It’s pervasive; it’s everywhere. It can even rig national elections according to some well-known experts and academics. No, we’re not talking about Vladimir Putin’s team of world-class cyber spies. We’re talking about the medium of social media.
Hate it or love it, social media is here to stay. It’s bringing us closer to one another, and it’s helping us keep in touch across vast distances. Hey, it’s even helping us reconnect with these long-lost, faraway people we thought we’d never hear from again. Like, ever. And on the other hand, it’s hard to remain anonymous these days.
There are many people who decide not to store and share information on their social networks in order to avoid risks
It is smarter to share content on social networks from a cyber-secure point of view than to try to do not to exist digitally
“The kind of information we share on social media is very personal and everyone posts what they concon disider necessary. However, we live in a hyper-connected society and there’s a lot of effort to be made to avoid leaving our mark on the Internet. Sooner or later, somebody ends up doing it for us. It is smarter to share content on social networks from a cyber-secure point of view than to try to do not to exist digitally. At least in the first case, what you have on the Internet is protected, “says Hervé Lambert, Global Consumer Operations Manager at Panda Security.
We are not saying we ought to pull the plug on this social media thing altogether. It has too many advantages to give up… But with the rise of fake news and cyber insecurity, we need to be protected.
Malware programs
As an example malware, short for malicious software, are computer programs that get installed on your device – often inadvertently. It may just be a brief moment of inattention, one rapid click, and boom! A malware installs itself on your hard drive if you are not protected.
Malware programs will then disrupt normal operations, and they might collect personal data like bank details, credit card information, and passwords. Briefly, anything valuable to any mildly talented crook. And let’s face it, by listening to the news, it’s seems that there are many of them out there.
Nothing is more important than the safety of the people who use Facebook, and the security of their data.
According to Facebook, “nothing is more important than the safety of the people who use Facebook, and the security of their data.” That’s re-assuring. The company has a Security Team dedicated to keeping you safe. Apparently, they’ve pioneered multiple defense systems against spam, viruses and phishing attacks. And even though Facebook has some automated enforcement mechanisms that are meant to shut down malicious apps, pages or accounts quickly, sometimes troubles makers manage to people like you.
Prevention is the best cure, therefore, why not implement these easy steps to protect your social media accounts?
- Step 1: Choose a secure password. The bottom line is you need a more robust password. Sorry to disappoint, but if you think pa55word is a safe option then think again. Someone figured that one out a long time ago.
- Step 2: Don’t put sensitive information in your profile. Why would anyone want to do this anyway? Like your mother would say: “if in doubt, leave it out.”
- Step 3: Refuse to let ANY application access your profile. That’s right, and we mean it: deny access to all of them. They promise to make your life easier, but they might end up making your life a nightmare instead!
- Step 4: Don’t click on suspicious links, however tempting they may look. It’s not worth it! Think before you take action.
- Step 5: adjust your privacy settings. There’s a reason why these settings exist, familiarize yourself with them and review them regularly. You’ll thank us later!
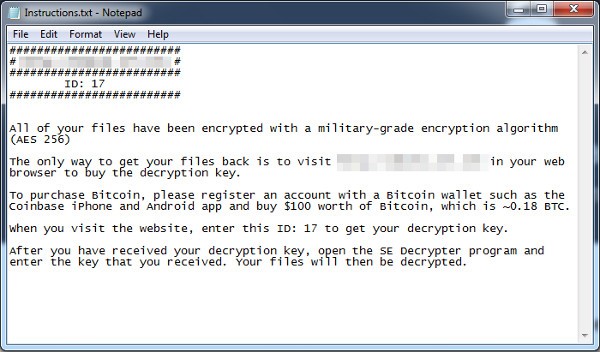
And remember that if you think your device may have been infected with malware, fear not: help is available. Anti-virus specialists like us propose an advanced, dynamic, ever-evolving cyber-security model based on the principles of artificial intelligence. In short: we’ve got your back.
We developed, patented sets of proactive technologies aimed at blocking unknown viruses, along with the Collective Intelligence model. This system is the first to automatically detect, analyze, and classify malware in real time. We are very proud of our product and remember, your safety is our priority!
The post Protect your social media account in these 5 simple steps appeared first on Panda Security Mediacenter.