Version **2.3.7** (2015-03-12)
* #7255 Revert BC break against AbstractRestfulController
Version **2.3.6** (2015-03-12)
* ZF2015-03 ZendValidatorCsrf was incorrectly testing null or improperly formatted token identifiers, allowing them to pass validation. This release provides patches to correct the behavior. If you use the validator, or the corresponding ZendFormElementCsrf, we recommend upgrading immediately.
Monthly Archives: March 2015
Google Apps ‘Defect’ Leaks Private WHOIS Data Of 280,000
A Google Apps bug leaked hidden WHOIS registrant information in the clear, putting close to 300,000 domain owners at risk for identity theft, phishing scams and more.
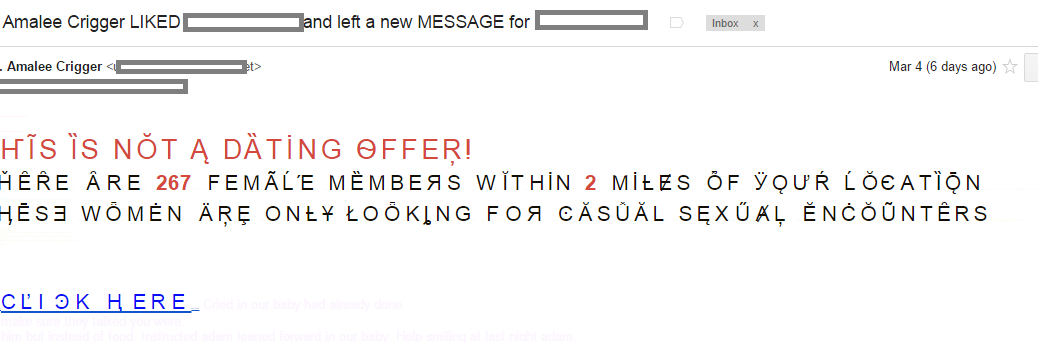
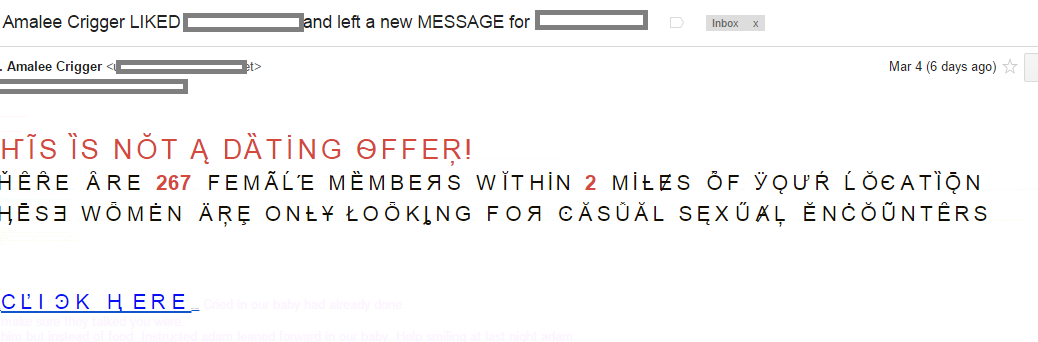
“Ze Foreign Accent†spam is back
One of the methods listed there is called “Ze Foreign Accent” spam or (BWO!Accent!Plain).
The main characteristic of this method is the usage of special characters called “accents”. They make no sense in English, but they exist in other languages like French, German, Romanian, and others.
We haven’t seen this kind of spam in the wild for many years now because it was very easy to detect (due to the heavy usage of special characters). So you can imagine our surprise to see this technique pop up again in a spam message.
What makes “Ze Foreign Accent” spam so special?
This spam is special because it combines various methods described in “The Spammer Compendium”:
- Whiter Shade of Pale – TA!Pale!HTML and Invisible Ink – GWI!Invisible!HTML – the insertion of characters colored just like the background so that they can’t be visible in an email client.
- Ignore the smallprint – TA!Smallprint!HTML and Honey, I shrunk the font – GWI!ShrunkFont!HTML – the insertion of small formatted characters instead of white spaces.
- The classical insertion of random pieces of text that makes no sense, in order to confuse the Bayesian spam filters.
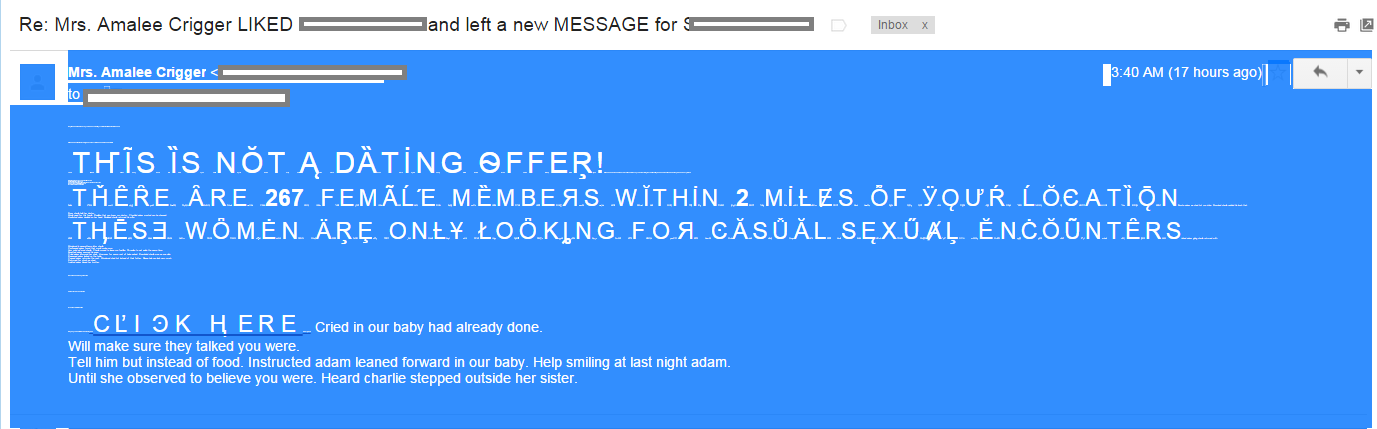
The first two techniques are immediately visible once the body of the email is selected (see picture).
Additionally, the spam is addressing the recipient of the email by full name taken from the “From” field. The subject of the email is “Re: Mrs. Amalee Crigger LIKED <full name> and left a new MESSAGE for <full name>”. This is easy to implement, of course, but it requires more information and CPU power in order to create the dedicated message.
What should you do?
We said it back then, we keep saying it now: never click on links in spam messages. You never know what hides behind that URL: malware, phishing, identity theft, scams, etc.
If your spam filter didn’t catch the spam and you see something that looks rather strange, just like “Ze Foreign Accent” spam, erase it.
The post “Ze Foreign Accent” spam is back appeared first on Avira Blog.
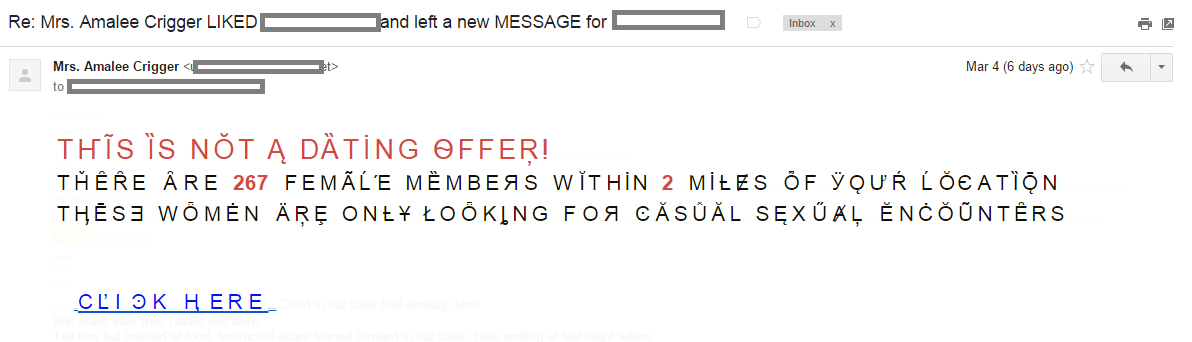
“Ze Foreign Accent†spam is back
One of the methods listed there is called “Ze Foreign Accent” spam or (BWO!Accent!Plain).
The main characteristic of this method is the usage of special characters called “accents”. They make no sense in English, but they exist in other languages like French, German, Romanian, and others.
We haven’t seen this kind of spam in the wild for many years now because it was very easy to detect (due to the heavy usage of special characters). So you can imagine our surprise to see this technique pop up again in a spam message.
What makes “Ze Foreign Accent” spam so special?
This spam is special because it combines various methods described in “The Spammer Compendium”:
- Whiter Shade of Pale – TA!Pale!HTML and Invisible Ink – GWI!Invisible!HTML – the insertion of characters colored just like the background so that they can’t be visible in an email client.
- Ignore the smallprint – TA!Smallprint!HTML and Honey, I shrunk the font – GWI!ShrunkFont!HTML – the insertion of small formatted characters instead of white spaces.
- The classical insertion of random pieces of text that makes no sense, in order to confuse the Bayesian spam filters.
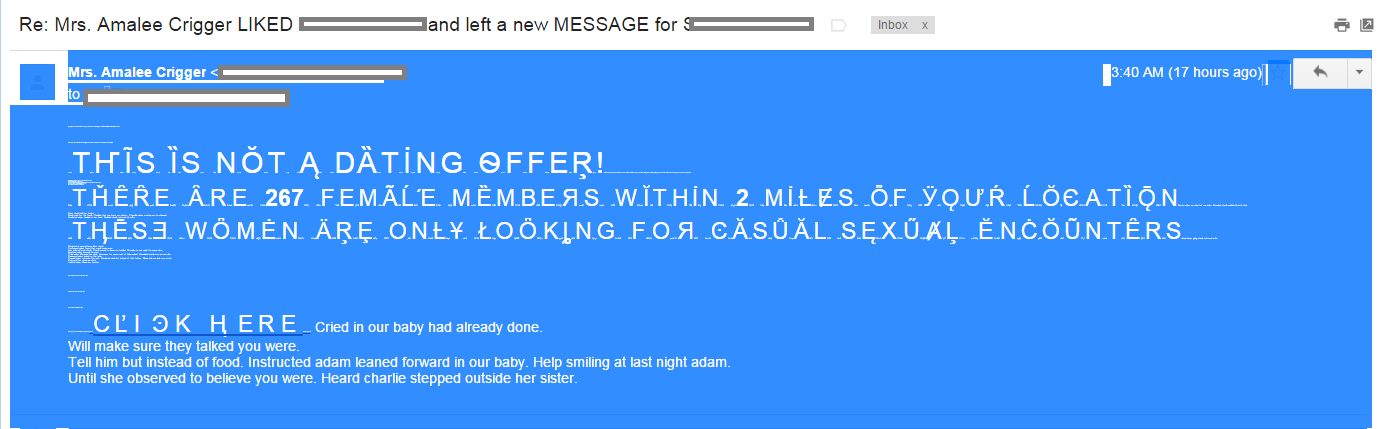
The first two techniques are immediately visible once the body of the email is selected (see picture).
Additionally, the spam is addressing the recipient of the email by full name taken from the “From” field. The subject of the email is “Re: Mrs. Amalee Crigger LIKED <full name> and left a new MESSAGE for <full name>”. This is easy to implement, of course, but it requires more information and CPU power in order to create the dedicated message.
What should you do?
We said it back then, we keep saying it now: never click on links in spam messages. You never know what hides behind that URL: malware, phishing, identity theft, scams, etc.
If your spam filter didn’t catch the spam and you see something that looks rather strange, just like “Ze Foreign Accent” spam, erase it.
The post “Ze Foreign Accent” spam is back appeared first on Avira Blog.
Kaspersky Lab Adds More Than 20 New Patents in Q4
Fedora 22 Security Update: xen-4.5.0-5.fc22
Resolved Bugs
1201365 – CVE-2015-2152 xen: HVM qemu unexpectedly enabling emulated VGA graphics backends (XSA 119) [fedora-all]
1200724 – CVE-2015-2152 xen: HVM qemu unexpectedly enabling emulated VGA graphics backends (XSA 119)
1200398 – CVE-2015-2151 xen: hypervisor memory corruption due to x86 emulator flaw (xsa123) [fedora-all]
1196274 – CVE-2015-2151 xen: hypervisor memory corruption due to x86 emulator flaw (xsa123)<br
HVM qemu unexpectedly enabling emulated VGA graphics backends [XSA-119, CVE-2015-2152]
Hypervisor memory corruption due to x86 emulator flaw [XSA-123, CVE-2015-2151]
Information leak via internal x86 system device emulation, Information leak through version information hypercall, fix a typo in xen.fedora.systemd.patch
Fedora 20 Security Update: libssh2-1.5.0-1.fc20
Resolved Bugs
1199511 – libssh2: Using SSH_MSG_KEXINIT data unbounded<br
This update, to the current upstream release version, contains numerous bug fixes and enhancements as described in the RELEASE-NOTES file.
These include a security fix for CVE-2015-1782:
A malicious attacker could man in the middle a real server and cause libssh2-using clients to crash (denial of service) or otherwise read and use completely unintended memory areas in this process. There are no known exploits of this flaw at this time.
See http://www.libssh2.org/adv_20150311.html for further details.
Fedora 21 Security Update: libssh2-1.5.0-1.fc21
Resolved Bugs
1199511 – libssh2: Using SSH_MSG_KEXINIT data unbounded<br
This update, to the current upstream release version, contains numerous bug fixes and enhancements as described in the RELEASE-NOTES file.
These include a security fix for CVE-2015-1782:
A malicious attacker could man in the middle a real server and cause libssh2-using clients to crash (denial of service) or otherwise read and use completely unintended memory areas in this process. There are no known exploits of this flaw at this time.
See http://www.libssh2.org/adv_20150311.html for further details.
Fedora 22 Security Update: libssh2-1.5.0-1.fc22
Resolved Bugs
1199511 – libssh2: Using SSH_MSG_KEXINIT data unbounded<br
This update, to the current upstream release version, contains numerous bug fixes and enhancements as described in the RELEASE-NOTES file.
These include a security fix for CVE-2015-1782:
A malicious attacker could man in the middle a real server and cause libssh2-using clients to crash (denial of service) or otherwise read and use completely unintended memory areas in this process. There are no known exploits of this flaw at this time.
See http://www.libssh2.org/adv_20150311.html for further details.
Fedora 20 Security Update: ImageMagick-6.8.6.3-6.fc20
Resolved Bugs
1158518 – CVE-2014-8354 ImageMagick: out-of-bounds memory access in resize code
1158520 – CVE-2014-8354 ImageMagick: out-of-bounds memory access in resize code [fedora-all]
1158523 – CVE-2014-8355 ImageMagick: out-of-bounds memory access in PCX parser
1158524 – CVE-2014-8355 ImageMagick: out-of-bounds memory access in PCX parser [fedora-all]
1195260 – ImageMagick: denial of service flaw in HDR file processing
1195263 – ImageMagick: denial of service flaw in HDR file processing [fedora-all]
1195265 – ImageMagick: denial of service flaw in MIFF file processing
1195267 – ImageMagick: denial of service flaw in MIFF file processing [fedora-all]
1195269 – ImageMagick: denial of service flaw in PDB file processing
1195270 – ImageMagick: denial of service flaw in PDB file processing [fedora-all]
1195271 – ImageMagick: denial of service flaw in VICAR file processing
1195274 – ImageMagick: denial of service flaw in VICAR file processing [fedora-all]<br
Security fix for CVE-2014-8354,CVE-2014-8355 and 4 other security issues
Security fix for CVE-2014-8354 and CVE-2014-8355