Dennis Fisher and Mike Mimoso discuss the Ghost glibc vulnerability and its repercussions, the Apple iOS and OSX patches, the link between the Regin APT platform and the NSA. Plus Super Bowl predictions!
Tag Archives: Malware
MSIL/Agent.PYO: Have botnet, will travel
ESET’s researchers recently encountered a piece of malware targeting the filling of the forms belonging to the Consulate of Poland. To understand why it is first necessary to have a brief look at the application process for visas.
The post MSIL/Agent.PYO: Have botnet, will travel appeared first on We Live Security.
The Biggest Hacks of 2014
There were a number of big security breaches during 2014, but which was the biggest? We count down the top 5.
The post The Biggest Hacks of 2014 appeared first on We Live Security.
Of Ghost glibc Vulnerability Patching and Exploits
Experts urge system administrators to patch the Ghost vulnerability in glibc immediately, but counter that as well that exploiting the bug may be challenging.
Analysis of Flash Zero Day Shows Layers of Obfuscation
The Flash zero day that made its way into the Angler exploit kit was wrapped in multiple layers of obfuscation and has the ability to inject its malicious payload straight into users’ browsers. In the last week, since the news broke of the Adobe Flash zero-day flaw appearing in the Angler kit, security researchers have […]
Researchers Link Regin to Malware Disclosed in Recent Snowden Documents
Kaspersky Lab has found shared code and functionality between the Regin malware platform and a keylogger described in recently disclosed Snowden documents.
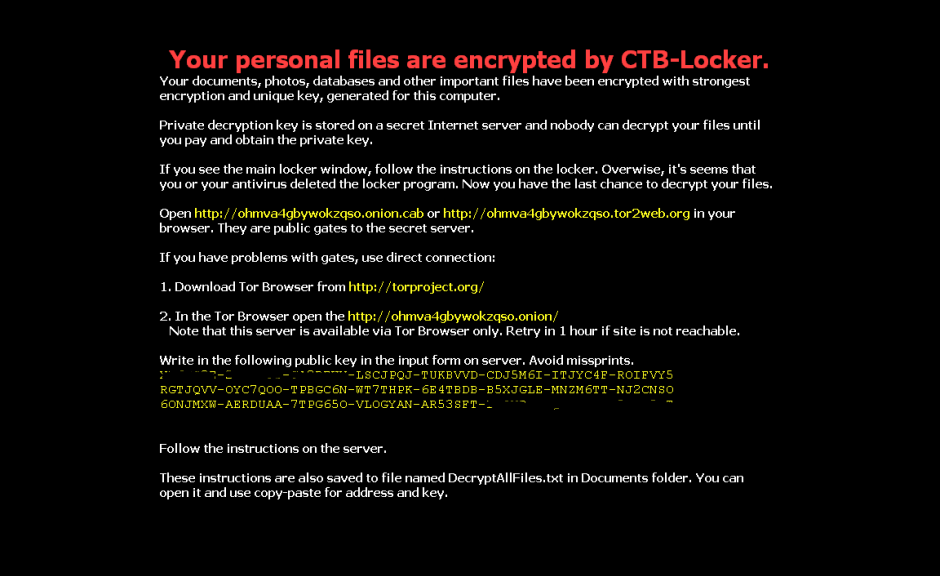
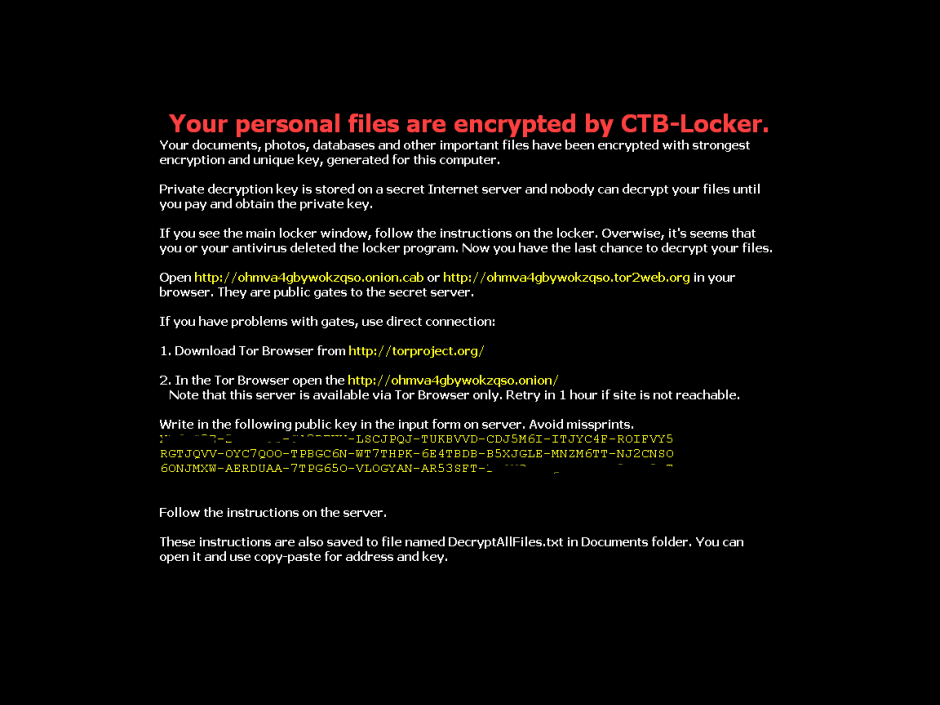
A new strain of ransomware is on the loose! Watch out!
Our colleagues at PandaLabs have detected a new strain of ransomware: Trj/RansomCrypt.B. Known as CTB-Locker, what is different about this example is that if you pay, you can access all the locked files.
This type of malware normally reaches users via email, convincing the user that it’s a legitimate message and getting them to run the file. When run, the malware encrypts image files and documents on the victim’s computer and changes the desktop wallpaper for the following image. It also creates a text file with the same information.
However, if you have any of our Internet security software, you can rest assured, as Panda Security detects and blocks this threat.
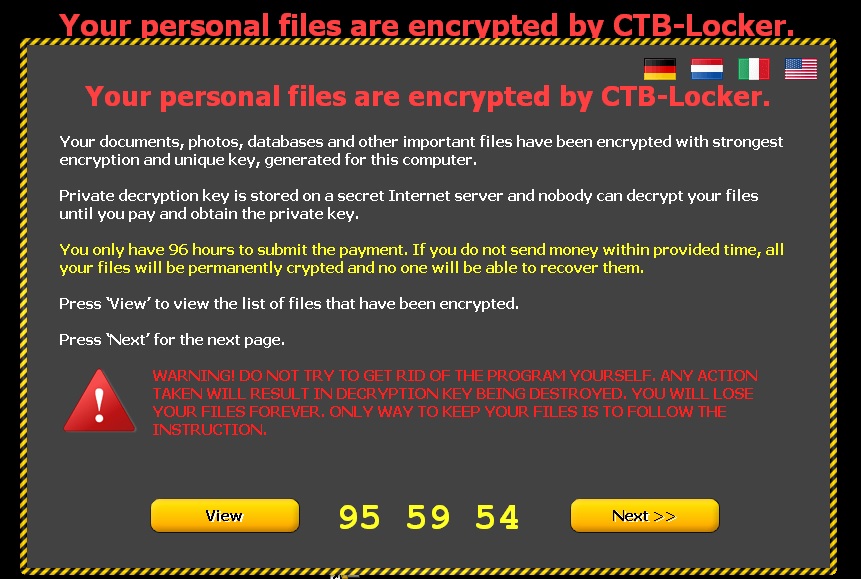
The following screen then appears, demanding a ransom before the specified time. If the ransom is not paid in time, the amount of money demanded increases.
Clicking ‘Next’ leads to the following window informing victims that if they pay, the files will be unlocked. To demonstrate that this is true, five documents are released.
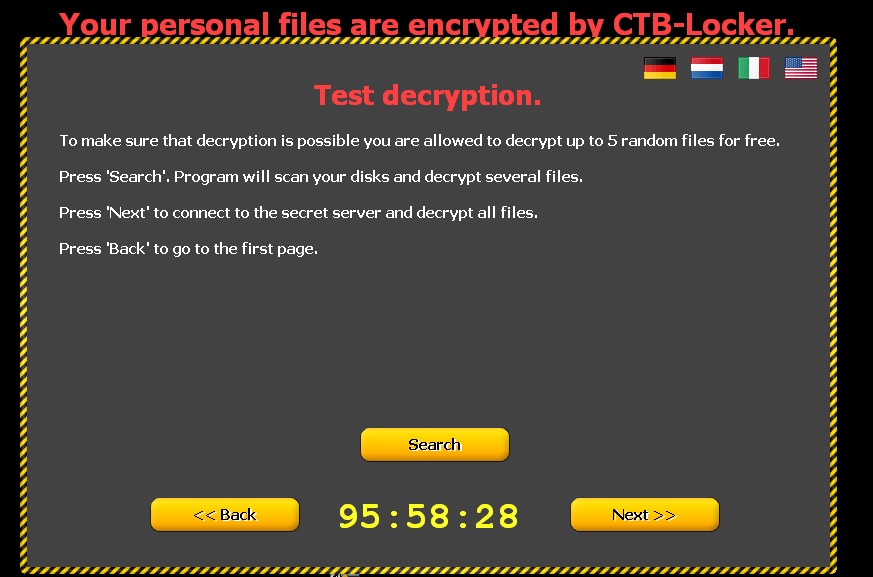
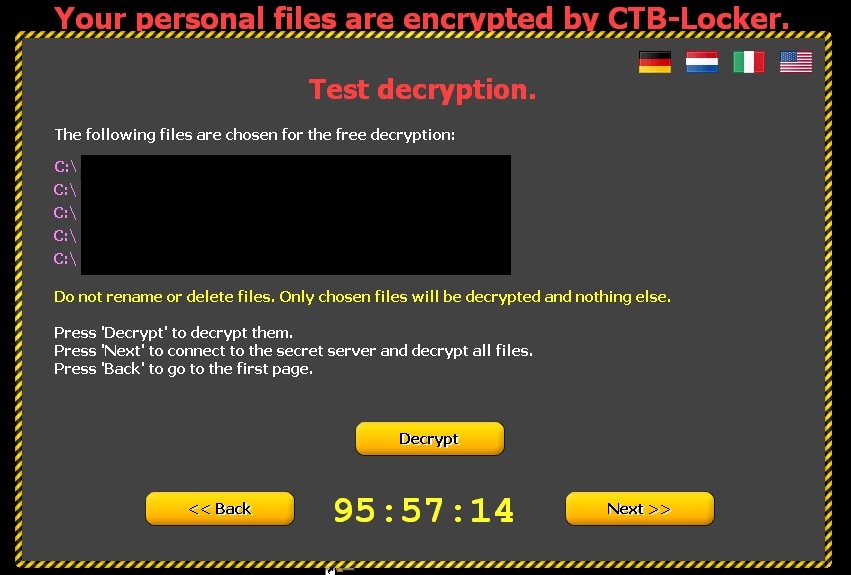
How to recognize CTB-Locker?
- This malware comes in an email with an attachment. This is either a Word file with a .doc or .rtf extension, or a compressed file (.zip) containing a .scr file.
- Some variants, in addition to encrypting files on the computer, also steal the address book to identify new potential victims. Worse still, they fake the address of the sender so the message may appear to have been sent from a known contact.
- You can see some examples of these emails here.
How to avoid Ransomware?
- Keep your operating system up-to-dateto prevent security flaws.
Make sure you have antivirus software installed and up-to-date.
- Don’t open emails or files from unknown sources.
- Don’t browse suspect web pagesor those with unverified content.
The post A new strain of ransomware is on the loose! Watch out! appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.
Adobe Patches One Zero Day in Flash, Will Patch a Second Flaw Next Week
UPDATE–Adobe has released an emergency update for Flash to address a zero-day vulnerability that is being actively exploited. The company also is looking into reports of exploits for a separate Flash bug not fixed in the new release, which is being used in attacks by the Angler exploit kit. The vulnerability that Adobe patched Thursday is […]
Careful with FileZilla! There is malware that imitates it perfectly
Anyone who has a website will be familiar with the term FTP (File Transfer Protocol), a protocol for transferring files over the Internet. When designing a website, you will have to use this quick method for storing the files that you want users to see (pages, pictures, documents, etc.) on a server.
There are also various types of programs for transporting data: these are called FTP clients, which connect your computer to the machine on which the information will be stored. One of the most widely-used is FileZilla, open and free software used by amateurs to professional web developers.
The first program, developed by Tim Kosse, was launched in 2001. Now it can be run on the most common operating systems (Windows, Linux and Mac OS X).
If you use this tool regularly, be on the lookout: malware has been detected in some versions (Filezilla v3.5.3 and Filezilla v3.7.3). The false application is installed in exactly the same way as the official version; it simulates the wizard interface perfectly and runs without any hitches.
The functioning of programs like FileZilla is simple: they allow web files to be arranged as if they were just another directory on your computer. In fact, you are managing a space in the memory of another computer (or several, if you work with various servers). You can save the data in different folders and arrange them as you please.
As you add more documents, they are transferred to this hard drive, which could be located in another country. This is where the activity of the malicious software comes in, which acts like a Trojan. It identifies each connection you establish with your server and communicates with another computer to which it sends the address where the information is housed and your FTP account login credentials.
Some addresses have been detected to which the malware transfers the stolen data, both with a Russian domain. These are ‘aliserv2013.ru’ and ‘go-upload.ru’, created in the domain register Naunet.ru, associated to fraudulent activity such as spamming. This platform hides its customers’ details and ignores demands to suspend its illegal domains.
Although this fraudulent version seems to work like the secure programs, certain characteristics give it away.
The main difference lies in the information in the About window in the program’s menu.
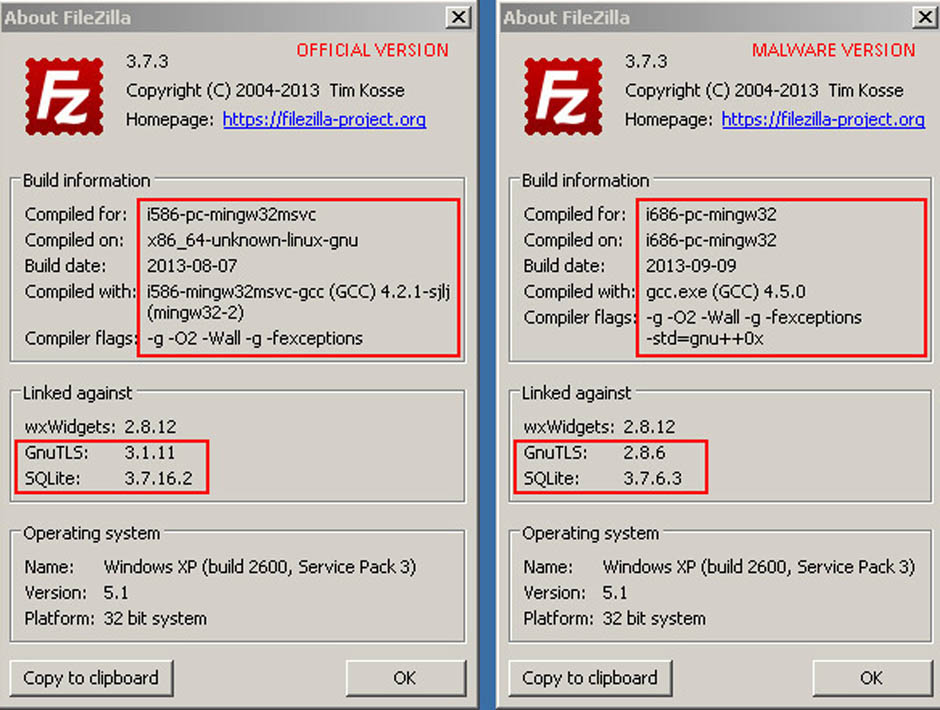
In this section you will find different references in the ‘Linked against’ option. In the malformed software, the versions of GnuTLS and SQLite are earlier versions than in the official program. In addition, you will find that the program does not allow you to update them.
GnuTLS (GNU Transport layer Security Library) and SQLite are two systems that guarantee that an application uses a secure transport layer (encrypted) to send data. These two systems are also open and free.
By using an outdated version of these programs, you risk a cybercriminal being able to monitor the login credentials used by FileZilla and decrypt the supposedly secure connections established.
Another difference with the flaw-free version is the presence of two additional libraries (ibgcc_s_dw2-1.dll and libstdc++-6.dll), although these do not seem to have any malicious effects.
Just follow these clues in order to check if the version you have installed is a spoof or the official program. In any case, make sure that you only download freeware like FileZilla from a website that offers security guarantees.
The post Careful with FileZilla! There is malware that imitates it perfectly appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.
Google AdWords Campaigns Hijacked by Malvertisers
Two Google AdWords campaigns have been hijacked by malvertisers and users are being redirected to fraud sites without even clicking the poisoned ads.