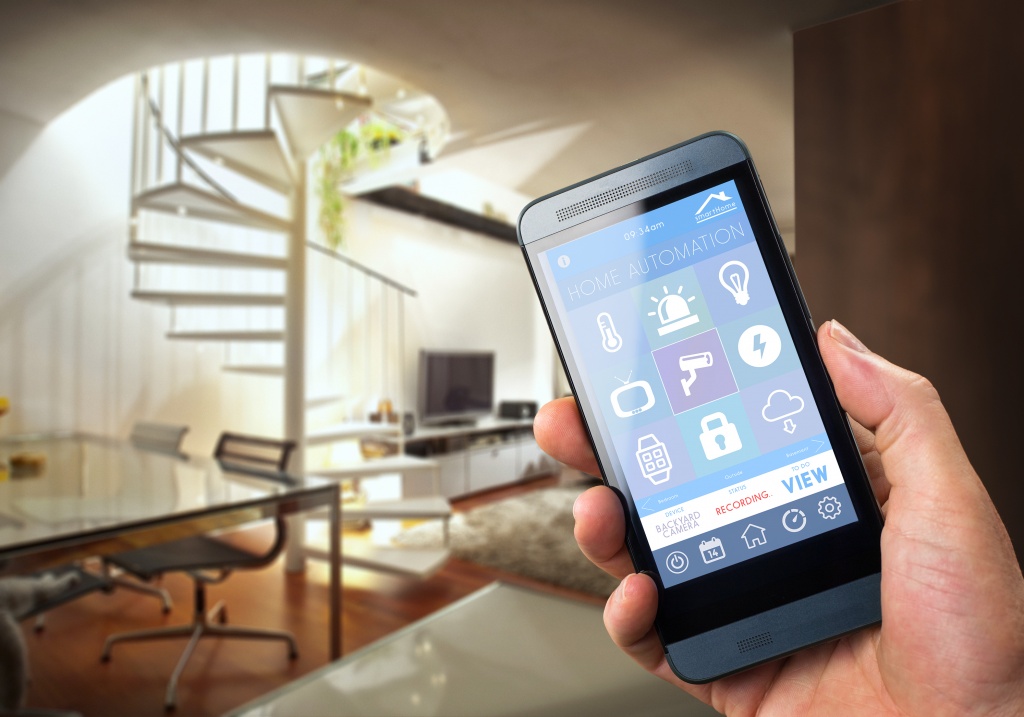
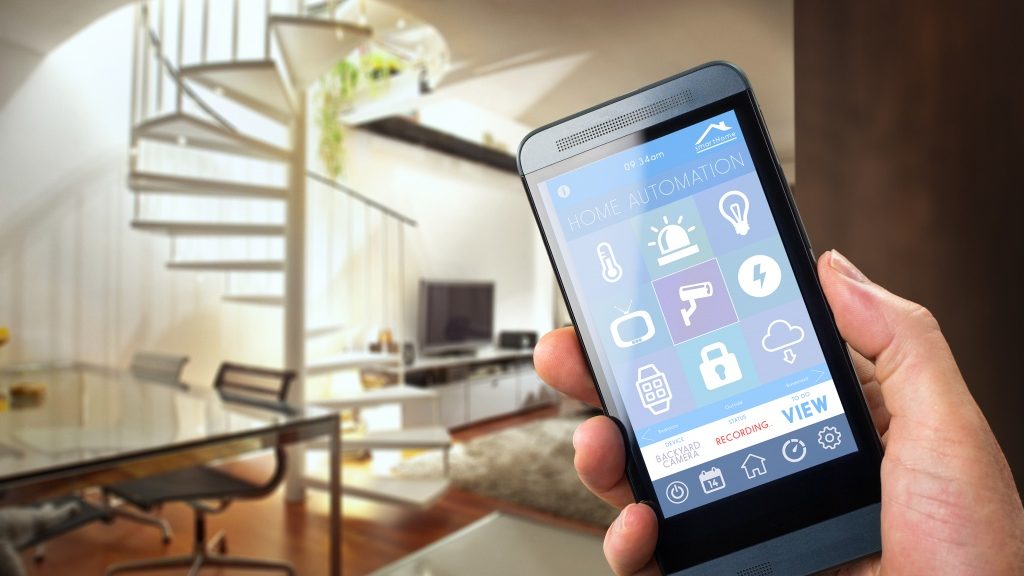
With great power comes great responsibility. Powerful words. We’re not talking about a web-slinging superhero though, but a different type of web altogether -the World Wide Web- and with the ongoing expansion of the Internet of Things, its increasing connection to the physical world is inspiring awe and wonder, but also a growing necessity for out-of-the-box thinking and creative risk assessment from cyber security experts the world over.
Here at Panda Security, we have gathered a few of our ideas on ways that hackers could get unprecedented access to your daily lives through the app-integrated devices you keep at home.
Ways hackers could get unprecedented access to your daily lives
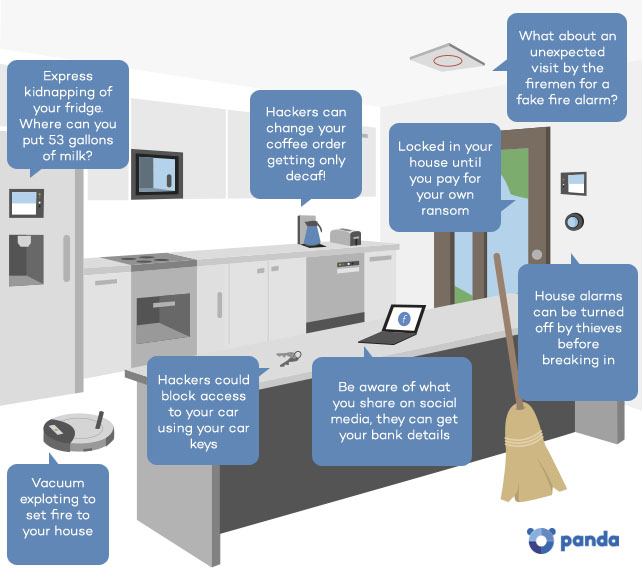
A Doorway Ransom?
As the Internet of Things continues to integrate seemingly inane and unrelated objects, an entire comprehensive home operating system seems increasingly likely. While this will turn your house into a streamlined living space completely catered to your comfort, it could also put you at greater risk of falling victim to a cyber attack in your own home.
Central to any future smart home’s security would surely be its locking system.
Recent investigation, though, has shown that smart locks are alarmingly easy to hack, making them embarrassingly unable to guarantee the function they are there to provide in the first place.
Current systems simply make it too easy for a cyber hacker to actually physically enter your home.
We’ve thought further ahead though; what if a hacker were to completely invert their use of this technological weak spot in the future? If a smart lock can be compromised in order to open it, maybe hackers will find a way to keep your doorway completely shut.
The future’s equivalent of a home invasion could be completely silent, a hacker controlling events from a distance, perhaps asking for a sizeable ransom before letting you out of your own home.
It may make a terrible idea for a film script (Home Very Alone) but it’s a terrifying thought nonetheless. If all of your security devices are interlinked, cyber attackers could potentially also have access to your house alarm and even your car keys.
Smoke Screen Smoke Alarm
One safety feature that is already incorporated into some smart smoke detectors available on the market is the ability to let a smart house pull information from, and manipulate, other smart devices so that they can react accordingly in case of an emergency. This feature is implemented for the user’s safety, allowing a house that detects a fire, for example, to unlock all the doors in the house in aid of a speedy exit.
That is a great example of the way IoT businesses are working to seamlessly integrate and interconnect devices within smart homes. However, there is one strong reservation; if this technology is breached by a cyber attacker, there is the potential for setting off a chain reaction that could greatly reduce the safety of a smart home.
Another way that a hacker could potentially intrude from afar is by setting off a false smoke alarm that will send for the fire services. The chaotic scene could act as a smoke screen, making you a soft target for other potentially malicious cyber attacks.
The Hoover of Death
One of our wilder ideas perhaps, but with all the furor about exploding mobile phones at the moment, we’re aware that IoT is increasingly putting us in the position of giving hackers access to potentially explosive devices!
Could this be manipulated in a cyber attack? Attackers typically work en masse, such as in distributed denial of service attacks (DDOS), where thousands of emails or requests are sent to a server to slow down or crash the intended target’s servers.
If that’s the case we could face a future in which hackers try to send as many machines into overdrive as possible in the hope that some will malfunction. A terrifying prospect, and perhaps part of the reason for which government agencies have been liaising on the potential dangers of IoT related cyber attacks.
Beware the Fridge
Remember that Simpsons episode in which Marge falls for a Pierce Brosnan voiced AI house operating system that does the cooking and is secretly planning to “get rid” of the rest of the family? As bemusing as it may seem we may only be a few small technological leaps away from mirroring the events of that hilarious, yet horrifying, HAL parody.
Ok, granted your fridge isn’t about to have an intelligent conversation with you, and much less hatch a murderous scheme against your family. However, as far back as two years ago, the CIA were highlighting the threat of smart refrigerators in people’s homes.
The Central Intelligence Agency were alarmed when a refrigerator was used as part of a “zombie” network to perform a DDOS attack. All of this unbeknownst to its owners, who had no idea their fridge had taken on a, quite devilish, new purpose aside from keeping tomorrow’s lunch cool.
What’s next?
As these devices become smarter, tracking your shopping habits and ordering deliveries for the home, could a hacker gain access to your bank details or disrupt your order? All we know is that AI and fridges are best left as a spooky cartoon vision for now!
The post Are (IoT) Smart Homes of the Future As Smart As They Say? appeared first on Panda Security Mediacenter.






 New, but not that dangerous… why the panic?
New, but not that dangerous… why the panic?
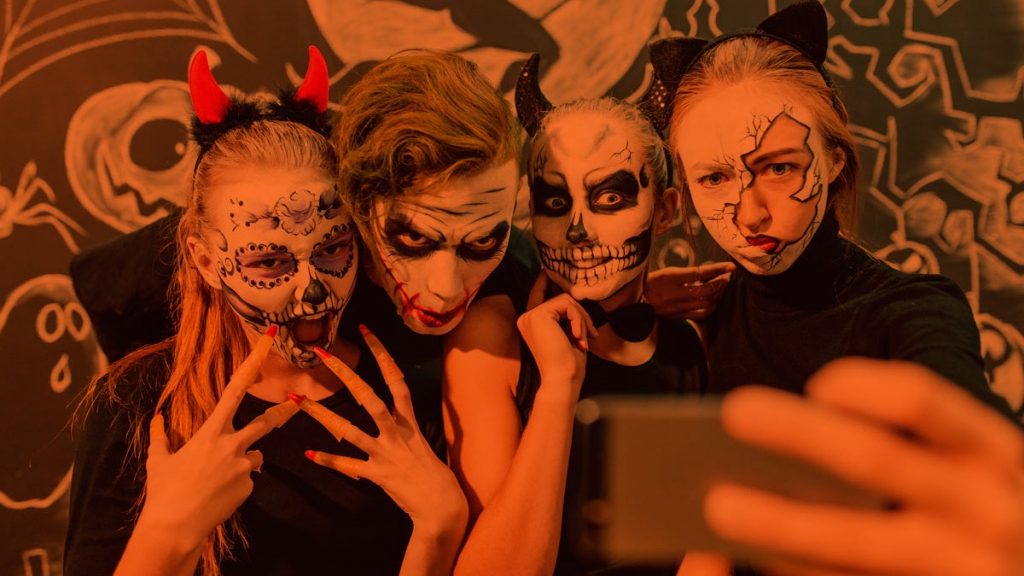

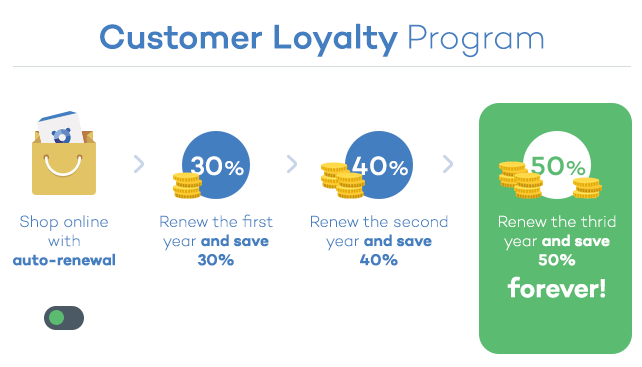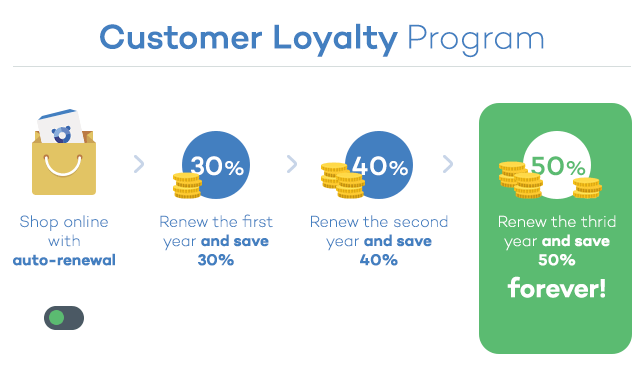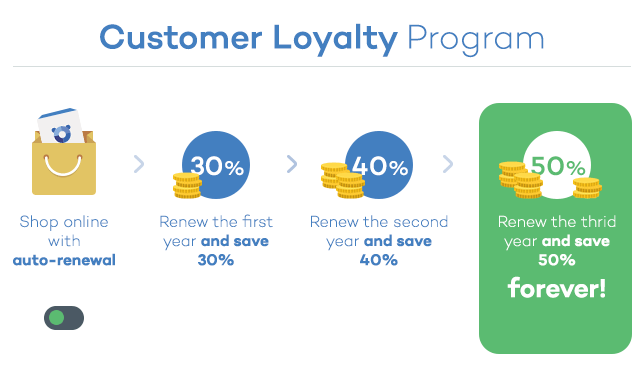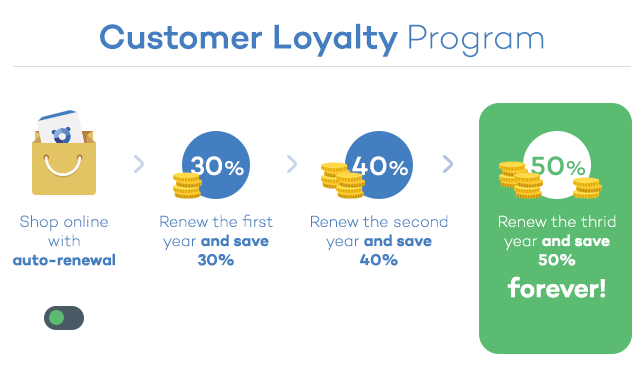








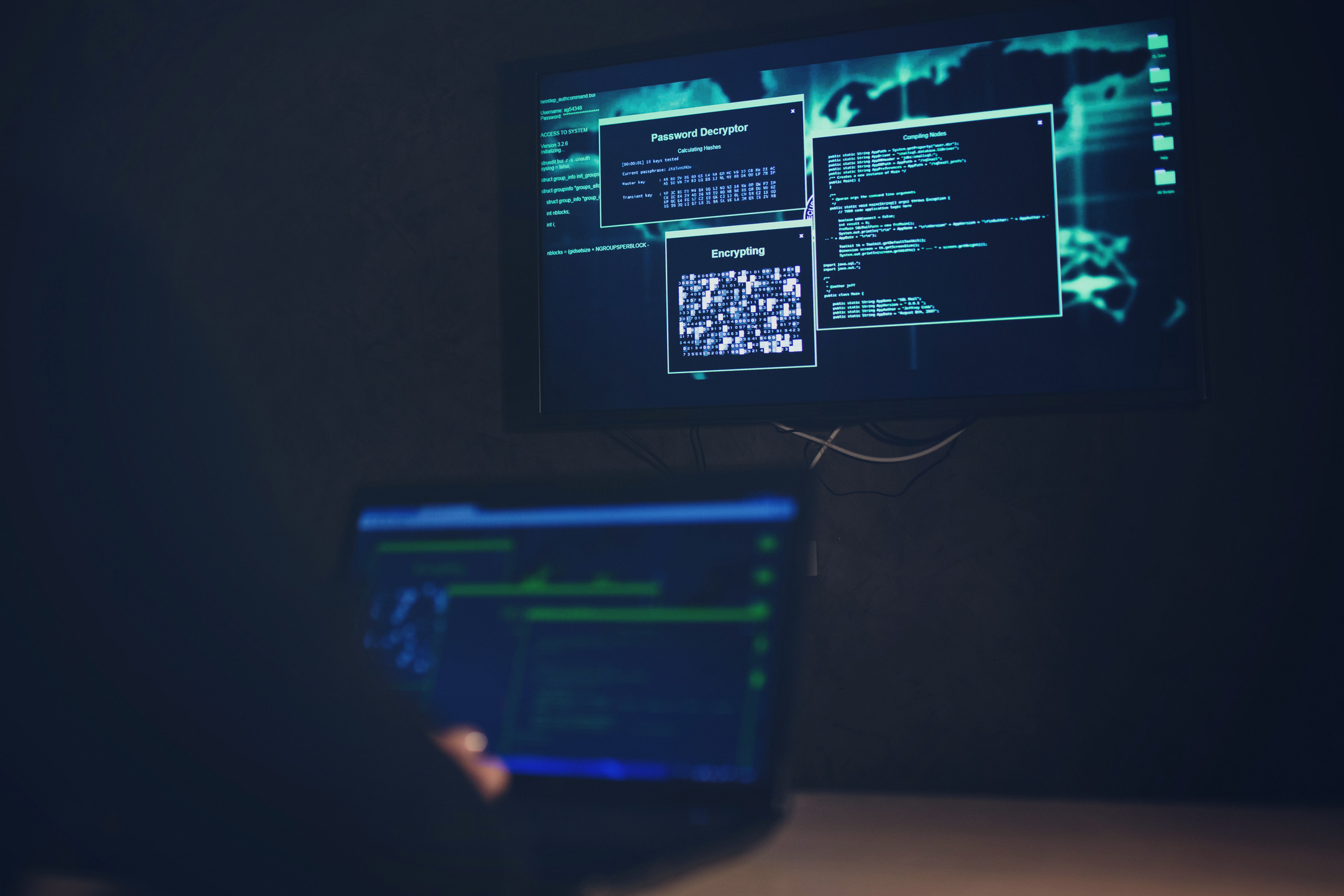
 Knock knock! Trick or treat! Companies and cybercriminals play the same game. You could be opening back doors to cybercriminals this year, without even knowing it. You’ll lose this game if you don’t fight back. Ransomware attacks will capture your documents and the attackers will be expecting a big juicy reward (if you want your files back, that is). This Halloween, beware!
Knock knock! Trick or treat! Companies and cybercriminals play the same game. You could be opening back doors to cybercriminals this year, without even knowing it. You’ll lose this game if you don’t fight back. Ransomware attacks will capture your documents and the attackers will be expecting a big juicy reward (if you want your files back, that is). This Halloween, beware! Attacks by staff with privileged access represents one of the greatest threats for the security of the corporate information and data of your customers. Research conducted by
Attacks by staff with privileged access represents one of the greatest threats for the security of the corporate information and data of your customers. Research conducted by  At the beginning of this month, an employee from the US government, Harold Thomas Martin,
At the beginning of this month, an employee from the US government, Harold Thomas Martin,  Start using a cybersecurity solution that has advanced protection features, and that also has the capacity to detect and remedy possible threats.
Start using a cybersecurity solution that has advanced protection features, and that also has the capacity to detect and remedy possible threats.

