Our guest article Righard has been in the IT security world since the late 80’s, and “playing” with computers since the 70’s.
1- At the beginning, computer viruses were almost like a myth. However, over the years, computer attacks became real and they have evolved significantly, along with security solutions. To what extent are we doing things properly? It seems that today there are more attacks than ever before…
Obviously there are more attacks than ever before. In the beginning, having a computer was a novelty, on top of that, the underlying OS was rather diverse. Nowadays, almost everyone has one or more computers or devices. More devices makes the attack vector more interesting (higher chance of success for the cybercriminal) but as many more people are now “into” computers, there automatically are also more people that will exploit for ill purposes. It is inevitable. As in business, where there is an opportunity there will be an entrepreneur, likewise in cybercrime, if it can be exploited, someone will.
With the growth and evolution of the OS’s, security solutions followed. Actually not only the security solutions but also the general perception of security by the public. Guess banking Trojans and ransomware were useful to raise the awareness.

Senior Research Fellow, ESET
2- You developed your first antivirus in 1988. Back then, the number of viruses to detect was very small, despite the fact that they already used some really complex techniques. Considering the way computer threats have evolved, would it be possible for somebody today to develop an effective security solution by himself?
Why not? All you need is a good (new) idea and implement it. It may be the holy grail of heuristics and proactively block a complete new type of threat, or even multiple. That is how the current anti-malware products started in the late 80’s. Of course a single issue solution would nowadays not be enough anymore as customers expect a multi-layered, full protection solution and the sheer number of daily new malware will make it impossible to keep up just by yourself. So it will be more likely that you sell your technology to a larger company or you become a niche player in the 2nd opinion market. But… There is nothing wrong with that!
3- You’ve worked with groups that cooperate with governments, agencies and companies. In your opinion, who should be more interested in improving their IT security knowledge? Governments? Companies? The public sector and authorities?
Sadly all of the above. Education and Awareness is key here. New threats emerge all the time, and you need to be aware of the to defend yourself against it. Or at least be able to check if your security vendor is defending you against it.
Governments try to have all people use digital systems and guarantee people’s privacy, but can they? They say they do, but then, even at large public events like the 2016 elections for the US Presidency, where you would assume all the security is in place, ignorant security flaws pop up.
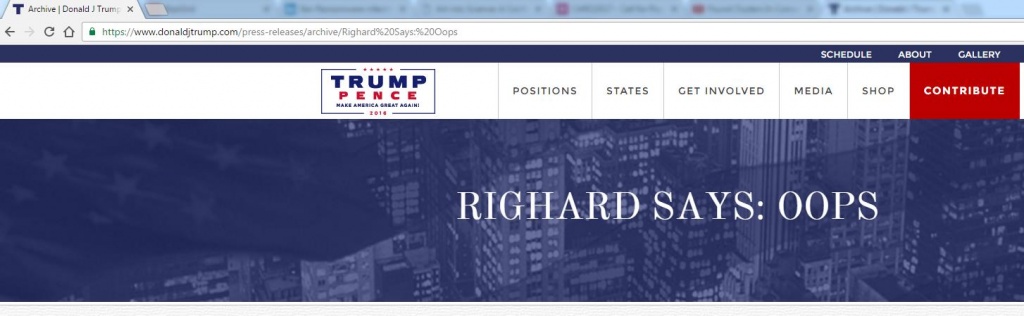
In the above case, the official website for – the now elected – Donald Trump allowed an arbitrary URL to show the header above the news archive. That can be used as a funny gimmick, but most likely also be exploited if the arbitrary URL is extended perhaps with script code.
4- You have collaborated with law enforcement agencies in multiple cases of cyber-crime. In your opinion, are law enforcement forces well prepared to fight cyber-crime? Do they have enough resources?
They are well prepared and most of the time have the resources to fight cyber-crime. You will be surprised what they actually know and can do. But what usually is the problematic issue is international laws. Cyber-crime is international, but we get stuck with national laws that may not be compatible in the fight against cyber-crime. On top of that, cyber-crime is digital and very fast moving. Too much legislation prevents swift actions. Politics has to catch up with more organic laws that “go with the flow” and do not takes ages to get updated against the latest threats, allowing law-enforcement to rightfully act against cyber-crime and not to have a case dismissed in court due to old-fashioned legislation.
New threats emerge all the time, and you need to be aware of them to defend yourself against it.
5- Is there an appropriate level of cooperation between law enforcement agencies and security vendors/experts, or do you think there is room for improvement?
Room for improvement is always there. But LEO’s and the private sector already do work together (although as mentioned hindered by (local) laws). Some new cooperation initiatives are actually about to be started and initiated by LEO’s. It clearly shows that working together, it will be easier to reach the mutual goal: to get cyber-criminals locked up, removing safe havens for them.
6- Ransomware attacks can have disastrous consequences for consumers, employees and companies in general. The cost of recovery from a security breach can be very high for an organization; however, what do you think of the expenses a company must face to prevent such attacks?
These must be seen as a preventive measure, a kind of insurance. You do invest for a lock on your door although the door can be closed, right? And when you compare the cost for preventive measurements against the cost after ransomware (the lost work, the lost time, checking and cleaning up the entire network (as you don’t know if it put some executable files of some stolen data somewhere on an open share, or if a backdoor was installed, etc.), the negative public PR, etc.), it isn’t all that expensive. Awareness (and thus proper education) is the key for all people to understand that reporting suspicious activity earlier can actually save a lot of money for the company. In this case, the cost of a report of suspicious activity that turns out to be false is nullified by the cost saved by that single report of suspicious activity where it turns out the threat is real.
Awareness (and thus proper education) is the key for all people to understand that reporting suspicious activity earlier can actually save a lot of money for the company.
7- Righard, you’ve been working with AMTSO (Anti-Malware Testing Standards Organization) since its inception. During this time, you’ve had the opportunity to work in different positions within the organization: CEO, CTO, and now you are a member of the board. What influence has AMTSO had on the world of security solution testing? What difference has it made?
AMTSO had – in my perception – a tremendous influence on the world of security solution testing. Yes of course, it was a struggle in the beginning, errors were made, but now, after repairing the organizational flaws, AMTSO came up with Guidelines and Recommendations that were adopted by testers and vendors, making sure that all testing was done fair and equally. This has also caught the eye of other organizations that are now recommending AMTSO and AMTSO “compliant” tests or to get a product certified by a tester that has adopted the AMTSO Guidelines and Recommendations.
8- What challenges will AMTSO have to face in the near future?
AMTSO is growing and is now changing the Guidelines and Recommendations into real Standard Documents. This is a delicate procedure to complete, but when completed and done properly, a big step forward. As AMTSO is growing and getting more members of different industries, but also from the same industry with motivations or ways of thinking that are different than the established industry, with older and newer companies, keeping it all together to continue to build AMTSO broader and going for AMTSO’s goals, that will be a challenge. But I am sure the new management will be able to do so. I would not have stepped down as CEO/President if I didn’t believe it would be in good hands!
The post “Cyber-crime is international, but we get stuck with national laws that may not be compatible in this fight”, Righard Zwienenberg appeared first on Panda Security Mediacenter.











 Unwanted calendar invitations have invaded the calendars of iOS and Mac users for the past week. These messages seem to be targeted to everyone with an
Unwanted calendar invitations have invaded the calendars of iOS and Mac users for the past week. These messages seem to be targeted to everyone with an