In recent months, there’s been a significant uptick in PandaLabs reports of malware that is installed using a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). Every day, we witness thousands of infection attempts using ransomware, hijacking systems for bitcoin mining, etc., which all have one thing in common: access via RDP after gaining entry with credentials obtained using the brute force method.
There are plenty of useful purposes for an RDP, but unfortunately in the wrong hands it can become a weapon for cybercriminals. We’ve already spoken of a shared history between RDP and ransomware, especially in the corporate environment.
The new attack discovered uses the same technique of entry, but its goal is completely different from those analyzed previously. This time, after infiltrating the system, it focuses on finding Point of Sale Terminals (POS’s) and ATMs. The reason for this is that they are simple terminals to attack anonymously from the Internet, and the economic profit of selling stolen information is high.
RDPPatcher: Selling system access on the black market
In the present case, the brute force attack lasted a little over two months until, in January 2017, they hit upon the correct credentials and gained access to the system. Once the system was compromised, the cybercriminals attempted to infect it with malware. They found their attempts blocked by Adaptive Defense, at which point they modified the malware and tried again, without success. Since Panda’s advanced cybersecurity solution is not based on signatures and does not rely on previous knowledge of malware in order to block it, modifying the malware didn’t change the result.
It’s clear from the malware analysis what the purpose of the attack is. The hashes of the two file are the following:
MD5 d78be752e991ccbec16f11e4fc6b2115
SHA1 4cc9d2c98f22aefab50ee217c1a0d872e93ce541
MD5 950e8614db5c567f66d0900ad09e45ac
SHA1 9355a60dd51cfd02a921444e92e012e25d0a6be
Both were programmed on Delphi and packaged with Aspack. After unpacking them, we found that they were very similar to each other. We analyzed the most recent of them: (950e8614db5c567f66d0900ad09e45ac).
This Trojan, detected as Trj/RDPPatcher.A modifies the Windows records in order to change the type of RDP validation. These are the entries that the system modifies:
And deletes the following entries if they are present in the system:
Subsequently, it leaves another file (MD5: 78D4E9BA8F641970162260273722C887) in the %TEMP% directory. This file is a version of the application rdpwrap and is run via the runas command with the parameters “-i –s” in order to activate concurrent RDP sessions on the system.
It then proceeds to profile the machine and obtain its information:
- Username
- Device name
- Amount of time the device has been turned on
- Operating system version
- Language
- Virtual maching
- Memory
- Processor name
- Number of processor cores
- Processor speed
- Antivirus
It then connects to the control server (C&C server) to access a list of services that measure the speed of connection to the Internet, and later saves the data related to upload and download speed. Next it checks which antivirus is installed on the computer. Contrary to what we are accustomed to seeing in most malware attacks, it does not do this to remove the installed antivirus or to change its behavior. It is simply gathering data.
This is the list that we have extracted from the binary with the processes that it searches:
See Table 1
Once this is done, it begins to search for different types of software to continue profiling the computer. It mainly looks for POS, ATM, and online gambling software. What follows is a small part of the list of software that it searches (in total there are several hundred):
It also combs through browsing history, where another list is contained, categorized by areas of interest:
See Table 3
These chains are searched for in the browser history by the malware itself. They’re used to “label” the computer based on software used and webpages visited.
Once it’s finished with the data gathering from the system, it makes a web petition to the C&C. In order to hide the sending of the information via web traffic from detection systems, it first encrypts it with AES128 using the password “8c@mj}||v*{hGqvYUG”, which is embedded in the sample analyzed. It then codifies it on base64.

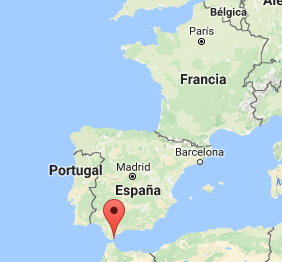
The C&C server used for this malware sample is located in Gibraltar:
Conclusion
As we’ve seen, the first thing the attacker seeks to do is to inventory the computer, compiling all types of information (hardware, software, webpages visited, Internet connection speed), and install an application that allows multiple RDP sessions at once. At no point does credentials theft, or any other data theft, occur.
The explanation for this is very simple: the cybercriminals behind these attacks sell access to these computers for a very small fee. Being in possession of so much data from every system allows them to sell access to other groups of cybercriminals specializing in different fields. For example, groups that specialize in the theft of card data can acquire computers with POS software, and so on. Cybercrime has indeed become a profitable racket.
The post RDPPatcher, the Attack that Sells Access to your Computer at a Low Price appeared first on Panda Security Mediacenter.