Resulting technology integration will enable organizations to prevent, detect, correlate, and take action against threats
![]()
It doesn’t happen too often thanks to the rigorous checks apps go through, but occassionally a fake app will slip onto the Google Play Store. How does it happen?
Here’s what cheating developers do:
When an Android app developer creates a malicious app and wants it to get attention fast, the easiest way to do it is to make it look like some other app that is already popular, like Waze. The impatient developer names it “Waze Tips” so it looks like customers will learn something useful. Then he puts it onto the Google Play Store and creates fake comments and ratings so it looks legit. After that, he’s set for success.
That’s the logic behind fake Android apps. Not surprisingly, there actually is an app that uses all these methods called “Free Waze Traffic GPS Maps Tip”.
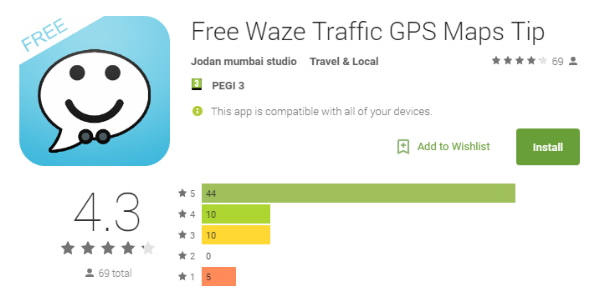
This fake app uses all the tricks to fool users into installing
![]()
The ssl.match_hostname function in CPython (aka Python) before 2.7.9 and 3.x before 3.3.3 does not properly handle wildcards in hostnames, which might allow man-in-the-middle attackers to spoof servers via a crafted certificate.
Multiple SQL injection vulnerabilities in the scoped_search function in app/controllers/katello/api/v2/api_controller.rb in Katello allow remote authenticated users to execute arbitrary SQL commands via the (1) sort_by or (2) sort_order parameter.
Apache Struts 2.3.20.x before 2.3.20.3, 2.3.24.x before 2.3.24.3, and 2.3.28.x before 2.3.28.1, when Dynamic Method Invocation is enabled, allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via vectors related to an ! (exclamation mark) operator to the REST Plugin.
Apache Struts 2.0.0 through 2.3.24.1 does not properly cache method references when used with OGNL before 3.0.12, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (block access to a web site) via unspecified vectors.
Virtual servers in F5 BIG-IP 11.5.4, when SSL profiles are enabled, allow remote attackers to cause a denial of service (resource consumption and Traffic Management Microkernel restart) via an SSL alert during the handshake.
Original release date: June 07, 2016
The Mozilla Foundation has released security updates to address vulnerabilities in Firefox, Firefox ESR, and Network Security Services (NSS). Exploitation of one of these vulnerabilities may allow a remote attacker to take control of an affected system.
Available updates include:
Users and administrators are encouraged to review the Security Advisories for Firefox, Firefox ESR, and NSS 2016-62 and apply the necessary updates.
This product is provided subject to this Notification and this Privacy & Use policy.
Rapid7 released its National Exposure Index, which measures the top 30 ports and protocols on IPv4 and quantifies unsecured services running on the Internet.
With ransomware running rampant we asked Americans if they thought the US federal government was doing enough to catch and prosecute computer criminals.
The post Is the federal government doing enough to catch and prosecute computer criminals? appeared first on We Live Security.
![]()