The latest version of Panda Safe Web offers us new features that are essential for navigating the internet safely. Maximize your web browser now without risking your security!
Tag Archives: featured1
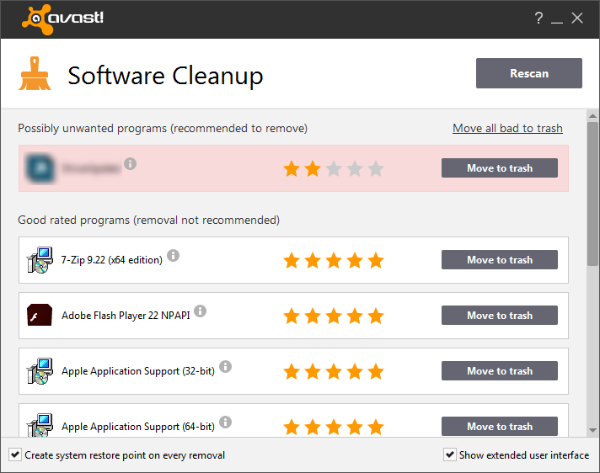
Technology beta test: Avast Software Cleanup
![]()
Republican National Convention delegates unknowingly use fake Wi-Fi networks
More than 1,200 RNC attendees unknowingly connect to Avast’s bogus Wi-Fi hotspots outside the 2016 Republican National Convention.

![]()
How the new EU cybersecurity regulations affect businesses
The 28 countries that form the European Union will have a common cybersecurity goal beginning July 6th. The European parliament has approved a new directive in which these countries will have to change their legislation in the next 21 months.
The sectors that are listed (energy, transport, banking) will have to guarantee that they are capable of preventing cyberattacks. Also, if a serious incident related to cybersecurity does occur, the companies will have to inform the national authorities. Suppliers of digital services like Amazon or Google, are all required to facilitate this information.
The EU countries have 21 months to shift this into their legislation
The EU countries should strengthen cooperation in this area by designating one or more national authorities to the cybersecurity workload and strategize how to fight IT threats.
The EU’s approved directive establishes obligations for “basic service operators” (most of all in sectors that are already cited), and each country will have six months to transition their national legislation to the new EU rules.
Each country will have six months to transition their national legislation to the new rules.
Some businesses in the digital economy (e-commerce pages, search engines, cloud services) will also have to adopt measures in order to guarantee their infrastructure security. They will have to notify the authorities of any unusual incidents but micro and small businesses will be exempt from this rule.
We have already seen that this approval has come at a delicate moment in cyber-history. The European Union calculates that the cost of cyberattacks on businesses and citizens can be between 260,000 and 340,000 millions of Euros. According to a survey by Eurobarometro, 85% of internet users are concerned by the increasing risk of cybercrime attacks.
In this context, the goal of this directive is to boost trust between EU countries, sync security in the networks and IT systems, and overall, create an environment where information can be exchanged in order to prevent attacks, or at least communicate if a security incident occurs.
The post How the new EU cybersecurity regulations affect businesses appeared first on Panda Security Mediacenter.
The evolution of the Retefe banking Trojan
Three weeks ago, we published a blog post about the
Retefe banking Trojan
, which began targeting banking customers in the United Kingdom. The Trojan steals login credentials and other personal information. Retefe is usually spread via a phishing email. The email contains a document, which is embedded with malicious JavaScript and user interaction is needed to activate the Trojan.
Another UK bank has now been added to the list of affected banks. The main behavior of the Trojan has largely remained unchanged, with the exception of its malicious components. The infection vector, as well as the installation of the malicious certificate, are the same as we reported in our last blog post.
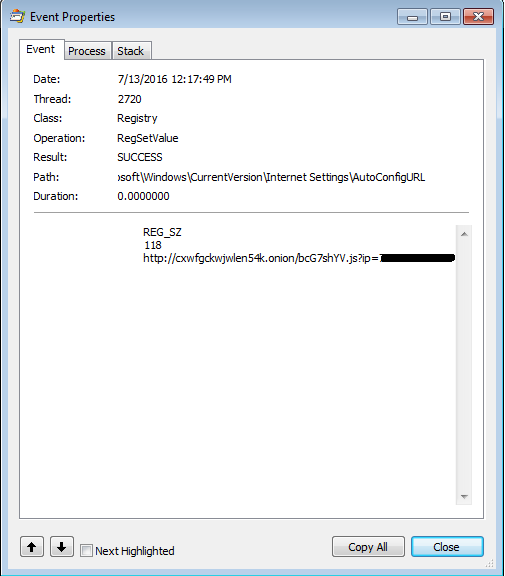
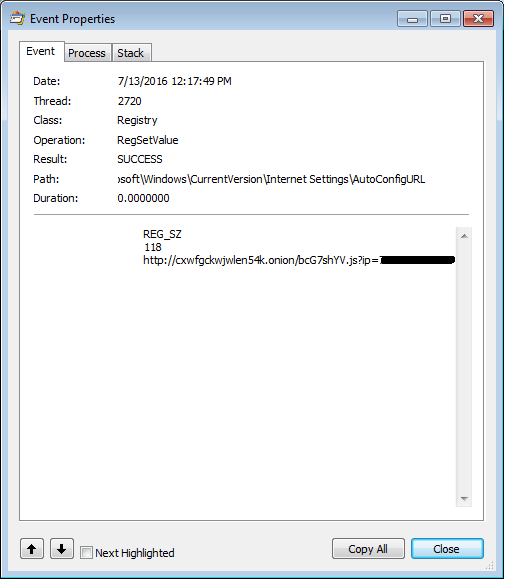
Once the JavaScript runs it attempts to kill open Web browser processes. It then installs a fake certificate and changes the proxy auto-config URL. All scripts are obfuscated with the Dean Edwards packer. This behavior is similar to the previous version of Retefe.
The JavaScript, however, now contains three powershell scripts, two of which are the same as in the previous version. ConfirmCert clicks “OK” in the window displayed during the installation of the rogue certificate and AddCertFF adds the rogue certificate to FireFox. InstallTP is the new powershell script. It downloads and installs three programs: Task Scheduler wrapper, Tor and Proxifier.
The Task Scheduler Managed Wrapper is downloaded from Codeplex. This adds the option to use the object “New-Object Microsoft.Win32.TaskScheduler.TaskService”, which is later used for establishing persistence.
The Tor client gives the Trojan the possibility to access .onion domains directly.
Proxifier, as stated on their website, “allows network applications that do not support working through proxy servers to operate through a SOCKS or HTTPS proxy and chains.”.
The AutoConfigURL contains a link to a .onion domain and it can be reached now because Tor was, installed.
![]()
5 questions with: Marek Chrenko

Get to know Marek Chrenko in the following Q&A.
Marek Chrenko came to Avast in the summer of 2014, when the mobile development startup Inmite joined the Avast team. Originally an Android developer, Marek started developing iOS products last year.
![]()
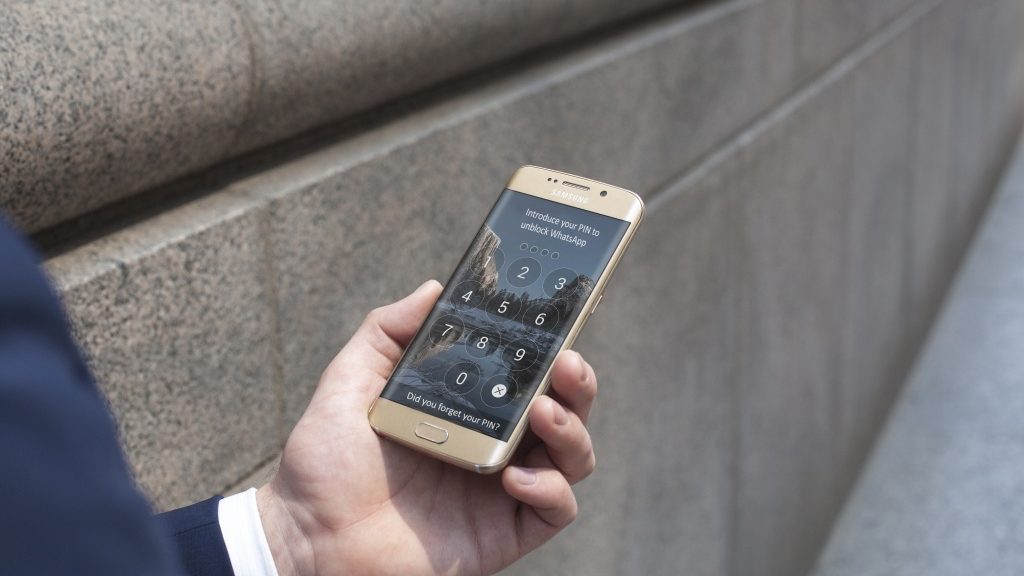
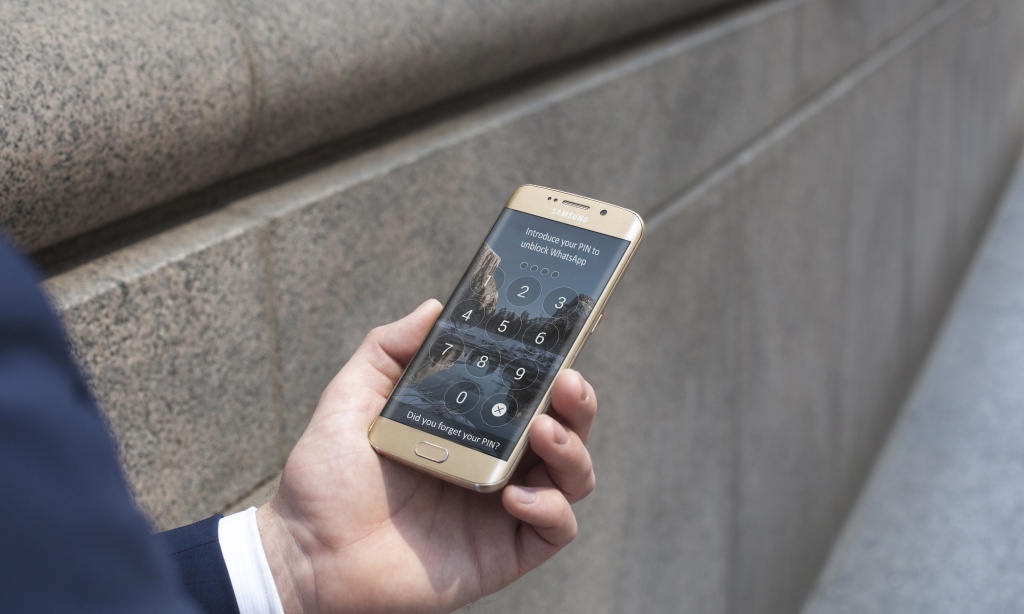
Control Access to Your Mobile Apps This Summer
Smartphones and mobile devices have become the greatest additions to the continuously booming technological industry, and our lives. If we leave our phones at home, we go back for them. We can’t wait for appointments without swiping through photos on our phones, we cook from recipes downloaded onto our tablets, and it is inconceivable to think of going to the gym without plugging-in a set of earbuds, draining our mobile data plans as we stream our favorite songs.
According to an annual mobile marketing study by IAB, 9 out of every 10 internet users have a Smartphone. 43% of users prefer to use their tablets.
It is easier to connect than ever with the outbreak of technological advances and innovations. We don’t have to worry about where we can connect to the internet and when; we can retweet current events, chat on Whatsapp, or even share a photo on Instagram wherever and whenever we want. What we should worry about is this: how can we do this securely?
Don’t let your guard down. Control those apps!
Social media permanently sits in the favorites bar as these sites continue to be the top visited. Just imagine all of the information these social media sites gather…how very frightening it is to think about the amount of information that exists about us online. Sometimes we are conscience of the personal information they take, but most of the time, we aren’t.
It is time to take a step in the right direction. Do you want to have complete control over who can access your apps? Do you want to prevent prying eyes from peeking at your personal information? Secure your privacy with the latest version of Panda Mobile Security with the newest addition to the Panda Mobile Security family, App Lock: Panda’s application control feature.
Do not hesitate! Download it with our summer promotion and test all the benefits at zero cost!
 Application control allows you to block access to your apps using a PIN code. You will be able to block access to your private information. With this feature, you can:
Application control allows you to block access to your apps using a PIN code. You will be able to block access to your private information. With this feature, you can:
Protect your privacy. Block unauthorized access to all of your apps, from messaging services or social networks (email, Facebook, Twitter, Whatsapp, Skype, Instagram, LinkedIn), to bank apps. If you use messaging services like Whatsapp you already know how important encryption is; End-to-end encryption makes sure your messages travel from point-A to point-B and prevents attackers from reading your messages.
App control, limits the little ones from accessing certain apps or games. Knowing that the little ones only use the safest apps is a parent’s biggest priority. With the newest version of Panda Mobile Security, the user can create a PIN to set the Apps they want to block or unblock. In case the user forgets their PIN, they can create a new one on their Panda account.
What are you waiting for? Try this new feature and take advantage of our summer promo. Enjoy your vacation knowing you are protected! Use the activation code and enjoy a 30-day trial of our PRO system for free. Just type in the code: PROMOMS
Secure your apps and have fun in the sun!
The post Control Access to Your Mobile Apps This Summer appeared first on Panda Security Mediacenter.
Tales from Ransomwhere
Last week, Pandalabs received a question about a specific family of ransomware that was using PowerShell, a Microsoft tool that is included in Windows 10 and that has been abused by cybercriminals for some time. We get these questions every now and then, we find those questions amusing as we consider ourselves the best ones stopping ransomware attacks. But to be honest I must admit we do not write that much about it as we should, we don’t share all our findings with the community, which is why we have decided to do it on a regular basis from now on in this “Tales of Ransomwhere” series.
it comes via a phishing email that has a Word document attached
The specific ransomware we were asked about sounded like old news to us, and in fact, our colleagues from Carbon Black wrote about it back in March. The attack flow is easy to follow: it comes via a phishing email that has a Word document attached. Once opened, a macro in the document will run cmd.exe to execute PowerShell, first to download a script from the Internet, and then will run PowerShell again using that downloaded script as input to perform the ransomware tasks.
This Powerware, as named by Carbon Black, is yet another ransomware of the thousands we see. We were blocking it even before we were aware of this particular family (as in 99.99% of the cases, did I already mention we are the best ones in the world stopping ransomware attacks?) although I have to admit that for some security companies this particular family is a bigger challenger than the rest. Why is that? Well, a number of these “Next Generation AVs” or whatever they call themselves, rely a lot on signatures (wait, weren’t they the ones that claim they do not use signatures?!?!) and at the same time their presence is stronger at the perimeter than at the endpoint. And as you can imagine, blocking Word documents at the perimeter is not really convenient. Once they have infected some customers they can add signatures and protect the rest (like blocking IPs where the script is being downloaded from) although the lack of a malware executable being downloaded from the Internet is a nightmare for them.
At the end of the day ransomware is a hell of a business for cybercriminals, and as such they invest a lot of resources into finding new ways to stay undetected by all kind of security solutions, being this Powerware just one example. The general behavior doesn’t change, but there are always subtle changes at least every week. These changes can apply to the ransomware itself (how it performs its actions) or the delivery (using new exploits, changing known exploits, changing the payload of the exploits, etc.)
A good example of new delivery methods is one we have seen recently: after exploiting Internet Explorer, it is executed CMD using the “echo” feature to create a script. Then a number of Windows files are executed in order to perform all actions to avoid detection of suspicious behavior by security solutions. The script is run by wscript, and it downloads a dll, then it uses CMD to run regsvr32, that will execute the dll (using rundll32). In most cases that DLL is a ransomware, so far we have blocked +500 infection attempts using this new trick.
so far we have blocked +500 infection attempts using this new trick
We haven’t looked at the exploit used (we really don’t care a lot as long as we are blocking it) but given the timeframe where this infection attempts have shown up (first on June 27th) it happened when AnglerEK had already disappeared, so probably attackers are using either Neutrino or Magnitude.
Every time we see something new like this, someone ends up publishing information about it a month later, so I am afraid we may have screwed up someone’s research, or at least it won’t look that new. To make up for it I have listed all the MD5s of the DLLs we have captured in the wild in those +500 infection attempts:
00d3a3cb7d003af0f52931f192998508
09fc4f2a6c05b3ab376fb310687099ce
1c0157ee4b861fc5887066dfc73fc3d7
1cda5e5de6518f68bf98dfcca04d1349
1db843ac14739bc2a3c91f652299538c
2c5550778d44df9a888382f32c519fe9
2dcb1a7b095124fa73a1a4bb9c2d5cb6
2f2ca33e04b5ac622a223d63a97192d2
38fb46845c2c135e2ccb41a199adbc2a
3ac5e4ca28f8a29c3d3234a034478766
4cb6c65f56eb4f6ddaebb4efc17a2227
562bf2f632f2662d144aad4dafc8e316
63dafdf41b6ff02267b62678829a44bb
67661eb72256b8f36deac4d9c0937f81
6dbc10dfa1ce3fb2ba8815a6a2fa0688
70e3abaf6175c470b384e7fd66f4ce39
783997157aee40be5674486a90ce09f2
7981aab439e80b89a461d6bf67582401
821b409d6b6838d0e78158b1e57f8e8c
96371a3f192729fd099ff9ba61950d4b
9d3bf048edacf14548a9b899812a2e41
a04081186912355b61f79a35a8f14356
a1aa1180390c98ba8dd72fa87ba43fd4
a68723bcb192e96db984b7c9eba9e2c1
abb71d93b8e0ff93e3d14a1a7b90cfbf
b1ac0c1064d9ca0881fd82f8e50bd3cb
b34f75716613b5c498b818db4881360e
b6e3feed51b61d147b8679bbd19038f4
bbf33b3074c1f3cf43a24d053e071bc5
cba169ffd1b92331cf5b8592c8ebcd6a
d4fee4a9d046e13d15a7fc00eea78222
d634ca7c73614d17d8a56e484a09e3b5
de15828ccbb7d3c81b3d768db2dec419
df92499518c0594a0f59b07fc4da697e
dfd9ea98fb0e998ad5eb72a1a0fd2442
e5c5c1a0077a66315c3a6be79299d835
The post Tales from Ransomwhere appeared first on Panda Security Mediacenter.
Pokémon Go real-world safety guide

The Pokémon Go augmented reality game has swept across the USA and is now continuing its journey around the world. Society has grown accustomed to people’s noses being stuck in their smartphones all the time, but Pokémon Go brings the addiction to new levels.
![]()
Mr. Robot Review: unm4sk-pt1.tc and unm4sk-pt2.tc
The two-part premiere of season two of Mr. Robot did not disappoint! The episodes focused more on the current state of the main characters than on hacking and a lot has changed since season one.
Elliot is trying to get his life back on track. He is living with his mom, has developed a routine, which includes attending a Church group, and keeps a journal. Mr. Robot does not like the new Elliot and is itching to get back to work, taunting Elliot. Darlene is leading fsociety in the meantime, but the group’s other main hackers seemed to have disappeared. Angela has joined the dark side and is working as a PR Manager for E Corp. Joanna, Tyrell’s wife, has found a new BDSM buddy to fill her missing husband’s void.
We were also introduced to some new characters and I am looking forward to learning more about them as the season goes on. There is the FBI agent investigating the E Corp hack and Elliot has also made a “new friend”, Ray. Ray wants to do business with Elliot, but Elliot is not interested – but Mr. Robot seems to be…

Image via: USA Network @whoismrrobot
![]()