A command execution vulnerability exists in Hewlett-Packard Data Protector. The vulnerability is due to a design weakness when handling requests to port 5555. A remote attacker can exploit this vulnerability by sending crafted packets to the target service. Successful exploitation could lead to arbitrary command execution with system privileges on the target server.
Monthly Archives: August 2014
What does the future hold for our privacy?
Nothing is ever certain about our future, but when it comes to privacy, we can take a look at current trends and make some educated guesses as to what we will see tomorrow, next year, or even in 10 years’ time…
Looking at those trends, it’s clear that no matter how people’s privacy is violated and taken away, there will always be new tools to help protect it combat them and most important of all, keep people in control of their own privacy.
Innovation helps both sides of the spectrum and will lead to many games of cat and mouse moving forward into the future. To be more specific though I see two primary areas where privacy will be influenced the most in the future: anonymity and user owned data.
Anonymity
Being anonymous is one of the hardest things to do, if not impossible, in this day and age. With the prevalence of online tracking, government surveillance, and login systems everywhere it is very difficult to keep things to yourself unless you are willing to forgo the online world. While there are many services that start to offer “anonymous†services such as Secret and Telegram, there is always something that is connecting your device to the posts you do or the interactions you make. That’s why I see a future where pseudo-anonymity is commonplace.
Pseudo-anonymity would allow people to be anonymous to others and possibly to the application they are interacting with, but still be able to put together a profile and have an account. Adopting a pseudo-anonymous system has potential far beyond simple messaging apps and in something like Bitcoin, has the potential to really change the world.
In Bitcoin, everyone has a public address where you can see where Bitcoins are being sent to and from, and follow transactions very publicly, but you can’t actually identify the person that has the addresses unless they specifically tell you. This form of pseudo-anonymity is regarded as a positive step for privacy as it allows for direct audits and transparency of information while still letting individuals control their identifiable data.
Bitcoin is just one example of pseudo-anonymous technology, while even Facebook is taking steps to allow for Facebook login where apps cannot access your identity but rather just verify you are a person. It’s important I think to separate out task of verifying users as real people and learning their identities. That way we can have quality services supported by real users but without them having to sacrifice their privacy. Pseudo-anonymityis a good bridge for these two things.
User Owned Data
Right now as you browse the web there are dozens of companies that are collecting information about what you search for, what pages you visit, what you watch, and more. These companies make inferences about you such as your gender, income bracket, and marital status. They then sell this information to advertisers who will try to serve you with more relevant ads so that you are more inclined to click on them. This is the current status quo but it relies heavily on inferences and guesswork, which means there is a limit to how accurate the information can be.
Currently many companies have tried to bring user control to this aspect of online data collection, but nobody has truly succeeded. To get users to willingly hand over their data to companies, there needs to be a high enough value proposition for the users. Facebook and Google do a great job of this currently by providing free services that we use every day in return for data to be used for advertising. Other companies are still trying to crack the code on what would be valuable enough to these users. Online advertising is still in a high growth phase though and has a strong outlook to expand and grow into the future. Once advertising matures enough, it may become worth enough for other companies to be able to provide proper incentives to users in return for access to their data.
While nobody can predict the future we can help build the future we want to be a part of. The next time you sign up for a site or enter a competition in exchange for your email address and phone number, consider what information you are really giving up, who is getting access to it, and how it will be used. If we want a future where we are all more in control of our privacy we must start to take better care of our data.
If you have any ideas of what would be ideal in your future for privacy, let us know in the comments or drop us a line on our Facebook page at https://www.facebook.com/AVG.
![]()
![]()
California Earthquake serves up privacy reminder
This weekend’s earthquake near American Canyon has highlighted the risk of living in the Bay Area and also given us all insight to how people behave in today’s connected world.
The speed at which tweets started appearing of people sharing their experiences shows that many of us are sleeping with a connected device next to the bed that is the first thing we grab for when awoken in the middle of the night. Now though, our connected devices are no longer relegated to the nightstand, but instead are in bed with us.
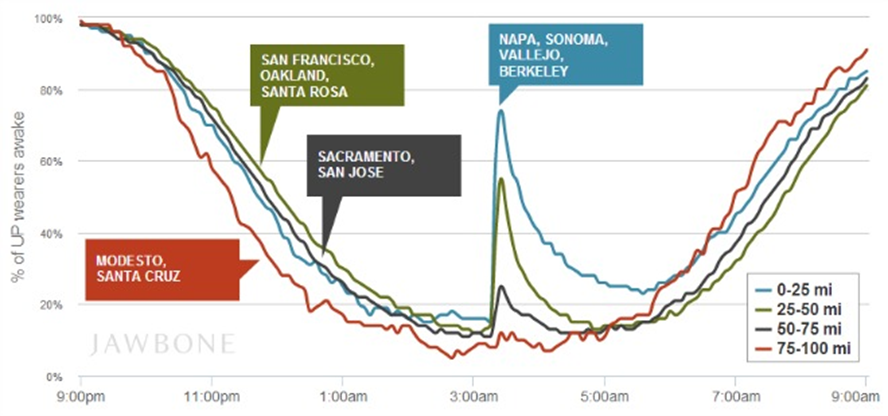
After the quake, an interesting story emerged from Jawbone, the manufacturer of a fitness/sleep tracker UP. They have released data on the number of people that were woken by the earthquake based on location and the epicenter. The data is interesting, 93 percent of UP wearers in Napa, Sonoma, Vallejo and Fairfield woke up instantly, while just over half in the areas of San Francisco and Oakland. And 45 percent of those within 15 miles of the epicenter then remained awake for the remainder of the night. The data gives you some indication on the magnitude and effect the earthquake had on people.
While the information is very interesting and offers fascinating insight into human behavior, it does also serve as a gentle reminder that as connect our lives to the Internet, that data takes on a life of its own.
I wonder if the users of fitness/sleep devices are aware that their data could be used for analysis such as this? While the data Jawbone shared was anonymous and pretty much harmless, it does make me think, what else is being collected? What other insights do they have into our daily lives?
Fitness/sleep trackers collect information about the user and most of it is of a very personal nature and includes name, gender, height, weight, date of birth and even what you eat and drink if you are logging this in the app. Now couple this with location data that is being collected and you may even be able to understand where people regularly work out or go to eat..
I use a fitness tracker and as a user I limit the sharing of my data, I have switched off the sharing through social media as I don’t think my friends and family really need to know how many steps I took today. But I do understand that many users bounce off their friends as motivation to do more exercise which is not a bad thing if that’s the way you get your motivation.
Checking privacy policies
It sounds boring but I would absolutely advise reading the privacy policy of a fitness tracker before purchasing/installing. It cannot hurt to be more informed about what you are agreeing to reveal about yourself and who you are happy to share that information with.
After all its your data, it should be up to you how it gets used.
![]()
![]()
Games hit by massive outage: Sony PSN, Blizzard, Riot and more affected
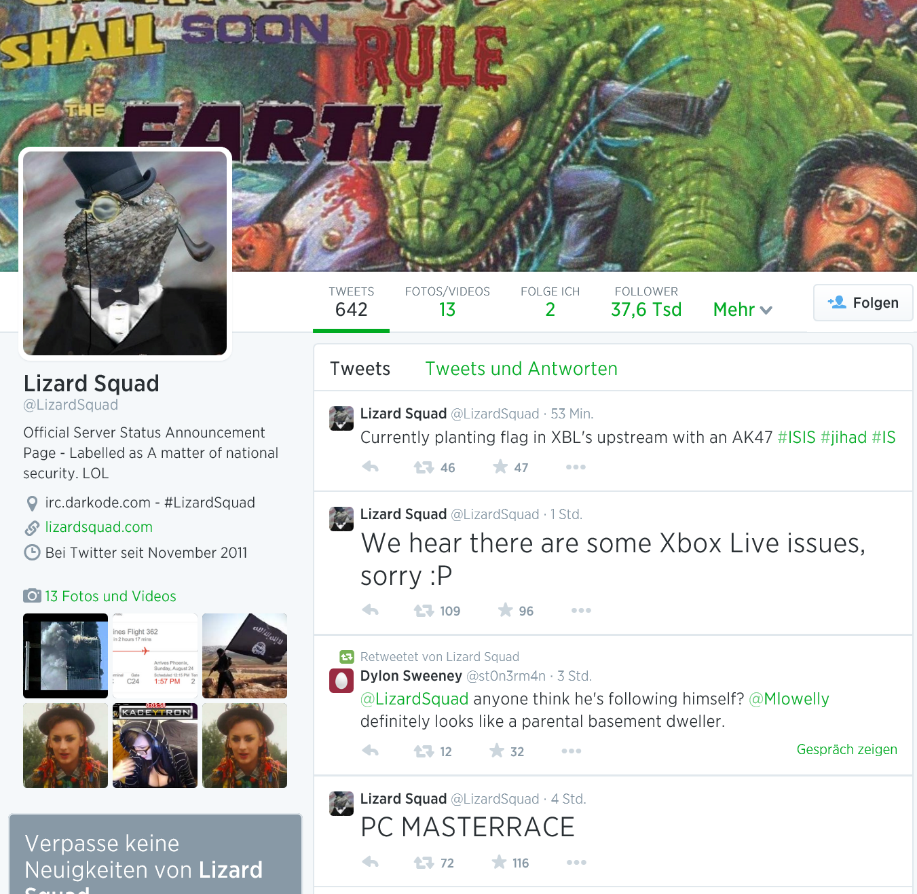
Gamers, you better dig out your good old offline games: some of the most popular online gaming networks are getting attacked by hackers. On Sunday, August 24th2014, a group which calls themselves the “Lizard Squadâ€:
They have started attacking Sony’s PlayStation network (PSN) though which the company sells all of their online games and which serves as a hub for all multiplayer games. The method used: DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service). Sony, being burned in 2011 by a massive hack attack, immediately issued a statement saying that no customer data was stolen this time and that it’s back up since Monday August 25th.
Riot, Blizzard, Xbox Live affected too
On Monday, however, the group moved on to Blizzard, the makers of World of Warcraft, and Riot Games, the ones behind games like League of Legends and continued to attack other sites. Here’s the latest:
PSN Network: Is back online, according to their statement on Monday, August 25th. Lizard attacked PSN for what they perceive to be a lack of PSN customer service: “Sony, yet another large company, but they aren’t spending the waves of cash they obtain on their customers’ PSN service. End the greed.â€
Blizzard: Battle.net, the online service behind World of Warcraft, seemed to be heavily affected on Sunday, but was in the process of stabilization on Monday. But other than the fact that Battle.net was a target, the group doesn’t seem to offer any reasons for hacking – other than their typical “lulz†by asking users to write the groups name on their forehead while playing Hearthstone and Dota 2 on Twitch.
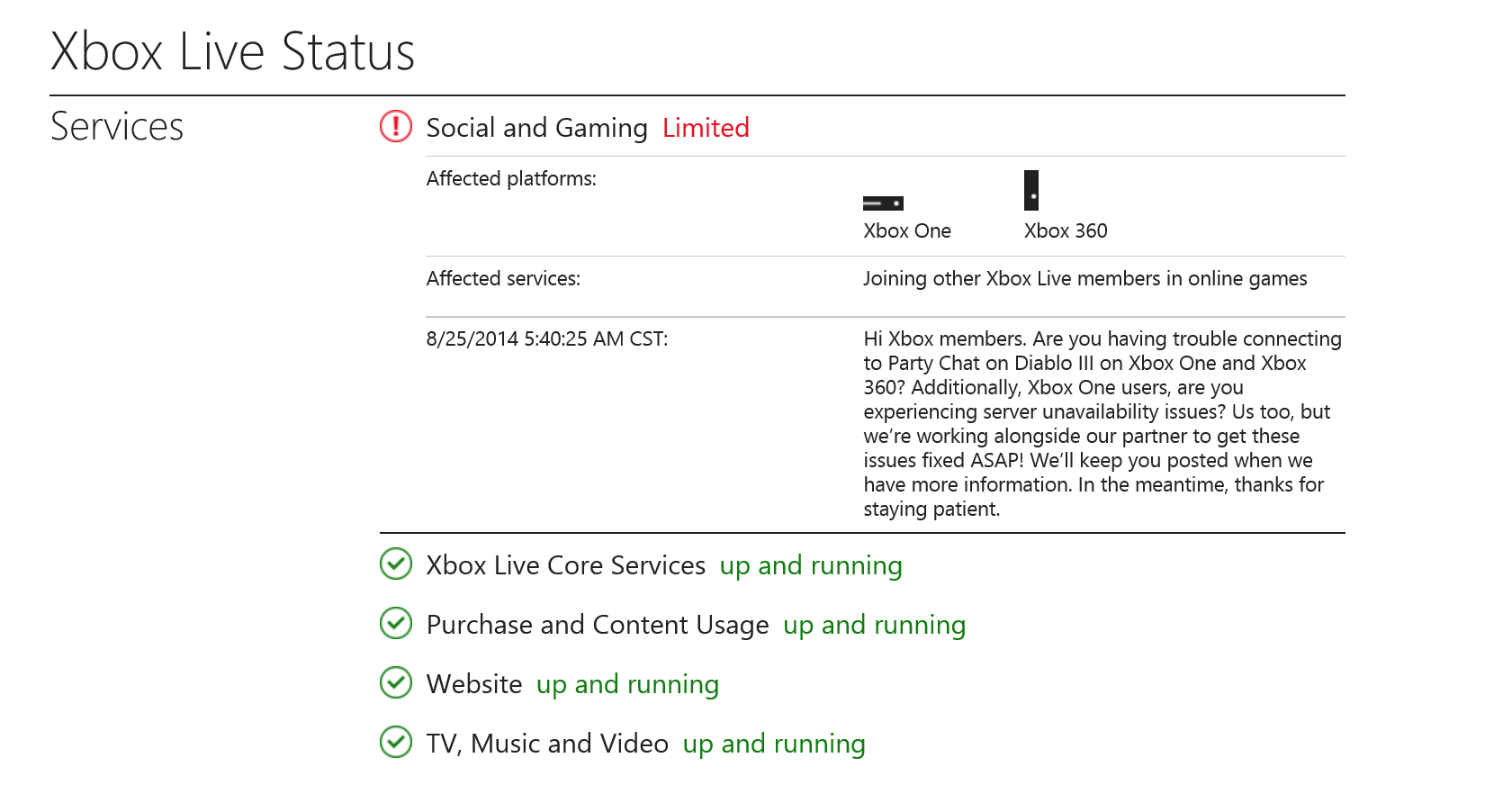
Xbox Live: in addition to the networks above, Microsofts Xbox Live network has been hit, too – users should regularly check the status here:
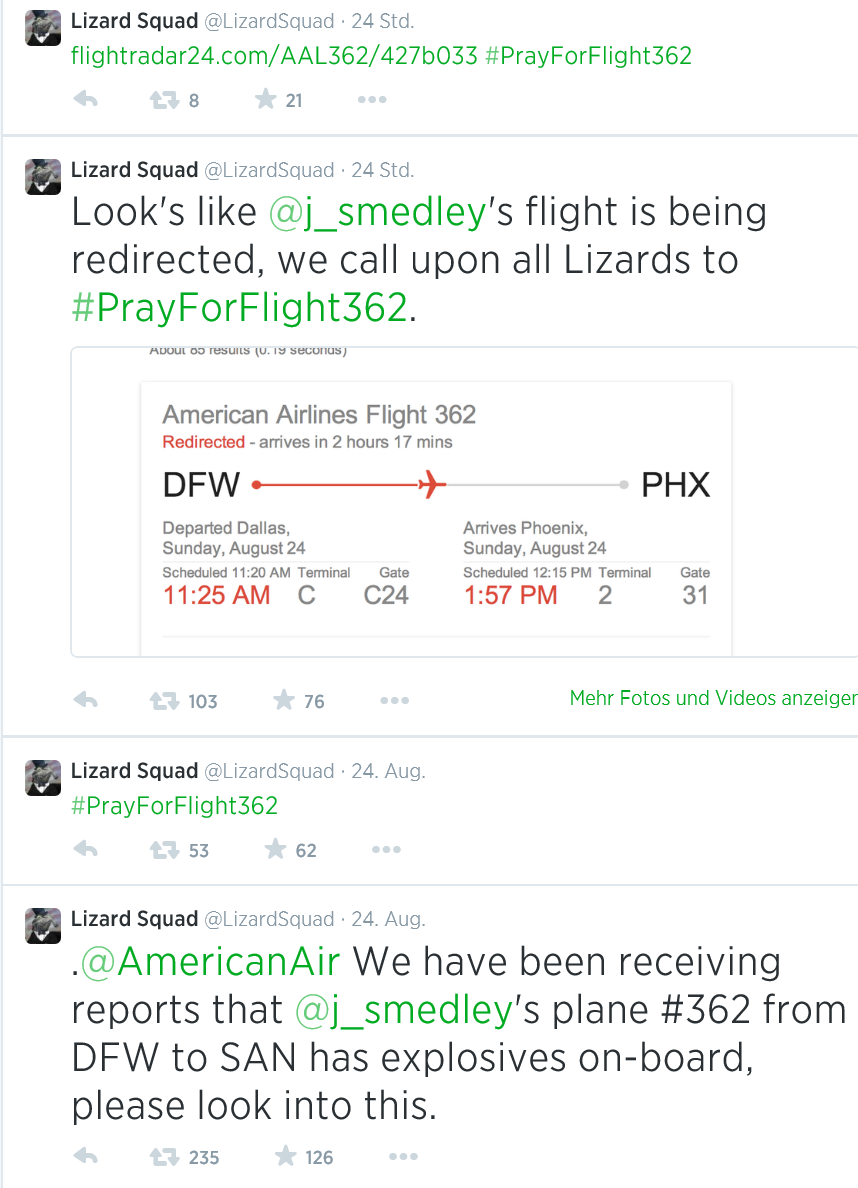
However, the negative “icing on the cake†came when the group announced that they’ve seen “reports of explosives†on board an American Airlines flight from Dallas to San Diego carrying Sony Online Entertainment president John Smedley.
American Airlines immediately redirected the plane, which just goes to show how much of an impact this series of DDoS attacks and its publicity just had on people.
Should you be worried?
For now: no! DDoS attacks are not traditional hacking attacks, but rather “clogging the Internet toilet†by which a server gets hits with hundreds of thousands of requests. So far, there appears to be no evidence of an actual hacking attack. We will keep you posted, but other than the major inconvenience for gamers, there seems to be no data compromised!
![]()
![]()
UPS stores attacked in the USA

UPS, the international courier service, may have been the victim of a cyber-attack using a virus detected in 51 of the company’s US stores.
A company spokesperson confirmed that the attack could have compromised confidential information, including customers’ names, card details and postal and email addresses. The earliest evidence of the presence of this malware at any location is January 20, 2014 and was eliminated as of August 11, 2014.
The attack has been traced back to the services that give employees remote access to the UPS system. Cyber-criminals exploited this to infect point-of-sale terminals and obtain information massively from the database.
UPS has informed customers of the stores that have been affected by the malware.
Attack on Target
This attack is similar to the one suffered by another US company, Target, which resulted in the theft of over 40 million credit card details.
Point-of-sale terminals are a highly-prized target for cyber-criminals. It’s not a question of chance, sooner or later someone will try to hack your terminals. To ensure protection you need a security solution that covers different aspects of the POS terminal and which can:
- Restrict the running of software, only allowing trusted processes to run.
- Identify vulnerable applications, warning you of any outdated software.
- Enforce the behavior of permitted processes to prevent vulnerability exploits in trusted processes.
- Traceability: If an incident occurs, your security solution should provide all the information needed to answer four basic questions: when the attack began; which users have been affected; what data has been accessed and what has happened to it; and how the attackers entered and from where.
These are not all the security measures that can be taken, although these four points at least must be covered.
The post UPS stores attacked in the USA appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.
Win a free avast! Mobile Premium license
AVAST is celebrating 100 million downloads of avast! Mobile Security & Antivirus for Android.
We want to protect your Android phone and tablets, so we’re giving you the chance to win a free license for the most trusted Android security product in the world!
How much do you know about your phone’s security?
Do you know all the ways to use avast! Mobile Security’s anti-theft feature to track your phone?
Do you know who is more at risk for getting malware on their mobile device?
Do you know how many phones are stolen every minute of every day?
Take the avast! Mobile Security quiz and find out! Answer all 5 questions correctly (don’t worry, we’ll give you hints) and you’ll be in the running to win a free 1-year license for avast! Mobile Premium! One lucky winner will win LIFETIME protection, and 10 lucky winners will receive a rare avast! teddy bear.
Here’s what to do:
- Become an AVAST fan on Facebook
- Enter the quiz and answer 5 questions correctly
- Write what you think is the most serious threat to your mobile security
- Share the quiz with your friends
Take the avast! Mobile Security quiz now!
Make sure all the Android’s in your life have protection. Install avast! Mobile Security and Antivirus from the Google Play store, https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.avast.android.mobilesecurity
Thank you for using avast! Antivirus and recommending us to your friends and family. For all the latest news, fun and contest information, please follow us on Facebook, Twitter and Google+. Business owners – check out our business products.
CVE-2014-0480
The core.urlresolvers.reverse function in Django before 1.4.14, 1.5.x before 1.5.9, 1.6.x before 1.6.6, and 1.7 before release candidate 3 does not properly validate URLs, which allows remote attackers to conduct phishing attacks via a // (slash slash) in a URL, which triggers a scheme-relative URL to be generated. (CVSS:5.8) (Last Update:2014-09-04)
CVE-2014-0481
The default configuration for the file upload handling system in Django before 1.4.14, 1.5.x before 1.5.9, 1.6.x before 1.6.6, and 1.7 before release candidate 3 uses a sequential file name generation process when a file with a conflicting name is uploaded, which allows remote attackers to cause a denial of service (CPU consumption) by unloading a multiple files with the same name. (CVSS:4.3) (Last Update:2014-09-04)
CVE-2014-0483
The administrative interface (contrib.admin) in Django before 1.4.14, 1.5.x before 1.5.9, 1.6.x before 1.6.6, and 1.7 before release candidate 3 does not check if a field represents a relationship between models, which allows remote authenticated users to obtain sensitive information via a to_field parameter in a popup action to an admin change form page, as demonstrated by a /admin/auth/user/?pop=1&t=password URI. (CVSS:3.5) (Last Update:2014-09-04)
CVE-2014-0482
The contrib.auth.middleware.RemoteUserMiddleware middleware in Django before 1.4.14, 1.5.x before 1.5.9, 1.6.x before 1.6.6, and 1.7 before release candidate 3, when using the contrib.auth.backends.RemoteUserBackend backend, allows remote authenticated users to hijack web sessions via vectors related to the REMOTE_USER header. (CVSS:6.0) (Last Update:2014-09-04)