Some time ago, the most common mechanism for getting into an office was a simple key. Simple but vulnerable. Conventional locks do not identify people and can be used by anyone. In addition, it is impossible to control the number of hours worked.
Technology has provided a solution to this issue. There are now different techniques not just for opening doors but also for identifying staff and recording the time they enter and leave the premises. From a card to the voice, through the flash on a phone. There are many alternatives, but are these systems secure?
Using radio frequency-based methods -such as Bluetooth, NFC (Near Field Communication) or RFID– is simple. In the first two cases, all you need is a cell phone with this technology that can be recognized by a sensor. RFID chips are inserted in cards or even wristbands that open turnstiles and provide the employee’s details.

However, wireless malware exists. Attacks can compromise the company’s computers and users’ phones. Criminals with enough skill can remotely access the handset and take control of its functions, listen to calls or intercept messages.
There is also a risk of traditional robbery. If the smartphone is stolen from the employee’s pocket, the thief could access the premises without any problems. The same applies to cards.
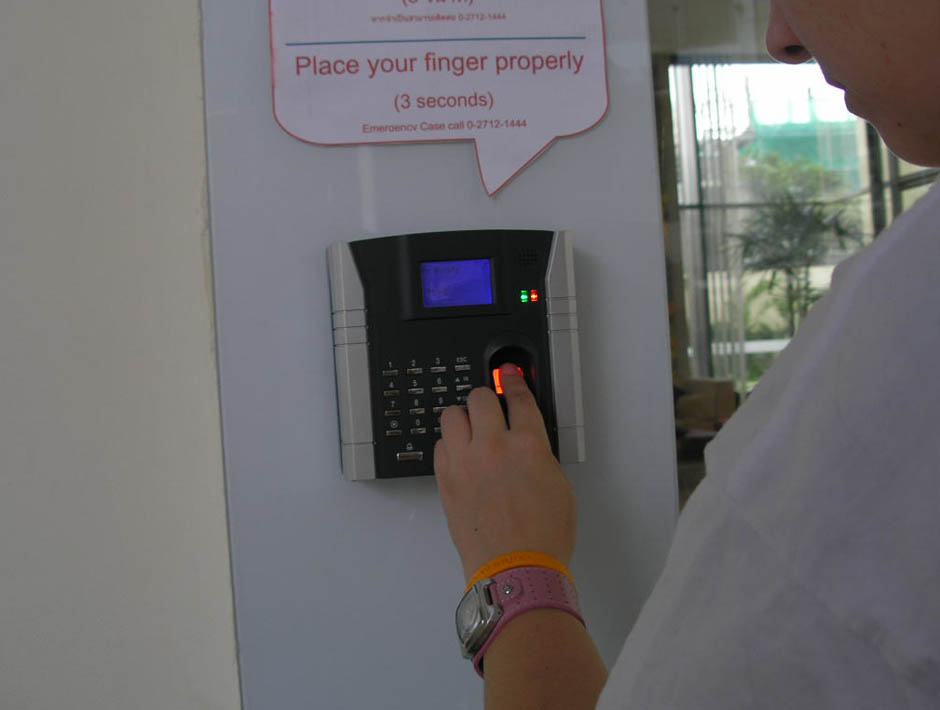
But nobody can steal a part of our body (and get it to still work). Biometric techniques are gaining importance in identification systems. The most widely used today are digital fingerprint scanners and, to a less extent, iris, voice and facial recognition sensors.
Voice recognition is based on comparing the unique mouth patterns and linguistic habits of each person. Something similar happens with the geometric variants of the face. The processing difficulty and the amount of patterns that the system must store mean that they are still minority systems.
Biometrics also has its drawbacks in terms of security. Remember that the fingerprint sensor on the iPhone (Touch ID) is vulnerable to certain types of attack. Criminals could make a replica of your finger or manipulate the sensors.
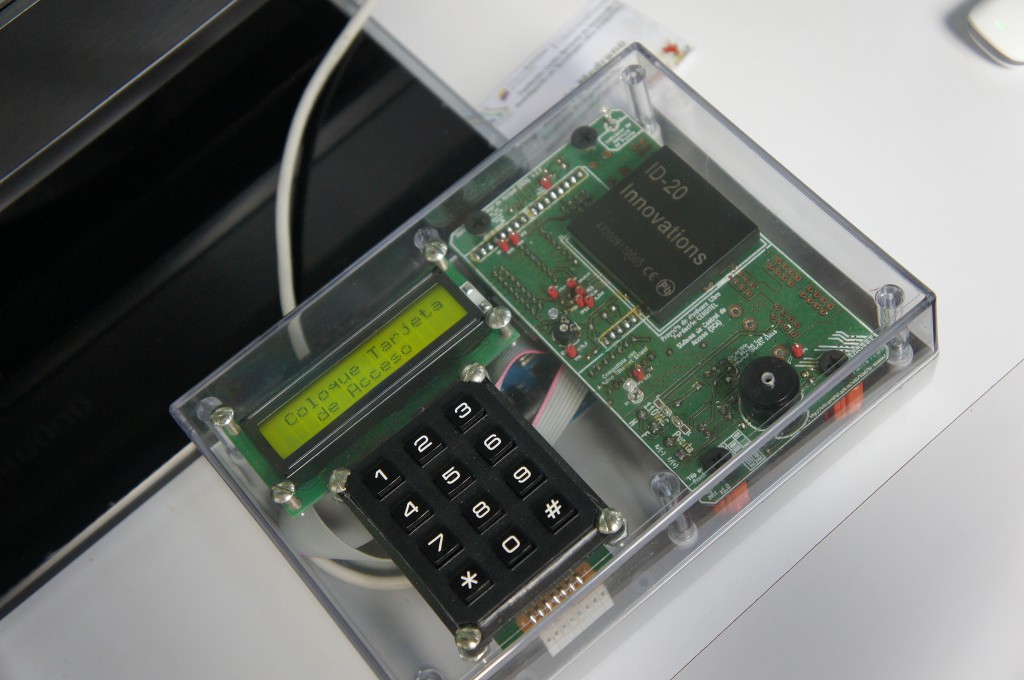

Other solutions admitted by phones are based on photonics or light recognition. The user simply needs to move the phone towards the lock, point the camera flash at the corresponding receiver and enter a password in an application. The door opens when the device detects the light signals, which form a regulated communication protocol and can transmit encrypted information.
One advantage of this technology is that only the receiver is placed at the entrance to the facilities. The data processing unit can be located inside, in a strategic place. Criminals will have to manipulate both devices in order to take total control of the system.
The majority of these techniques are still under development and they still have a long way to go before they become more widely used. The ideal solution would be to combine several of these to take advantage of the benefits of each one and reach a higher level of security.
The post Access control for companies: Which system is the most secure? appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.