It’s likely that one more than one occasion you’ve noticed the small green lock icon that appears in the address bar when you’re using the Internet. This little icon means that the site you are using is secure as the page is using HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure).
HTTPS encrypts all communications to protect confidential data on the web, from user names to passwords, messages, or credit card info. In order for this to work correctly, it is essential that banking websites or online stores use the secure version of GTTP.
The HTTPS system also guarantees that anyone using the Internet is able to access the official page of a company as opposed to a false one which has been designed to trick the user and steal their money or info. It also protects that website against third-parties which might try to intercept the connection in order to install a malware.
Google has spent a long time organizing a silent campaign in favor of the use of HTTPS with the hope that eventually all websites will end up using the system, putting an end to the risk of data theft for web users. It’s telling that even the government of the United States is concerned about the use of HTPPS, and requires that all of its web pages be encrypted with the service.
Less than a month ago, Google announced that it would favor the indexation of HTTPS sites that had a HTTP equivalent. What’s more, Google has decided to offer new tools to developers so that they can easily include this protocol. Now it is trying to publicly list the owners of websites that aren’t using this protocol, a project that the security team already debated at its forums in 2014.
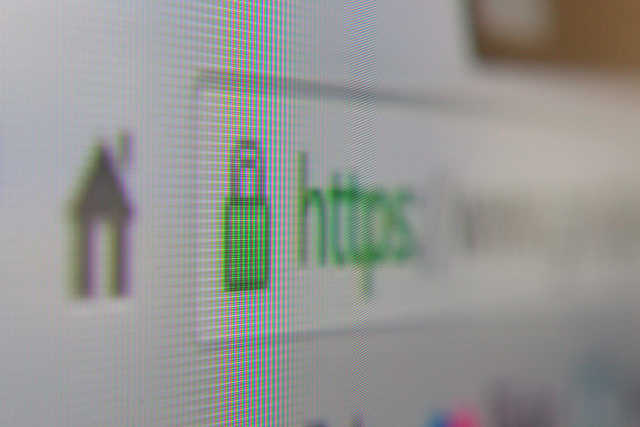
Up to now, on Chrome there was a red X on the gray lock when the browser detected problems with the TSL/SSL certification of the website which guarantees the establishment of secure communications on the Internet, which makes it possible for a third-party to access the user data. It also shows us this warning when the web connection is encrypted, but Chrome has detected a mix of command sequences (a page based on HTTPS loads content based on HTTP), which could allow a third-party to take control of the page.
Google plans to openly display websites that use HTTP protocol by marking them with a red X. Parisa Tabriz, Chrome Security Engineering Manager, tweeted that she planned to highlight these pages: “HTTP, we’re readying to call you out for what you are: UNSAFE!”
A few days ago, at the Usenix Enigma security conference, an expert from CloudFlare showed how users can already decide if they want all pages that use HTTP protocol to appear with the red X symbol. To do this, all you need to do is enter chrome://flags and select “mark non-secure as” and then “mark non-secure origins as non-secure.” In this moment, a gray lock will be added to your address bar, indicating insecure webpages.
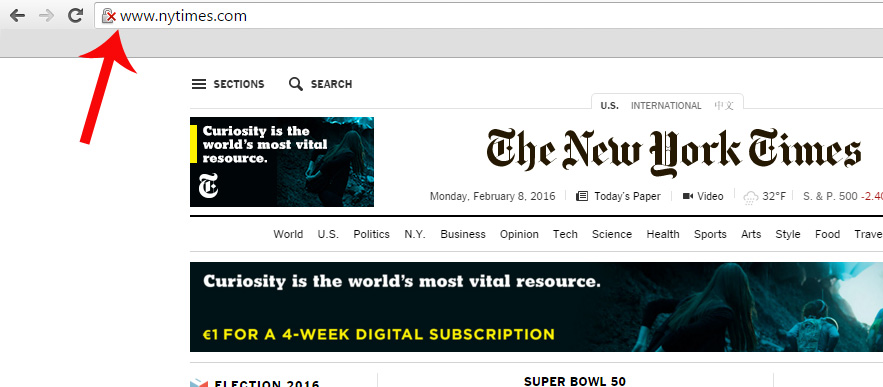
A Google employee, who wished to remain anonymous, has confirmed to Motherboard that the intention is that Chrome will include this alert by default and has assured there will be more clues in the near future.
For now, Google has yet to make an official announcement on the matter, so those who wish to know when a webpage isn’t secure need to manually select this option.
So, if we keep in mind that only 1 in 3 users take notice of the current SSL security warnings from Chrome which warn us if someone is trying to steal our confidential information, it’s likely that some will end up ignoring the red X, too. Due to this, it is necessary that we are more aware of the dangers that we face by leaving our data on insecure websites.
The post Google to publicly shame websites that aren’t using HTTPS appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.