Although it may be tempting to imagine hackers as being shy and socially inept types, whose only human interaction is via their computers, this is an assumption which rarely corresponds to the reality. In fact, in some cases, the social capabilities of hackers have worked greatly in their favor as a method of intrusion.
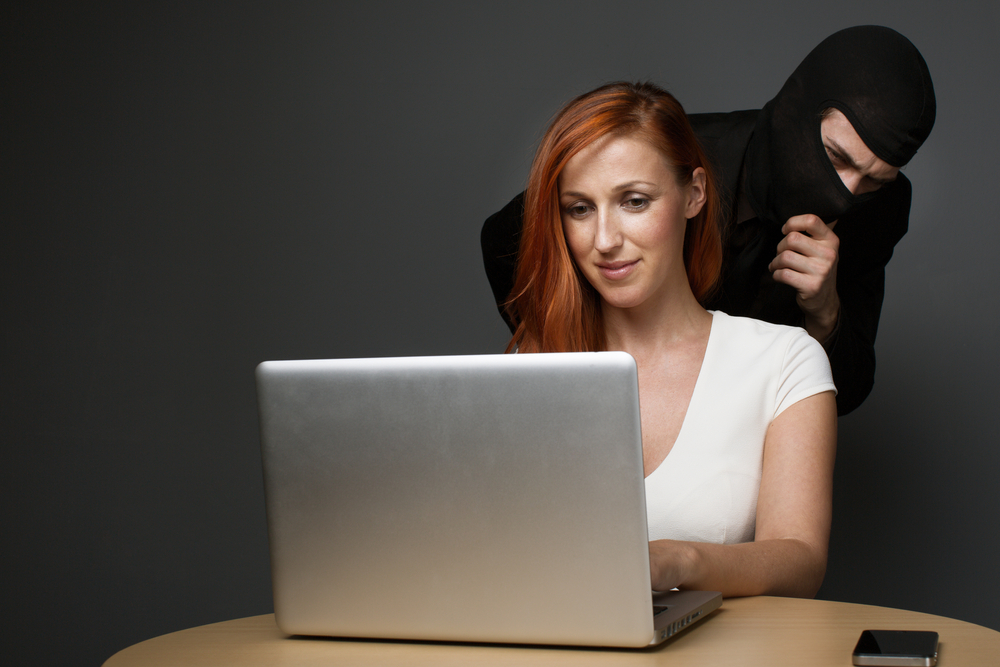
This technique is called social engineering and consists of tricking and manipulating the victim into committing a human error so as to compromise the security of IT systems.
Social psychology as a method of intrusion
This form of intrusion doesn’t rely on vulnerabilities in the IT system, but rather a social interaction (online, by telephone, or face-to-face) between the attacker and the weak link in the IT security chain – the user. The most successful social engineering techniques are based on the charisma and problem solving capabilities of the hacker, and almost always a deep knowledge of human psychology, of our irrational impulses, and of our feelings of trust, curiosity, attraction, and fear.
For example, the hacker will try to pass itself off as another person (such as a security personnel or a technician) or will pretend to have a role authority so as to coax confidential information from the victim. All of this is done without the victim realizing for one moment they are being duped.

Kevin Mitnick, one of the most notorious hackers in the 1990s, now works as a digital security consultor and says that social engineering is usually based on four fundamental principles:
- “We all want to help”
- “The first reaction is to trust in the other person”
- “We don’t like to say no”
- “Everyone likes to be praised”
An example is that of Chris Nickerson, the founder of Lares, an American security consultancy firm that used social engineering techniques to test the levels of security in businesses by means of “red team tests”. Armed with only information available to the public on the internet and a technician’s shirt from a known tele-operator, Nickerson tries (and usually succeeds) to access the company’s offices and manipulate the workstations in front of all the employees.
Brief classification of techniques
- Passive – based on observation and behavior analysis, with the aim of reconstructing their daily routine, to create an approximate psychological profile, etc.
- Non-present – based on requests for information via email or over the phone.
- Present but not aggressive – this includes actions such as spying on someone’s house or looking for personal documents in the trash.
- Aggressive and present – Psychological pressure and identity theft.

How do I stop my employees from becoming victims?
In their 2003 book, Hacking Linux Exposed, B. Hatch and J. Lee suggested adopting the following attitudes and they are still relevant today:
- “Train the users” – given that this type of attack is always launched against a person, the best way to avoid it is to ensure that all of your employees are aware of what to look out for when it comes to social engineering tactics.
- “Be paranoid” – the authors recommend “cultivating a healthy paranoia”, as it is normal that the hackers will be wary of using someone who doesn’t seem to trust them. “They look for the easiest objective”, they added.
- “Ask them everything” – it’s advisable to always ask the person you are dealing with why it is that they need the information that they request. “The majority of social engineering attacks fail by asking the attacker questions”.
- “Always check their sources” – if we are suspicious of a request sent my email, we should verify it by calling the person by telephone. If we speak face-to-face with someone we don’t know, we should demand to see some form of ID.
- “Learn to say no” – when a hacker is applying social engineering tactics, it is normal that he or she does it by straying from the norms of the business or tries to get the victim to do it. Keeping within the set rules is a good form of defense in these cases.
- Also recommended is that the business has a good EDR platform (to detect and protect against threats) such as Adaptive Defense 360.
This means that if a user falls for a trap and clicks on a link to download an infected application, it is blocked immediately. It will also inform, in real time, to the company’s security team so that they can act as soon as possible.
The post Social Engineering techniques – What they are and How businesses can avoid them appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.