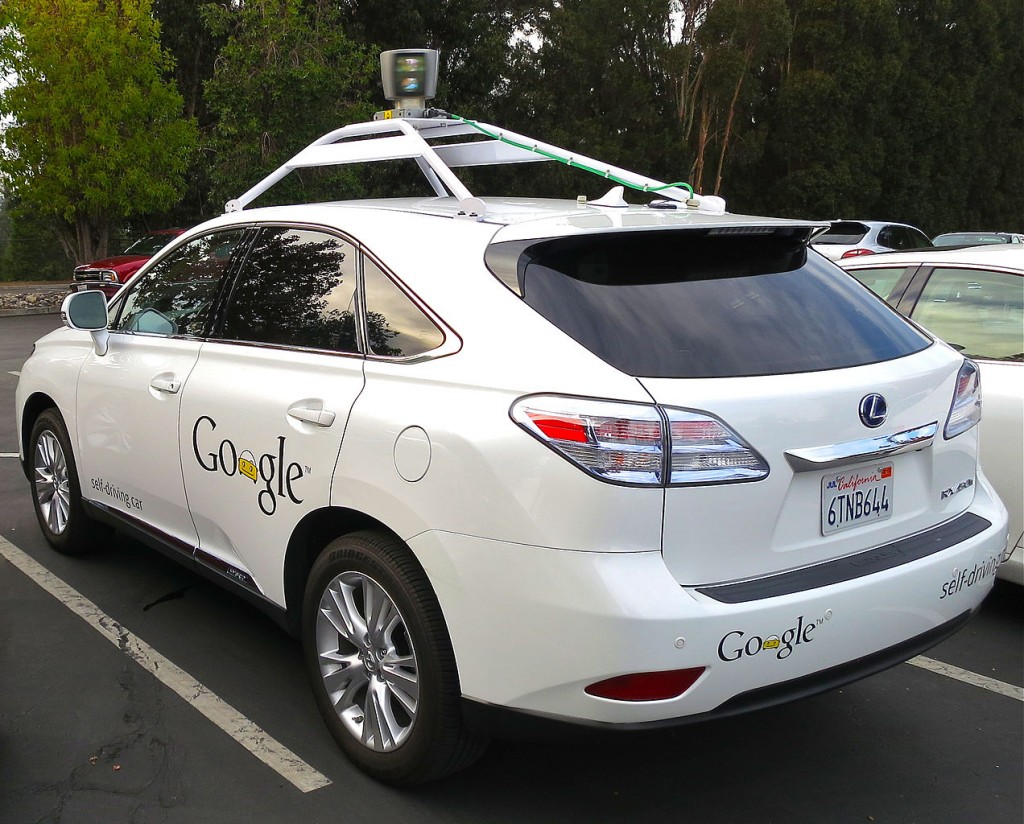
Besides radars, cameras, or a GPS system, Google decided that its driverless car would also have a powerful eye mounted on top of the vehicle which is capable of 360 degree vision. LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), the aforementioned eye, is capable of measuring distances thanks to a laser light which creates a 3D map of all that surrounds the vehicle.
Despite this technology allowing the car to hit the roads, driverless, without committing any of the errors that befall human drivers, the manufacturers of these autonomous cars aren’t claiming victory just yet as the LIDAR sensors aren’t fully bulletproof. Jonathan Petit, a security expert, has demonstrated their vulnerabilities by showing that they could be easily tricked by external sources.
The investigator managed to fool the sensor by using a laser pen and a pulse generator, which he also claims could be swapped for a Raspberry Pi or an Arduino. So, to trick a smart car, all you need to do is spend around 60 dollars (about 53 euro).
With this system, potential attackers could make the car believe that there is a wall, a person, or another car beside it, obliging it to reduce its speed. They could also send it false signals leading the car to stop itself completely for fear of crashing with these non-existent objects.
While the radars operate on private frequencies, which makes the less vulnerable, Petit was easily able to record and imitate the laser pulses emitted by the LIDAR system. He was able to make various copies of the false obstacles and even move them, thus confusing the sensor and making it believe that the illusion was real from distances of 20 to 350 meters.

Petit will present the details of his investigation at the upcoming Black Hat Europe conference, which takes place in Amsterdam in November. For the moment, however, all that he has revealed is that one of the main selling points of these cars is vulnerable.
Google’s driverless car uses the LIDAR technology of a company called Velodyne, which is based in Silicon Valley and has developed a device capable of storing more than a million pieces of data per second, allowing the car to continue its journey without incident.
This invention doesn’t come cheap, though. Each unit costs 85,000 dollars (around 75,000 euro) and this investigation shows that a high price doesn’t necessarily mean high security protection – even the most expensive ones are at risk.
Although attacks are limited to a specific device for the time being, this expert argues that all manufacturers should keep security in mind and take necessary steps to avoid any dangers on the roads. “If a self-driving car has poor inputs, it will make poor driving decisions,” claims Petit.
The problem could be resolved with a stronger detection system: “A strong system that does misbehavior detection could cross-check with other data and filter out those that aren’t plausible. But I don’t think carmakers have done it yet. This might be a good wake-up call for them.”
It’s not just Google that has tested out these LIDAR systems – the likes of Mercedes, Lexus, and Audi have also tried out prototypes on their cars, which means they also need to keep in mind any potential security risks if they want their driverless cars to become the next step in automobiles.
The post All it takes is a laser pen to confuse the so-called “smart car” appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.