During the last few months of 2015, a generous promotion by Primark (the well-known Irish clothing giant) started to do the rounds on Facebook in Spain, whereby users were promised the chance of winning a gift-card worth €500 by clicking like on a publication. The year previous also saw a similar offer by Zara, another clothing giant, which saw the company raffling off store credit if you invited friends to attend an event. However, neither of these pages, offers, or events were related to the store in question, nor to any of their employees.
It turns out that these were fraudulent offers created by fake profiles, which used social engineering techniques to take advantage of users. Although these cases involved well-known stores, any of Facebook’s users could see their profile copied and stolen.
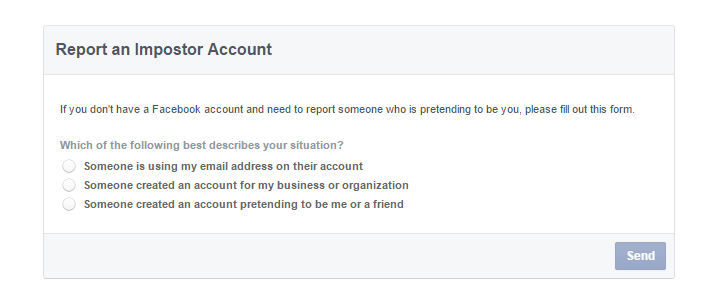
If you do ever come across a profile that is passing itself off as your own, or your company’s, then there is luckily a way to have it removed, as Facebook has a mechanism in place to report and stop the imposter in its tracks.
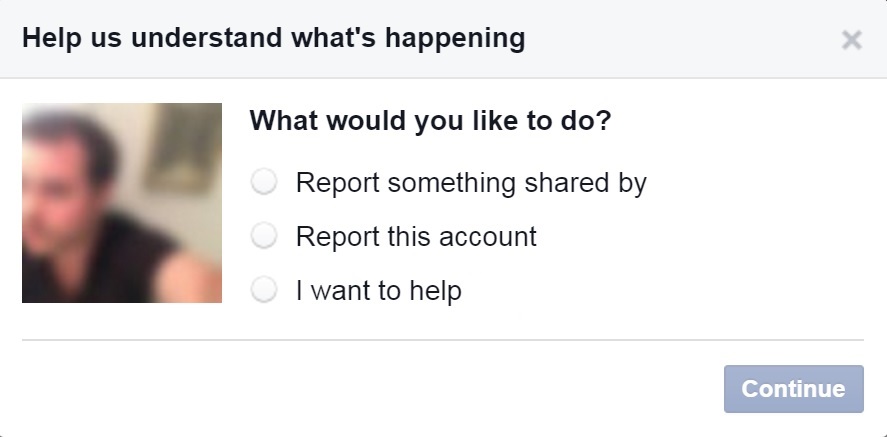
The first thing that you need to do is enter the fraudulent page (you can’t raise the alarm from your own profile), click on the button located to the right of the cover photo, and choose “report”. In the following window, which will open automatically, you have to select “report this account” and, later, follow the instructions on the screen.
However, there is also a chance that the imposter has blocked you, so that you can’t access the account. If this happens, you will have to ask a friend to report the false account. The friend will receive a message with a link to continue to process.
It is also possible that the person whose identity has been stolen doesn’t have a Facebook account. If this is the case, the social network has a section for events such as this in its help center.
Anyway, no matter what the situation, Facebook advises that you get in touch with a lawyer or a regulator before viewing the content that the imposter has posted on the page. The aim is to be informed fully of the situation and the legal options available to the affected party.
The social media website doesn’t just offer help to its users, but also provides information to the authorities to help them better understand how to act. What’s more, there is also a special section where they can present their own requests relating to an investigation.
The repercussions that an imposter may face depend on what the false account was being used for. In Spain, for example, identity theft over a prolonged period of time (to the point where others are tricked into believing the false identity) is considered a crime that is punishable by up to three years in prison.
If the profile is used to gain personal information on other users with the aim of committing a crime, the situation is even more serious.
We all hope that this never happens to us, or to anyone that we know, but as always it pays to be prepared to act quickly if it should arise.
The post What to do when someone steals your identity on Facebook appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.