CentOS Errata and Enhancement Advisory 2015:0659 Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHEA-2015-0659.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) i386: 5ef5c121021f092af2ffaece38fb90d564bae078c18df58f1c5955156f149468 dracut-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm b41823a5e5da7bc1cd27886c9a913523b4e911f8f4562b1687809455ffbabc33 dracut-caps-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm 1f3ecdc73b7edf345af17ec7541e83bc2d3e7f1377c3f9100b0a5944c3c50b85 dracut-fips-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm efdef3804eca64ae8f4a72ca2b9306031bd6d4af8608b1cb3b69cc55e19b0b09 dracut-fips-aesni-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm cb094fa6c58c83e3b5833797abed75243f108bf6a23b61b6c6d4d7933fb12320 dracut-generic-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm ec55582596b2d11cf14b4e0fc67e040982e65e27328a7a7c4478dc4367955550 dracut-kernel-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm ce0aa632236b81154e38f80ff32321da6f22dcd6676bddb81c387d25d1c12403 dracut-network-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm a62d9288e1aa13a2fee259d6eea842cc57b06f47965d4658e3bc8759852c8de7 dracut-tools-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm x86_64: 5ef5c121021f092af2ffaece38fb90d564bae078c18df58f1c5955156f149468 dracut-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm b41823a5e5da7bc1cd27886c9a913523b4e911f8f4562b1687809455ffbabc33 dracut-caps-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm 1f3ecdc73b7edf345af17ec7541e83bc2d3e7f1377c3f9100b0a5944c3c50b85 dracut-fips-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm efdef3804eca64ae8f4a72ca2b9306031bd6d4af8608b1cb3b69cc55e19b0b09 dracut-fips-aesni-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm cb094fa6c58c83e3b5833797abed75243f108bf6a23b61b6c6d4d7933fb12320 dracut-generic-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm ec55582596b2d11cf14b4e0fc67e040982e65e27328a7a7c4478dc4367955550 dracut-kernel-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm ce0aa632236b81154e38f80ff32321da6f22dcd6676bddb81c387d25d1c12403 dracut-network-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm a62d9288e1aa13a2fee259d6eea842cc57b06f47965d4658e3bc8759852c8de7 dracut-tools-004-356.el6_6.1.noarch.rpm Source: 39ef102e1db00f67f918352eb166ec0b13e7f22fe00b4dd4d1abd434d81d9a49 dracut-004-356.el6_6.1.src.rpm
Monthly Archives: March 2015
CEBA-2015:0657 CentOS 6 ibus FASTTRACK BugFixUpdate
CentOS Errata and Bugfix Advisory 2015:0657 Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHBA-2015-0657.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) i386: 6b526231f82870f9e91f374e0474d88e0dc60a3e21d930553e268cc1c56c0b0f ibus-1.3.4-8.el6.i686.rpm 3f82cfb9b1d1ed8aeb4f836d5066e99c7b4c532e8787c55fc3315e473c8dae1a ibus-devel-1.3.4-8.el6.i686.rpm b349a13129e4236d5417b379e353fd3ff6adc6e3d3d4af64374c4616da0d64df ibus-devel-docs-1.3.4-8.el6.i686.rpm ebd5819a065dc496ed3a1948388d1d38ddd235bdfa42ec26eb50093880b9e74e ibus-gtk-1.3.4-8.el6.i686.rpm 4e89ece8868febdbd057f00996dba61666eb5235ece4c1167826b86299b9aabf ibus-libs-1.3.4-8.el6.i686.rpm x86_64: 173727de6c620106d2ce16651850ff680c927a537b56e2497fb0730805e342b2 ibus-1.3.4-8.el6.x86_64.rpm 3f82cfb9b1d1ed8aeb4f836d5066e99c7b4c532e8787c55fc3315e473c8dae1a ibus-devel-1.3.4-8.el6.i686.rpm 578c964e0f5405e6228990ee4223c3c1f7ec95b231b76e455ecd070e2bb46f39 ibus-devel-1.3.4-8.el6.x86_64.rpm 480e04490a157e11b4d53b319237c24f6ed30521aa49ba4385870d3731d40b12 ibus-devel-docs-1.3.4-8.el6.x86_64.rpm ebd5819a065dc496ed3a1948388d1d38ddd235bdfa42ec26eb50093880b9e74e ibus-gtk-1.3.4-8.el6.i686.rpm 934285b9da0735efda4ced95056258c121b4064346ddd88c04217c16f773e8be ibus-gtk-1.3.4-8.el6.x86_64.rpm 4e89ece8868febdbd057f00996dba61666eb5235ece4c1167826b86299b9aabf ibus-libs-1.3.4-8.el6.i686.rpm 4e7cadc763708ebb2149c4bb87acd17bc523c5707b023e908fc0a55ab3dd4fa4 ibus-libs-1.3.4-8.el6.x86_64.rpm Source: d62c5b2a63200e5fbc1d506d86d1b9c95814563c51d4712133edcdfad4133033 ibus-1.3.4-8.el6.src.rpm
CEBA-2015:0658 CentOS 6 gnome-settings-daemon FASTTRACK BugFix Update
CentOS Errata and Bugfix Advisory 2015:0658 Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHBA-2015-0658.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) i386: 48b384cf0f6b80b2d7a425d97ab3912a5725d4513e13a9510fb49465a91f84c6 gnome-settings-daemon-2.28.2-31.el6.i686.rpm 702d8c3fc576d2d262769ce49e7a7cf7efee21aa8ae54196d8fe4385b0eaa402 gnome-settings-daemon-devel-2.28.2-31.el6.i686.rpm x86_64: 64ab82a89288713a30a97be818f1cabd67e96858b35baa128cde0bfc9aa58bce gnome-settings-daemon-2.28.2-31.el6.x86_64.rpm 702d8c3fc576d2d262769ce49e7a7cf7efee21aa8ae54196d8fe4385b0eaa402 gnome-settings-daemon-devel-2.28.2-31.el6.i686.rpm 0fd7cc3e85f4219d35ddbd1be27872702314c8c45c010c4123d5aa7e5aee4056 gnome-settings-daemon-devel-2.28.2-31.el6.x86_64.rpm Source: e34b6e98a2eddeaa89c80c6040f7f37ec6c85e6689435023e45be4dc75d56fc9 gnome-settings-daemon-2.28.2-31.el6.src.rpm
Panda Security: 25 years fighting against malware – Infographic
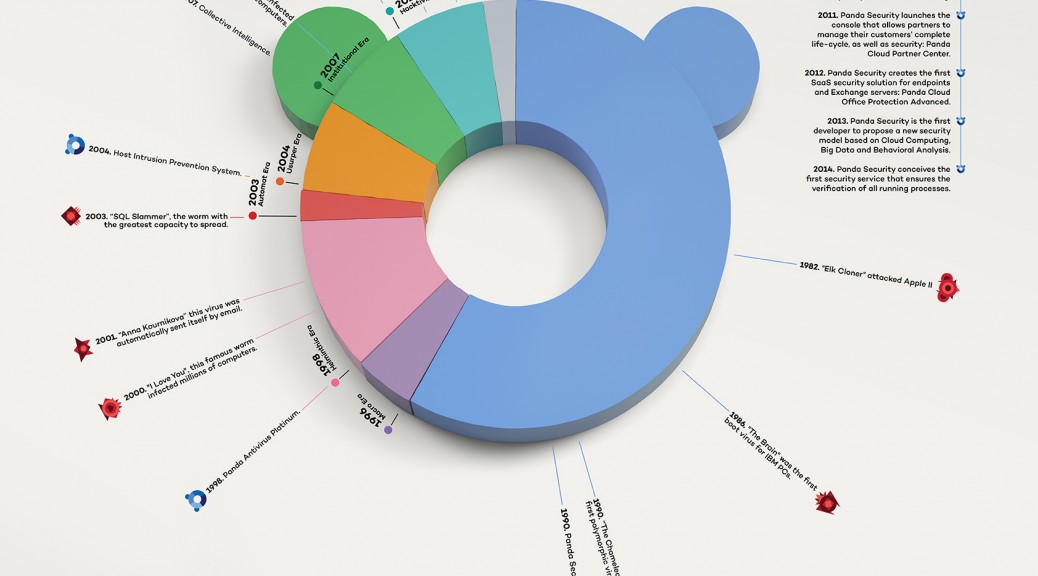
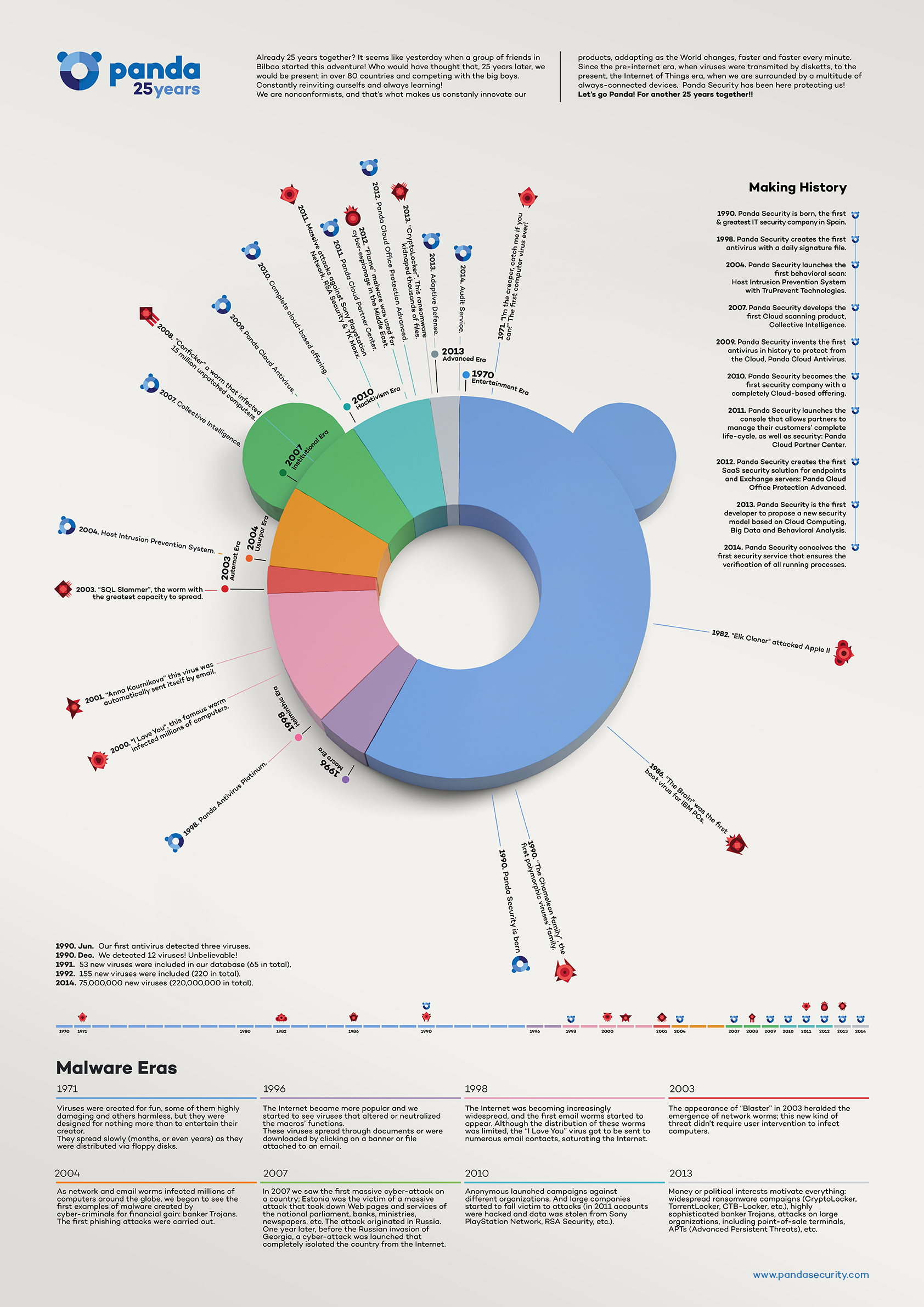
Already 25 years together? It seems like yesterday when a group of friends in Bilbao started this adventure! Who would have thought that, 25 years later, we would be present in over 80 countries and competing with the big boys. Constantly reinviting ourselfs and always learning! We are nonconformists, and that’s what makes us constanly innovate our products, addapting as the World changes, faster and faster every minute. Since the pre-internet era, when viruses were transmited by disketts, to the present, the Internet of Things era, when we are surrounded by a multitude of always-connected devices. Panda Security has been here protecting us!
Let’s go Panda! For another 25 years together!
Our technology
- 1998. We lunch the 1st antivirus with a daily signature file.
- 2004. We launch the 1st behavioral scan.
- 2007. We develop the 1st Cloud scanning product.
- 2009. We launch the 1st antivirus in history to protect from the Cloud.
- 2010. We become the 1stsecurity company with a completely Cloud-based offering.
- 2011. We launch a console for partners to manage their customers’ complete life-cycle & security.
- 2012. We launch the 1st SaaS security solution for endpoints & Exchange servers.
- 2013. We are the 1st developer to propose a disruptive security model based on Cloud Computing, Big Data and Behavioral Analysis.
- 2014. We launch the 1st security service that ensures all running processes.
Malware Eras
- Entertainment Era: From 1971
Viruses were created for fun, some of them highly damaging and others harmless, but they were designed for nothing more than to entertain their creator. They spread slowly (months, or even years) as they were distributed via floppy disks.
- Macro Era: From 1996
The Internet became more popular and we started to see viruses that altered or neutralized the macros’ functions. These viruses spread through documents or were downloaded by clicking on a banner or file attached to an email.
- Helminthic Era: From the end of 1998
The Internet was becoming increasingly widespread, and the first email worms started to appear. Although the distribution of these worms was limited, the “I Love You” virus got to be sent to numerous email contacts, saturating the Internet.
- Automat Era: From 2003
The appearance of “Blaster” in 2003 heralded the emergence of network worms; this new kind of threat didn’t require user intervention to infect computers.
- Usurper Era: From 2004
As network and email worms infected millions of computers around the globe, we began to see the first examples of malware created by cyber-criminals for financial gain: banker Trojans. The first phishing attacks were carried out.
- Institutional Era: From 2007
In 2007 we saw the first massive cyber-attack on a country; Estonia was the victim of a massive attack that took down Web pages and services of the national parliament, banks, ministries, newspapers, etc. The attack originated in Russia.
One year later, before the Russian invasion of Georgia, a cyber-attack was launched that completely isolated the country from the Internet.
- Hacktivism Era: From 2010
Anonymous launched campaigns against different organizations. And large companies started to fall victim to attacks (in 2011 accounts were hacked and data was stolen from Sony PlayStation Network, RSA Security, etc.).
- Advanced Era: From 2013
Money or political interests motivate everything: widespread ransomware campaigns (CryptoLocker, TorrentLocker, CTB-Locker, etc.), highly sophisticated banker Trojans, attacks on large organizations, including point-of-sale terminals, APTs (Advanced Persistent Threats), etc.
Want to share this infographic? Here is the code!
The post Panda Security: 25 years fighting against malware – Infographic appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.
CEBA-2015:0655 CentOS 6 pulseaudio FASTTRACKBugFix Update
CentOS Errata and Bugfix Advisory 2015:0655 Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHBA-2015-0655.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) i386: e4975f36073d153afc05f97df273e4bc27a530b00092571b5c374317bfbca084 pulseaudio-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm c4b6760734cdcc35bd09dab81db39245e7ced9b007e9028dd9c6fe20166179b2 pulseaudio-esound-compat-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 6df9ddacba16a4b8a50e6bb9ee9efddb789d51ba84bbfbc855dfe63c83f7e7fa pulseaudio-gdm-hooks-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 606f945f55cf25d4ad1560ea7adb1bf86a0ce0eb58df63cd8ecf87b32f1d4a3c pulseaudio-libs-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 58ddbfca845b279d2baf46205b7c7052db8f2423e9b4f7b7ba8c8036e8493fd1 pulseaudio-libs-devel-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm b546f6ad09df7f6add6f0d022132c59d3d94edeb70655caa36d221c4d3cc2eb7 pulseaudio-libs-glib2-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 84289b11dcf4bfb6eebdf0130c1820d737bf79341e3fb578d52be0dd628ec490 pulseaudio-libs-zeroconf-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 1d3744c299816f362b46c8e96c71346253f9089be67cc1a106b95a4b473fe29f pulseaudio-module-bluetooth-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm fa96af8f6c553d38d33239c34334dbd089aceeb32aeabd8e41d707d441d978b1 pulseaudio-module-gconf-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 751d3862eac2cb6a7cd17fb9202435aafb04aea8e77581469682f0a48afd7690 pulseaudio-module-x11-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 43398b3e806cb5640c603bdfe7ffa4b7cbd427f72808bae130362d74db8bc333 pulseaudio-module-zeroconf-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm b3badf869a14b2992de00f4c32910af0cbda62e17e74d60b604fb6597b93c25a pulseaudio-utils-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm x86_64: 3e4ca86ddc297736944bcfdb50d14ecba40fa398eb61d8cb7c1d68130c860914 pulseaudio-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm 7dae9e466bc41225817518d596c87fefaef7cca3059d8563a87782d18d97dc91 pulseaudio-esound-compat-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm e588fb3c36c15d0864c9c26550b75ebf26f7ac9669c83fca31d821b835cf2940 pulseaudio-gdm-hooks-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm 606f945f55cf25d4ad1560ea7adb1bf86a0ce0eb58df63cd8ecf87b32f1d4a3c pulseaudio-libs-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm a5ec585204e0fe6ae10b05bbadf820bc657136c800bffcdfee4ee38b25d3e99a pulseaudio-libs-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm 58ddbfca845b279d2baf46205b7c7052db8f2423e9b4f7b7ba8c8036e8493fd1 pulseaudio-libs-devel-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm cf66ae46082155294cfb5212acf3999469c97ffc1dba7bde60480e0ec1378b5a pulseaudio-libs-devel-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm b546f6ad09df7f6add6f0d022132c59d3d94edeb70655caa36d221c4d3cc2eb7 pulseaudio-libs-glib2-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm ce2f148217e9b43203d84e94a81f2c5dbc23c772a75b6bc4db2e6161b7d95559 pulseaudio-libs-glib2-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm 84289b11dcf4bfb6eebdf0130c1820d737bf79341e3fb578d52be0dd628ec490 pulseaudio-libs-zeroconf-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 0dd762ab50c4c0ffa5e359f795a43161bc5a234345acc29dd762b84742f0c932 pulseaudio-libs-zeroconf-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm 83d8629cab3f5be0f5072a06e614c07e515afbf3ecdcaa58c7da936313ac8050 pulseaudio-module-bluetooth-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm 0d4aae1732a1a949f414f2049fd43ab164f2426dbe7ac952a7548d1b89c1375e pulseaudio-module-gconf-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm 7781369b6293235b6796ca4ba3177a1fa4f2a50f1074766e0d0402b29fad05e5 pulseaudio-module-x11-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm 58d151fd55edebc23c7c8cc6ce7327f8ca8ed96a9752f6f4eebb167a381dd7f0 pulseaudio-module-zeroconf-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm b3badf869a14b2992de00f4c32910af0cbda62e17e74d60b604fb6597b93c25a pulseaudio-utils-0.9.21-21.el6.i686.rpm 449fdb518b34061ab3933efb484a859843fbefe5b1368b0adf241de312cac66b pulseaudio-utils-0.9.21-21.el6.x86_64.rpm Source: 8528b5febbcff3b6f345d9b4e7d2e375609bbc392c2b4ed583a242502266f54c pulseaudio-0.9.21-21.el6.src.rpm
CEBA-2015:0656 CentOS 6 SDL FASTTRACK BugFixUpdate
CentOS Errata and Bugfix Advisory 2015:0656 Upstream details at : https://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHBA-2015-0656.html The following updated files have been uploaded and are currently syncing to the mirrors: ( sha256sum Filename ) i386: bf3bafe68d3abd91f30147567c45b5eef23fea8cac523246cdfd4b7b5dc281fe SDL-1.2.14-5.el6.i686.rpm 8a1b27cca8488110b529a6085756cd2f3d33578a49df0dc50f7495f820a739a9 SDL-devel-1.2.14-5.el6.i686.rpm 8ec87e0bd1cb8fe6a175d3b223c708d29afca6b9bc32e5a64d127cb38bfb2f19 SDL-static-1.2.14-5.el6.i686.rpm x86_64: bf3bafe68d3abd91f30147567c45b5eef23fea8cac523246cdfd4b7b5dc281fe SDL-1.2.14-5.el6.i686.rpm 084ff20db17fd85e361adf285c199eb559cf163497d54dc0b8025fd38eb7bc43 SDL-1.2.14-5.el6.x86_64.rpm 8a1b27cca8488110b529a6085756cd2f3d33578a49df0dc50f7495f820a739a9 SDL-devel-1.2.14-5.el6.i686.rpm 5af4f3c72c2f5f9dbcd40756ffe8275969f8626f14092e2c2ce2e06b48ef594d SDL-devel-1.2.14-5.el6.x86_64.rpm 5b7ac557132dbfa19a8d57c66f7c0979ae8701bb5b7cbeb6fc9bddc5108e5ec8 SDL-static-1.2.14-5.el6.x86_64.rpm Source: 551f82cb41e3d8bc22b78d7a192e9f8501db90d4f75ca428bf79688ae5b72032 SDL-1.2.14-5.el6.src.rpm
Equation APT Group Attack Platform A Study in Stealth
The EquationDrug cyberespionage platform is a complicated system that is used selectively against only certain target machines, one that can be extended via a collection of 116 malware plug-ins, researchers at Kaspersky Lab said.
CVE-2015-0005 (windows_2003_server, windows_server_2008, windows_server_2012)
The NETLOGON service in Microsoft Windows Server 2003 SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2 and R2 SP1, and Windows Server 2012 Gold and R2, when a Domain Controller is configured, allows remote attackers to spoof the computer name of a secure channel’s endpoint, and obtain sensitive session information, by running a crafted application and leveraging the ability to sniff network traffic, aka “NETLOGON Spoofing Vulnerability.”
CVE-2015-0032 (internet_explorer, vbscript)
vbscript.dll in Microsoft VBScript 5.6 through 5.8, as used with Internet Explorer 8 through 11 and other products, allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted web site, aka “VBScript Memory Corruption Vulnerability.”
CVE-2015-0056 (internet_explorer)
Microsoft Internet Explorer 11 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code or cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted web site, aka “Internet Explorer Memory Corruption Vulnerability,” a different vulnerability than CVE-2015-1623 and CVE-2015-1626.