The Internet is a child of the United States of America, so it does not come as a surprise that only Latin letters and some scientific characters were used when the systems and the software (then called ARPANET) were designed. In today’s world, where roughly half the global population, with its different letters and alphabets uses the Internet, things look different.
The Need for Internationalization
You might have seen a so-called IDN before. IDN stands for internationalized domain name and all it boils down to, is a web address with special characters. This can be of great help for Internet users that live in regions where the primary alphabet in use is not Latin-based or is extended with special characters. Take Swedish for instance: the letters ä, ö and å augment the standard Latin alphabet. Without the support of IDNs, you would have to agree on a different (Latin) character for domains – like a or aa instead of å. Instead of visiting the website of your favorite Swedish bakery with www.pågen.se, you would have to go to www.pagen.se. This is okay until another company with the name Pagen appears and wants to claim that domain name. It becomes confusing very quickly for the visitors.
Wait…IDN what?
The Domain Name Service (short: DNS), which is used to translate a web address to something the computer understands, only accepts Latin characters. To make internationalized domains work, a system called punycode is used. A complete explanation of the algorithm is way out of scope for this article, but here is a short one. Whenever you enter an address like pågen.se, punycode prepends xn--, skips all non-Latin characters of the domain (å) and appends a dash to the remaining characters (pgen). So far, the result is xn--pgen-. Now, some black magic (finite state machines and generalized variable length integers) is used to represent the location and the identity of the skipped characters. In the end, the result looks like xn--pgen-qoa.se. This is the domain that your browser will access. You, as a user, will not feel any difference as this is done transparently by your browser. Arguably the first internationalized domain (rather subdomain in this case) was http://räksmörgås.josefsson.org.
How it affects you?
There are alphabets which contain letters similar to the ones in other alphabets. Take the Cyrillic script for instance: the Cyrillic letter а resembles the Latin character a. In a so-called IDN homograph attack, a cyber-criminal uses exactly this resemblance to mimic trusted websites. Imagine the domain in the following pictures.

Internationalized version of a domain. The first a is Cyrillic, not Latin
From the looks of it, it is paypal.com. You would almost have to be psychic to note that the first a is a Cyrillic letter. Now the attacker only needs to design a page that looks exactly like PayPal’s and send the login credentials to his or her email address – Mission accomplished.
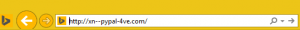
If the domain is considered suspicious, modern browsers will show the punycoded variant
Not all is lost
Fortunately, it is not that simple to deceive unsuspecting users anymore. Modern day browsers indicate that you are browsing an internationalized website as the image below shows.

Internationalization feature of Internet Explorer: shows a small icon in the address bar
In contrast to typosquatted URLs, where you might be able to spot phishy URLs by looking at them twice, IDNs can pose a real problem. You have to rely even more on a strong Web protection. It shows that common sense does not protect you from everything on the Internet and that it is crucial to have an up-to-date antimalware solution on all your devices.
Recommended Reading & Resources
Internationalized Domain Name
Punycode
Internet Usage Statistics
Internet
Homograph Attack
DNS
The post Internationalization and the Internet appeared first on Avira Blog.