Mobile World Congress is the largest gathering of the mobile industry and takes place at the end of February every year. According to the latest attendance numbers, it was bigger and more attended than any previous congress. Every possible brand associated with smartphones you can think of was there and even some of the brands you may not know but they provide the stuff to make it all work behind the scenes.
There is a dramatic change afoot in this industry and it’s clear to see at MWC. The focus of this year’s show is very much about the Internet of Things (IoT). Most of us consider this to mean fitness trackers, a few connected fridges, and maybe for the select few, a car.
IoT is going to affect all of us in ways that we can’t yet imagine — everything will be connected and adding data to a world that will operate based on the analysis of everything around us. This may sound like a science-fiction movie, it’s not. There’s technology on its way that really does mean that there are very few things that won’t be connected.
What was hot at this year’s MWC 2016?
There is a device for tracking everything from fitness to air quality. While they’re exciting toys and gadgets for us to own and play with, the bigger story is how these stepping stones are being placed for a far more connected world. We continually hear about self-driving cars and other cool innovations, but for many of us these are still news stories rather than reality. One such company is Seat’s connected car tech that allows drivers to check the availability of parking spaces, access breakdown services and connect to household appliances.

Do you ever leave home in the morning having missed a tooth when brushing? With Oral-B’s smart toothbrush it will be a thing of the past! A smartphone app connects to the toothbrush and detects which teeth are still dirty.
Visa announced their new payment system, the Visa Ready program, which will allow transactions to be made from any suitable connected device. For anyone traveling through London recently, they may have seen people waving their phones on the tube payment terminals to pay for their trip. With the new service from Visa, this facility will be extended to other devices and use tokens rather than card details. This means that personal data is never transmitted in a similar way that Apple Pay and Android Pay work and should be considered a security enhancement over the current process.
Honda has already signed up to the program to use an in-car fuel app that will be integrated into their vehicles dashboards. Once the car is running low on fuel the driver will be automatically be directed to the nearest gas station. The app will know the exact amount of fuel needed and pay for the fuel and calculate the cost. Of course, this does mean the pump needs to accept wireless payments and you will still need to get out and actually put the fuel hose into the car.
Virtual reality
A technology that has been heard about for years is about to become both affordable and usable, and will soon establish itself as a normal part of our lives. I was lucky enough to get a full hands-on demo of Intel’s RealSense™ virtual reality technology that is being made available to developers in the next few months.
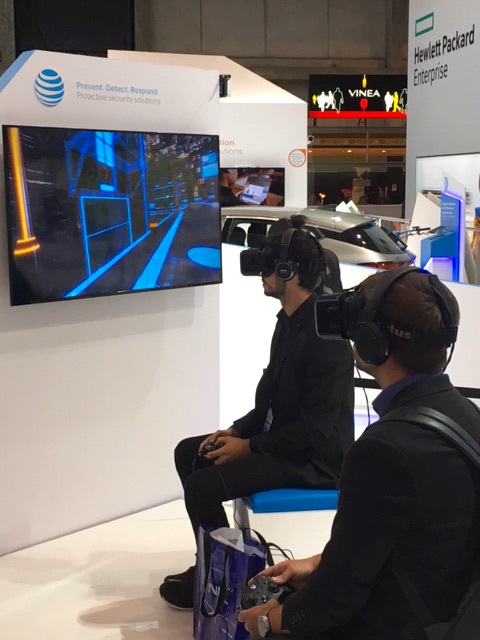

Put the headset on and be immersed in a virtual world where you can actually interact using your hands. Yes, they actually appear in the virtual world allowing you to move objects and to be part of what you are seeing. Or allow the headset to map, in real-time, the environment you are in and to add things to it — you can mix our physical world with a virtual one. For example using the demo headset I scanned a table and then a cat jumped up onto it. I moved away and the cat jumped off the table. The possibilities for this technology in our normal lives, especially if you are a gamer, are really exciting and I can’t wait to see them realized.
There is a common concern with all the new IoT devices and cool services that they deliver, that is one of security. With every connected device a new opportunity is created for hackers to attempt to breach the device and access your personal data. While many device manufacturers may create their products using a ‘secure by design’ approach, this may not be the case with the small innovative companies that have the hottest technology.
The concern should not stop with hackers. Devices are collecting data that we may not realize. This raises questions about who has access to our data and what is it being used for — did you read the privacy policy of every connected device you already own, and will you read the privacy policy of all the new ones? Unfortunately, the answer is most likely no. Besides presenting us with new and impressive connected devices, Mobile World Congress has also highlighted the need for us to be aware of the “what” and “who” is holding our data and for what intent.
![]()
![]()