GDPR is coming into play in May 2018, but a lot of companies remain unprepared, which could have implications on how they process data.
The post 10 ways to prepare your organization for GDPR appeared first on WeLiveSecurity
![]()
GDPR is coming into play in May 2018, but a lot of companies remain unprepared, which could have implications on how they process data.
The post 10 ways to prepare your organization for GDPR appeared first on WeLiveSecurity
![]()

A NFC chip the size of a rice could turn you into a cyborg.
The post Here come the new office cyborgs: One of them could be you appeared first on Avira Blog.

You’re receiving more and more advertising emails. But where do these ads come from? And where did the companies get your data from?
The post Advertising and the value of your personal data appeared first on Avira Blog.
Ransomware is not going anywhere. Here, we’ve rounded up vital tips and advice from three ESET experts: Lysa Myers, Stephen Cobb and David Harley.
The post Ransomware: Key insights from infosec experts appeared first on WeLiveSecurity
![]()

The current digital economy revolves around data. Giving up our data is the price we pay for signing up for free internet services, as the companies who provide these services use this personal information in order to fine-tune ads paid for by their true clients: advertisers.
Data is the Internet’s oil. Unlike this limited fossil fuel, however, data is increased in quantity every day. In 2013, it was reported that 90% of the world’s data had been generated in the two previous years, in other words, between 2011 and 2012. The trend has not shifted since then. The companies and countries who control the world’s data reserves will have, as with petroleum, a highly valuable resource on their hands.
90% of all the data in the world in the year 2013 was generated between 2011 and 2012
So, where is the majority of the digital era’s black gold stored? For now, the winner is, by far, the United States. 63.5% of services analyzed by Jorge Morell, expert in the terms and conditions of these kinds of companies, store their data in the US.
A far cry from that figure, weighing in at 1.9%, it appears that Europe has not jumped on the bandwagon of Big Data, so for now it looks like the American domination of the digital market is here for the long haul.
For a more detailed look, 58% of the most visited websites in a country like Spain, the subject of Morell’s research, do not reveal where they store their users’ personal information. As of now, they are not obligated to do so, so many of them make no mention of it in their terms and conditions.
Among those who are transparent in this regard, the clear winner is, again, the United States (36% of all analyzed services), although it is rarely cited as the only one. The ambiguous “and other countries” is thrown into the report haphazardly, as well as the tags Canada, China, or the vague “Outside of the European Economic Area (EEA)”.
When data crosses the pond, companies are legally bound by the Safe Harbor or Privacy Shield agreements to declare where it is stored, hence the fact that national companies are more likely to keep this information a secret.
However, all websites that until now have been silent will soon be required to declare openly the country in which their users’ personal information is stored. The new General Regulation of Personal Data Protection, with which all countries in the EU will have to be in accordance starting in May 2018, will make it compulsory that companies who maintain operations in Europe reveal the whereabouts of their personal data storage for all users, whether companies or the general public.
Such being the case, we shall soon be able to answer with greater certainty the question, “Where do the leading apps keep your information?” For now, we know beyond the shadow of a doubt that in most cases your personal information ends up in or passes through the United States at some point as it bounces around the net.
The post Where the leading apps keep your company’s data appeared first on Panda Security Mediacenter.

Data Science — from university to industry in the area around the Lake of Constance (Bodensee), Vorarlberg, St. Galler Rheintal, and Liechtenstein. Everyone is welcome to join and to exchange experiences about big data, machine learning, predictive modeling, data visualization, and all related topics on how to extract knowledge from data.
The post Data Science Meetup hosted by Avira (Data Science @Avira) appeared first on Avira Blog.
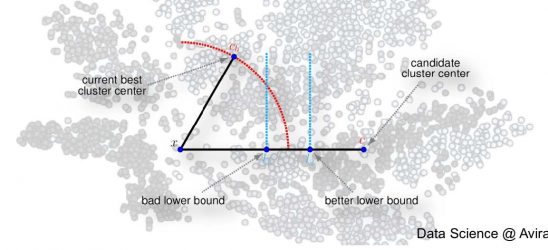
Avira Antivirus needs to handle huge amounts of data to detect malicious files – here we provide insights into one of our core machine learning methods.
The post Speeding up k-means via blockification – Data Science @Avira appeared first on Avira Blog.

Avira is a data-driven company – we now share our data stories with the world.
The post From Data to Insights: Data Science @Avira appeared first on Avira Blog.
If you are a parent you’re probably doing everything to protect your child. That’s the reason the latest trick Mattel pulled with their “Hello Barbie” dolls has not received the warmest of welcomes (at least here in Germany – but I’m sure elsewhere, too).
The post VTech data breach: Your kid’s personel information is out there appeared first on Avira Blog.

Tech companies’ privacy policies have the ability to help or hinder users.
When was the last time you sat down and read through the entirety of a tech company’s privacy policy, even if you visit the site every day?
In an article recently published by TIME in collaboration with the Center for Plain Language, a selection of the world’s leading and regularly visited tech websites were ranked in a list in relation to their privacy policies. In short, they rated the companies based on the manner in which they communicated with the public while walking them through their privacy policies. In this case, it wasn’t the actual data that these companies collect from current and potential new users that was being analyzed. Instead, this study looked at the way in which that information is brought to the attention of these users.
When picking apart a company’s policy, it’s important to think about how users can actually benefit from taking the time to read it. While that may sound obvious, we’ve all come across our fair share of unfortunate company pages (such as T&Cs, FAQs, or even About Us sections) that add up to a bunch of unintelligible language that we ultimately digest as gibberish. Regarding the level of clarity in a company’s policy, TIME writes:
Does the policy, for instance, make it easy for people to limit the ways in which the company collects their personal information? Or are instructions about opting out obscured in the policy’s hinterlands with no hyperlinks?
In addition to Google, within the list are three social media platforms that many of us use on a regular (if not daily) basis: Facebook, LinkedIn and Twitter. When taking a closer look at these four websites’ policies, it becomes clear that they approach the issue of individuals’ privacy and personal information in very different ways:
1. Google: Unsurprisingly, Google does a great job of spelling out their policies using language that users can easily understand – hence, it came in first place in this study. The Center for Plain Language concluded that by reading through Google’s privacy policy, users’ trust in the company can actually increase. Impressive, considering that most people’s trust in Google is already considerably high to begin with.
2. Facebook: While certain policies simply acknowledge that they store and analyze user information, Facebook’s “What kinds of information” section takes it a step further, breaking down each kind of interaction users have while using the site and clearly explaining which information is collected and stored while those interactions are being executed.

Photo via TIME
3. LinkedIn: Coming in at number three on the Center’s list, LinkedIn is an example of a company with a privacy policy that is mediocre in its clarity and messaging. However, LinkedIn does claim to have crafted “the policy to be as clear and straightforward as possible”, so the company’s third place rating could be a bit of subjective judgement call.

Photo via TIME
4. Twitter: Jump down to the second to last place on the list, and that’s where you’ll find Twitter. In a series of long and hard-to-read paragraphs, users are left wondering what it was that they just read when trying to pick apart Twitter’s privacy policy. This social media channel is a good example of what not to write when attempting to be transparent with audience members.
This study goes to show that it’s not only privacy policies that are crucial – it’s also important to pay attention to the way in which these policies are written and shared with users. Users should always be able to feel that they understand how and why their personal information is stored, analyzed, and/or shared on websites that they frequently use. Read the full report from the Center for Plain Language for a complete privacy policy analysis.
Follow Avast on Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Google+ where we keep you updated on cybersecurity news every day.
![]()