Earlier this week, security researchers unveiled a vulnerability that is believed to be the worst Android vulnerability yet discovered. The “Stagefright” bug exposes nearly 1 billion Android devices to malware. The vulnerability was found in “Stagefright”, an Android media library. Hackers can gain access to a device by exploiting the vulnerability and can then access contacts and other data, including photos and videos, and can access the device’s microphone and camera, and thus spy on you by recording sound and taking photos.
All devices running Android versions Froyo 2.2 to Lollipop 5.1.1 are affected, which are used by approximately 95% of all Android devices.
The scary part is that hackers only need your phone number to infect you. The malware is delivered via a multimedia message sent to any messenger app that can process MPEG4 video format – like an Android device’s native messaging app, Google Hangouts and WhatsApp. As these Android messaging apps auto-retrieve videos or audio content, the malicious code is executed without the user even doing anything – the vulnerability does not require the victim to open the message or to click on a link. This is unique, as mobile malware usually requires some action to be taken to infect the device. The malware could also be spread via link, which could be sent via email or shared on social networks, for example. This would, however, require user interaction, as the video would not load without the user opening a link. This exploit is extremely dangerous, because if abused via MMS, victims are not required to take any action and there are neither apparent nor visible effects. The attacker can execute the code and remove any signs that the device has been compromised, before victims are even aware that their device has been compromised.
A cybercriminal’s and dictator’s dream
Cybercriminals can take advantage of the vulnerability to collectively spy on millions of people – and even execute further malicious code. Repressive governments could abuse the bug to spy on their own people and enemies. The vulnerability, however, could also be used for non-political spying. Hackers can easily spy on people they know, like their spouse or neighbour – all they need to know is their victim’s phone number. Hackers can also steal personal information and use it to blackmail millions of people, or use the data for identity theft. The possible consequences of this vulnerability need to be taken seriously.
Fixes are urgently needed
Now comprehensive fixes need to be provided by the phone’s manufacturers in an over-the-air (OTA) firmware update for Android versions 2.2 and up. Unfortunately, updates for Android devices have historically taken a long time to reach users. Hopefully, manufacturers will respond quicker in this case. On a positive note, Google has already responded. HTC told Time “Google informed HTC of the issue and provided the necessary patches, which HTC began rolling into projects in early July. All projects going forward contain the required fix.”
In the meantime, what can you do to protect yourself?
We recommend users disable “auto retrieve MMS” within their default messaging app’s settings, as a precautionary measure for the moment. We have put together step-by-step instructions on how you can disable auto retrieve for MMS in various Android messaging apps:
Messages App:
Step 1: Open the Messages app and click on the three dots in the upper right hand corner  Step 2: Click on “Settings” in the dropdown menu
Step 2: Click on “Settings” in the dropdown menu  Step 3: Click on “Multimedia messages”
Step 3: Click on “Multimedia messages” 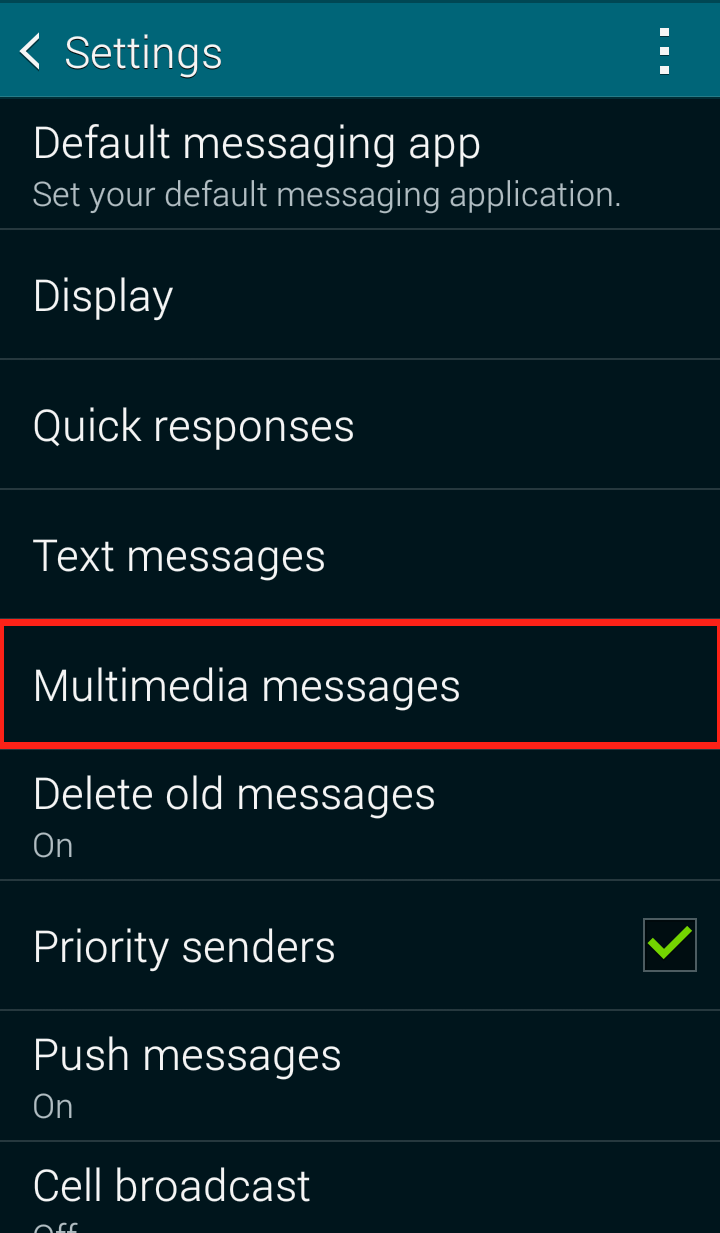 Step 4: Uncheck “Auto retrieve”
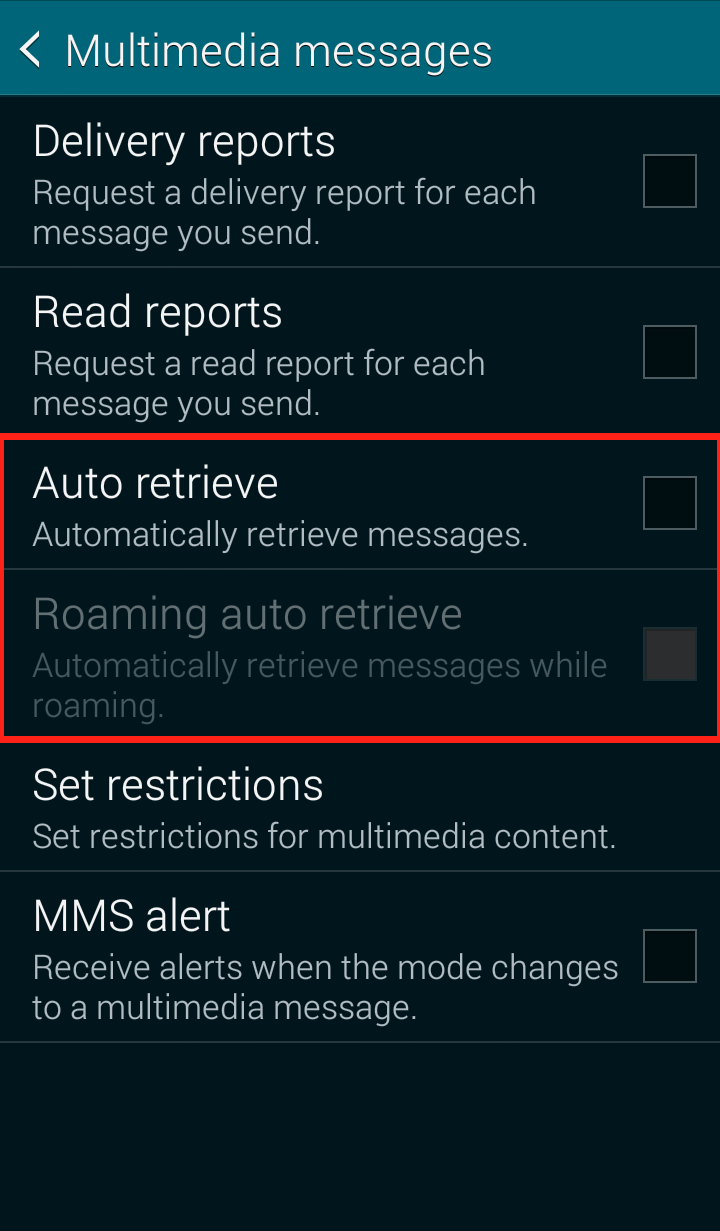
Step 4: Uncheck “Auto retrieve” 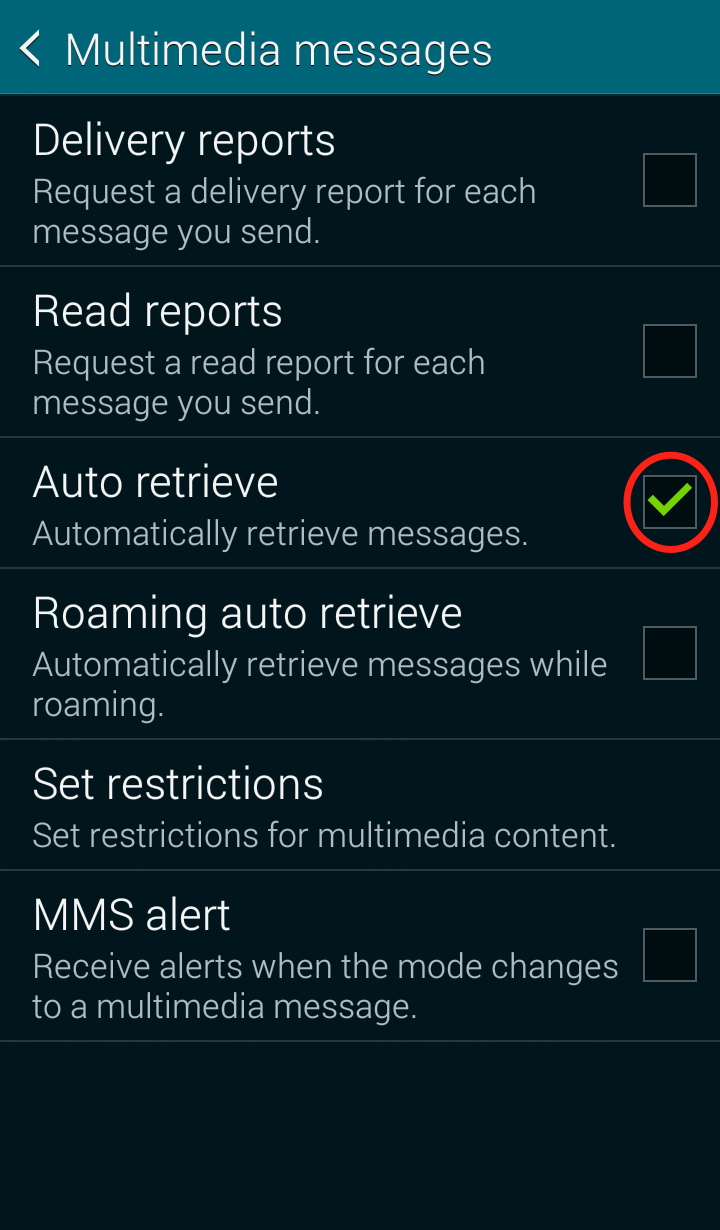 Your Messages “Multimedia messages” settings should now look like this:
Your Messages “Multimedia messages” settings should now look like this:
 Google Hangout
Google Hangout
Step 1: Open the Google Hangout app and click on the three lines in the upper left corner  Step 2: Click on “Settings”
Step 2: Click on “Settings”  Step 3: Click on “SMS”
Step 3: Click on “SMS”  Step 4: Scroll down to “Advanced” and uncheck “Auto retrieve MMS”
Step 4: Scroll down to “Advanced” and uncheck “Auto retrieve MMS” 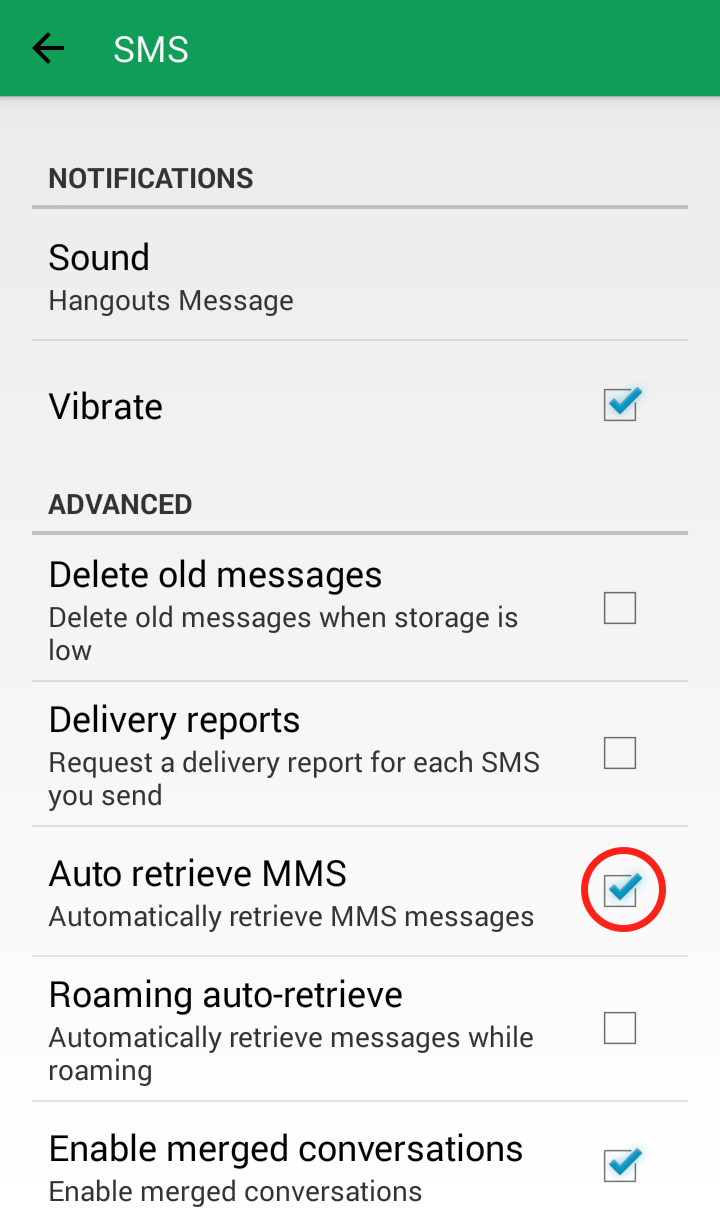 Your Google Hangout “SMS” settings should now look like this:
Your Google Hangout “SMS” settings should now look like this: 
Messenger App:
Step 1: Open the Messenger app and click on the three dots in the upper right hand corner 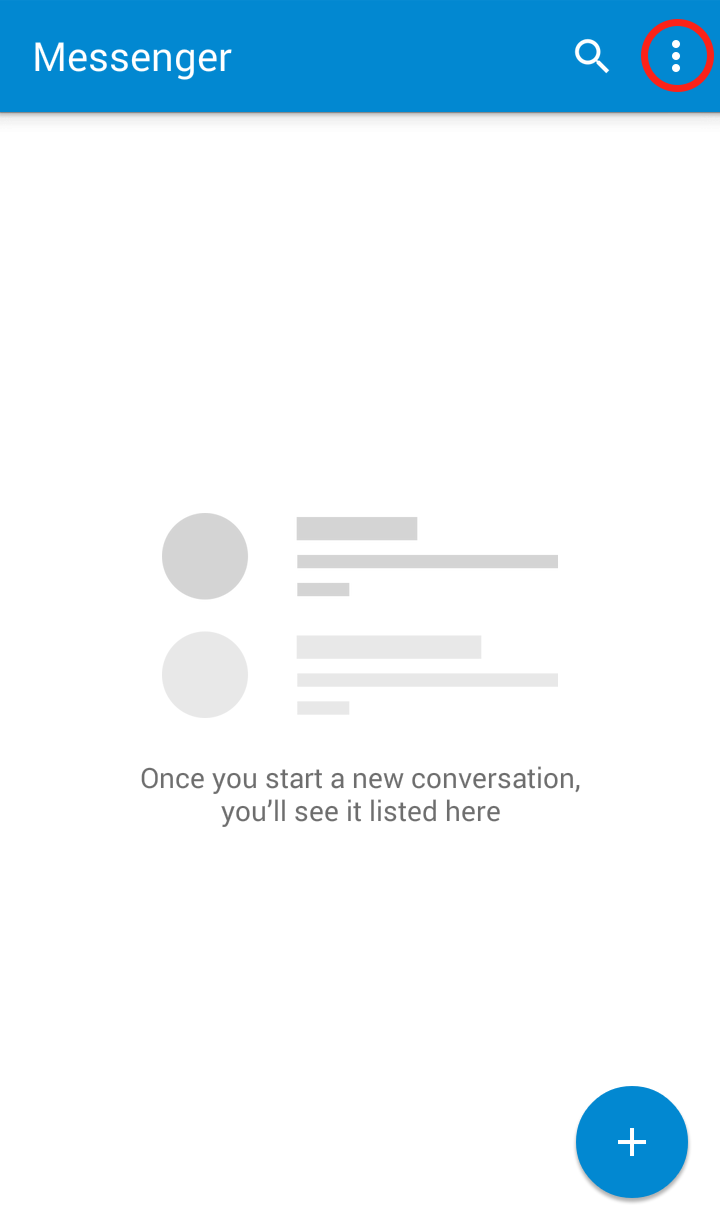 Step 2: Click on “Settings” in the dropdown menu
Step 2: Click on “Settings” in the dropdown menu 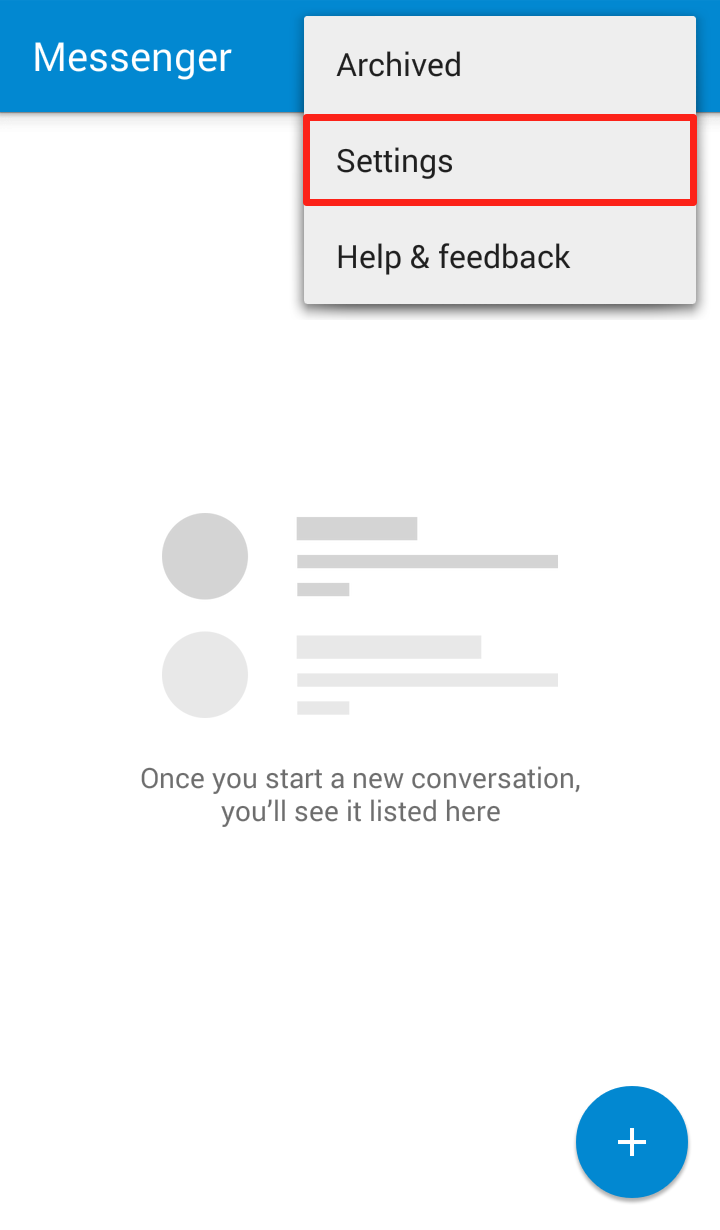 Step 3: Click on “Advanced”
Step 3: Click on “Advanced”  Step 4: Uncheck “Auto retrieve”
Step 4: Uncheck “Auto retrieve”  Your Messenger “Advanced Settings” should now look like this:
Your Messenger “Advanced Settings” should now look like this: 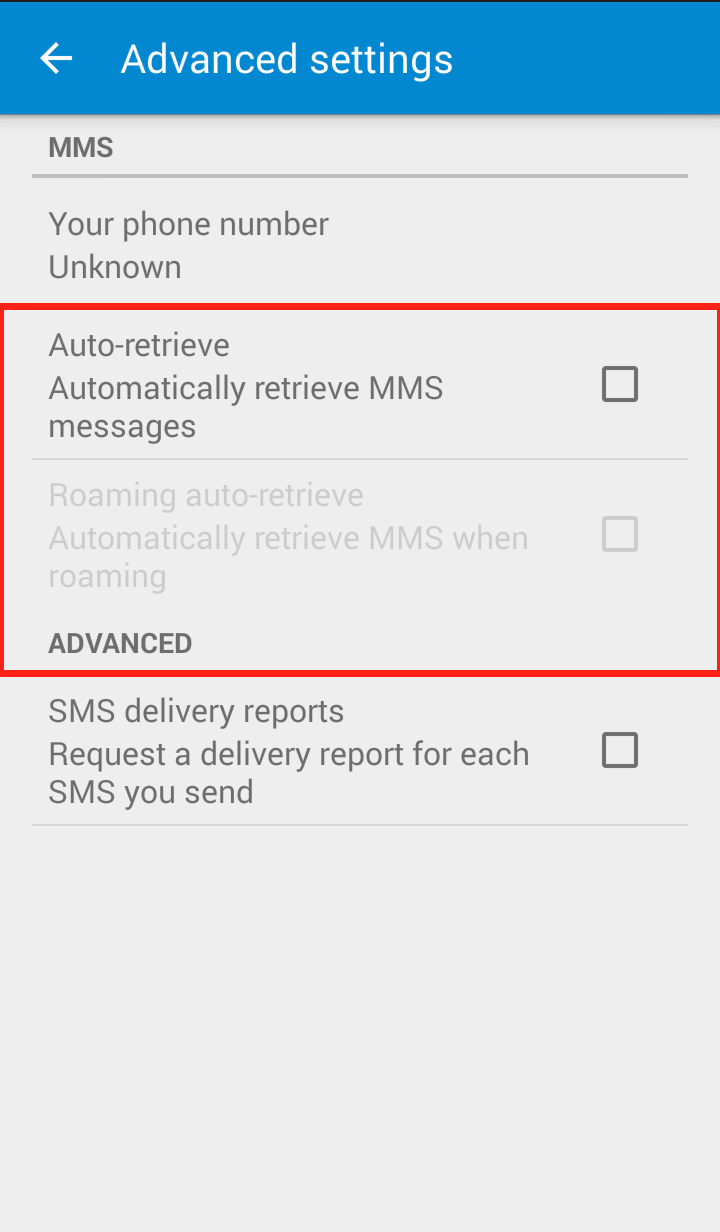
Messenger:
Step 1: Open the Messaging app and click on the three dots in the lower right hand corner 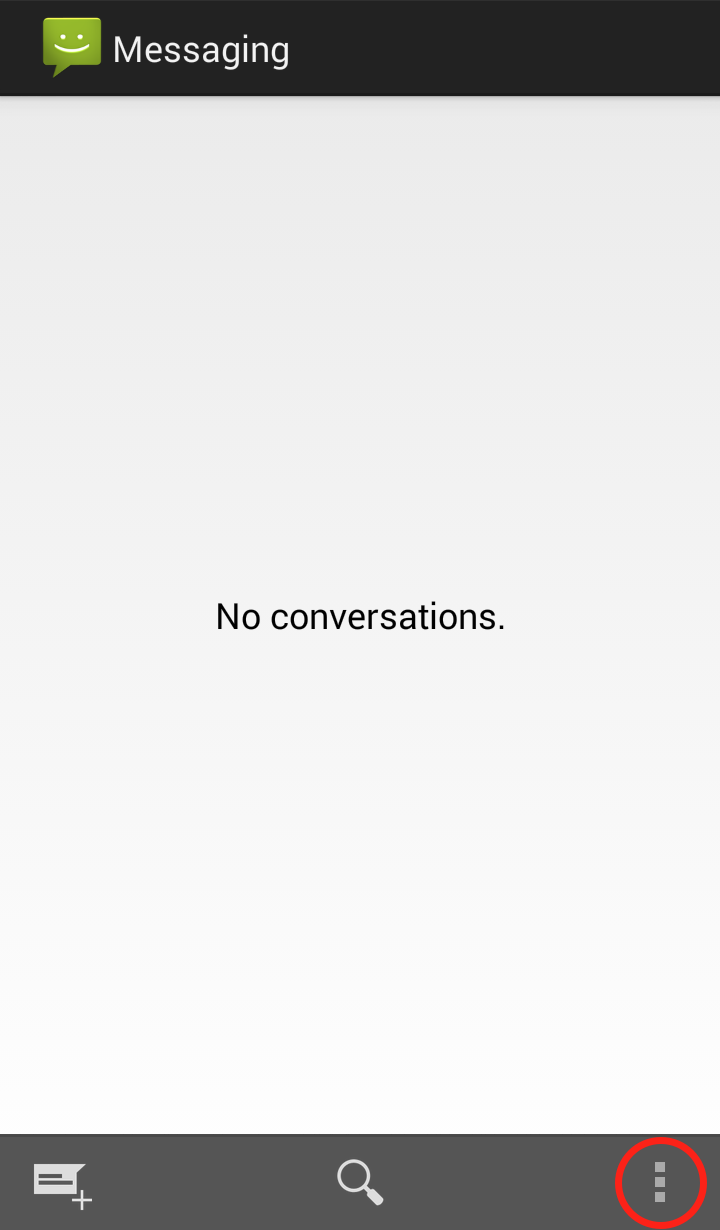 Step 2: Click on “Settings”
Step 2: Click on “Settings” 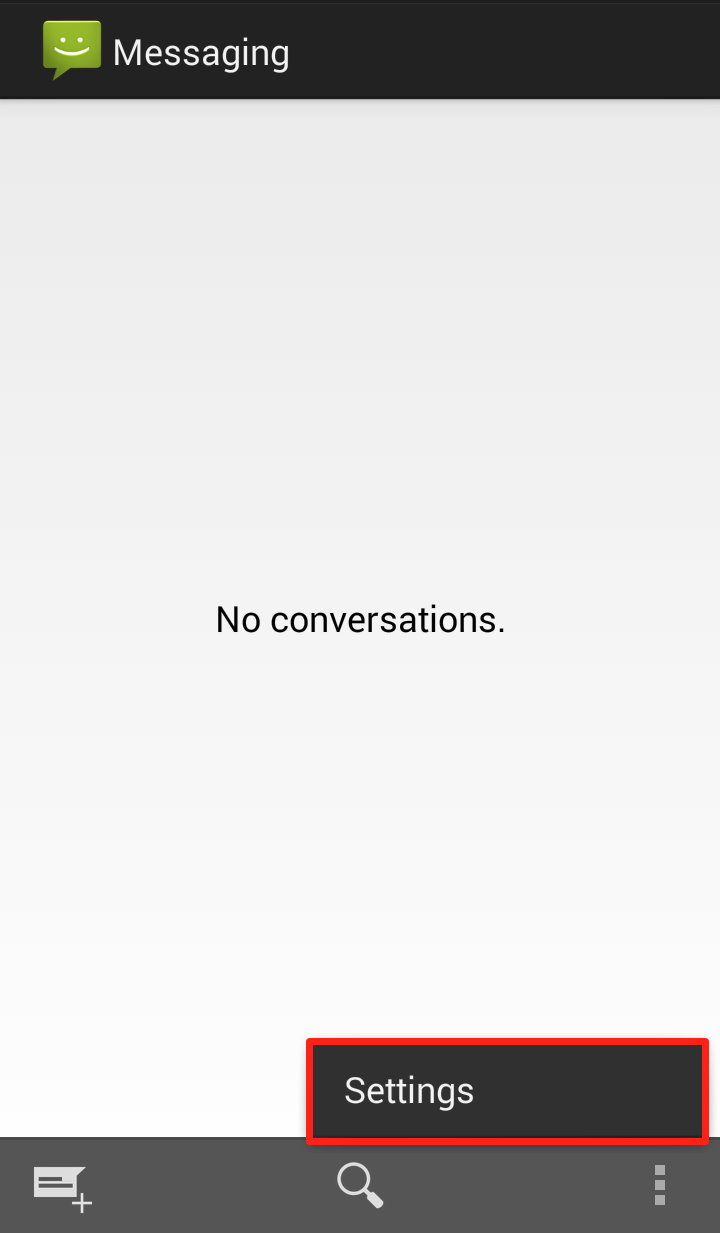 Step 3: Scroll down to “Multimedia (MMS) messages” and uncheck “Auto retrieve MMS”
Step 3: Scroll down to “Multimedia (MMS) messages” and uncheck “Auto retrieve MMS” 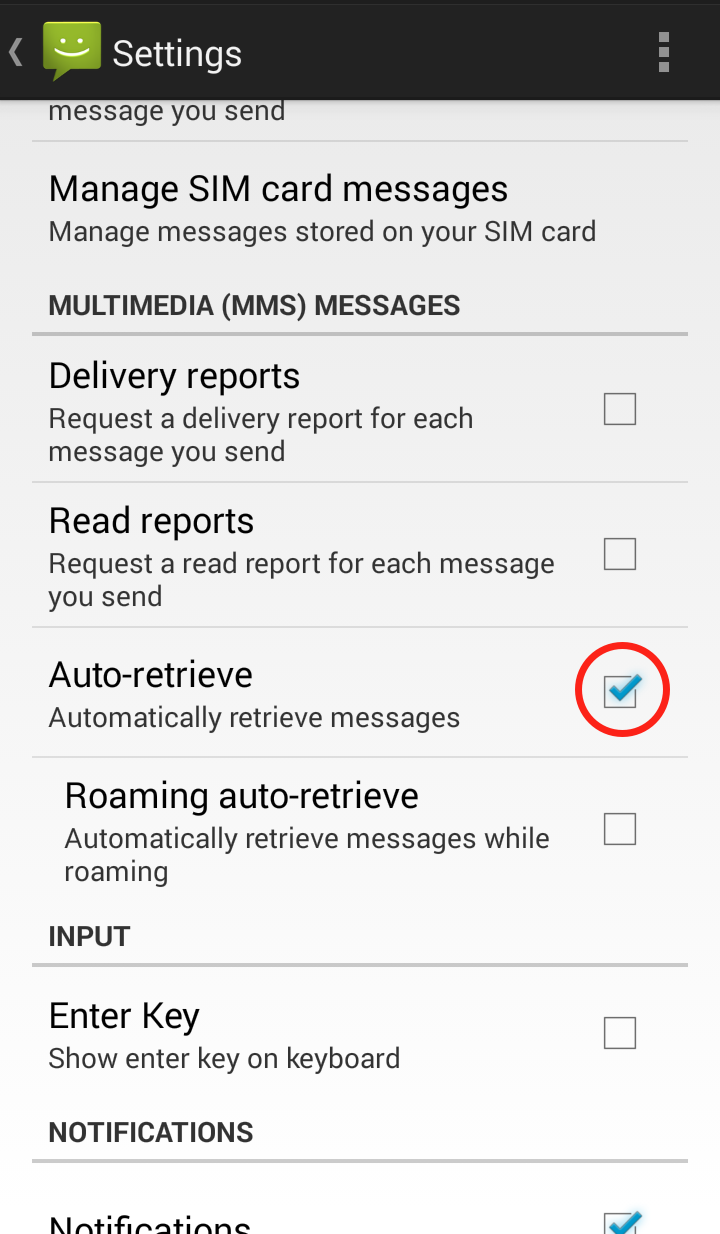 Your Messaging “Settings” should now look like this:
Your Messaging “Settings” should now look like this: 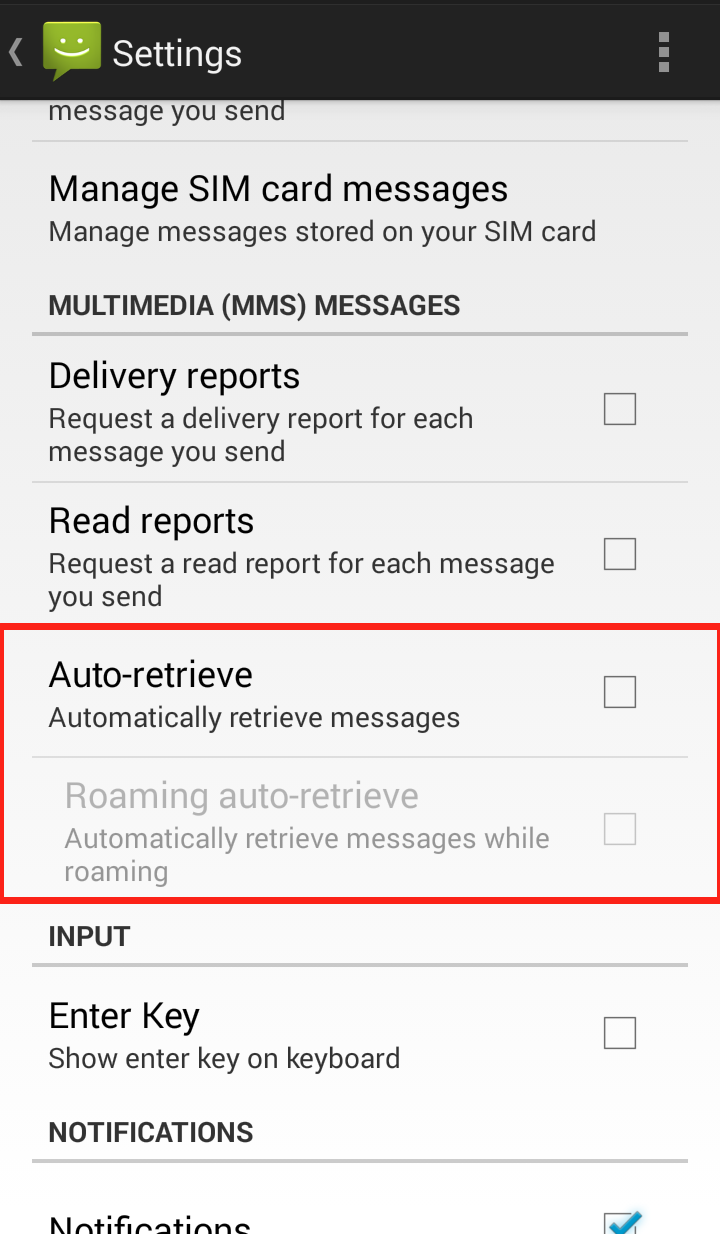
WhatsApp
Step 1: Open WhatsApp and click on the three dots in the upper right hand corner 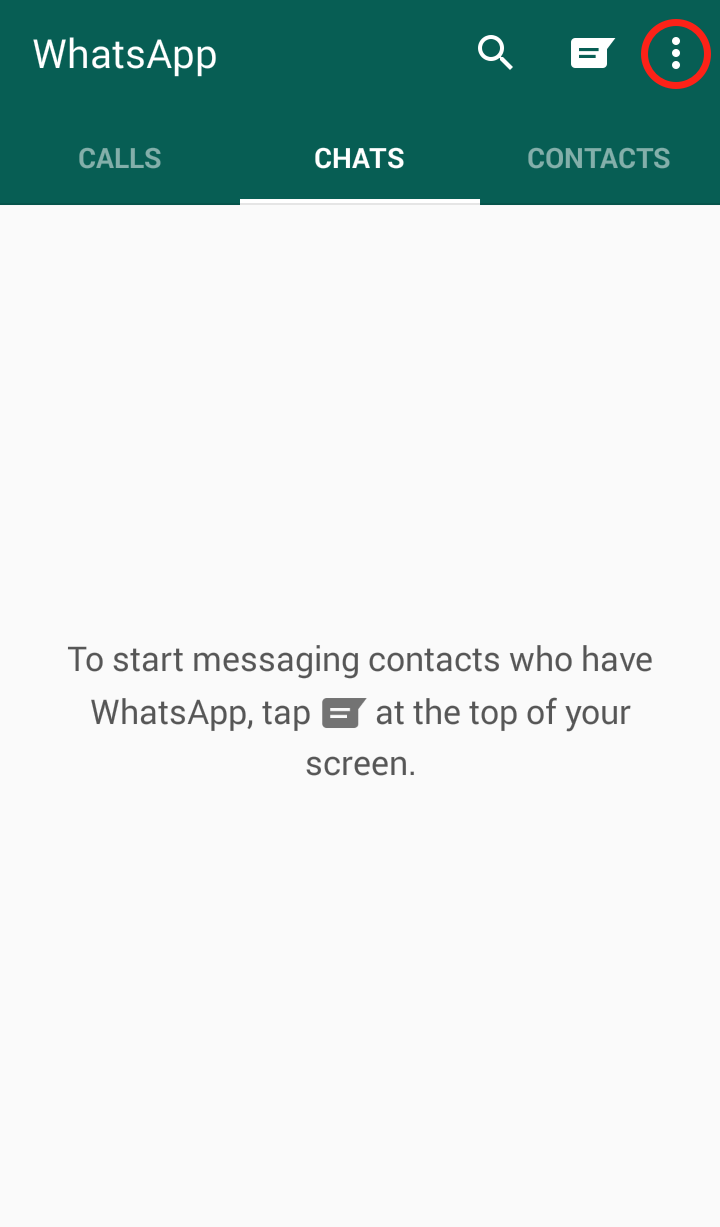 Step 2: Click on “Settings”
Step 2: Click on “Settings” 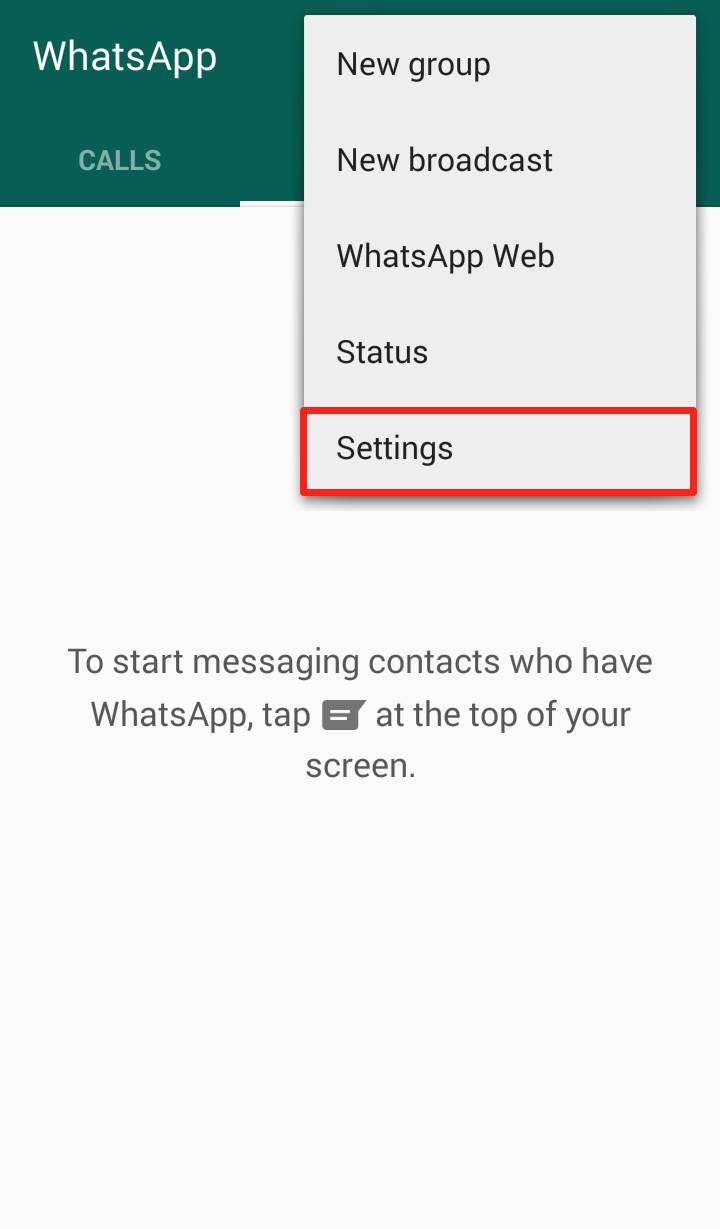 Step 3: Click on “Chat Settings”
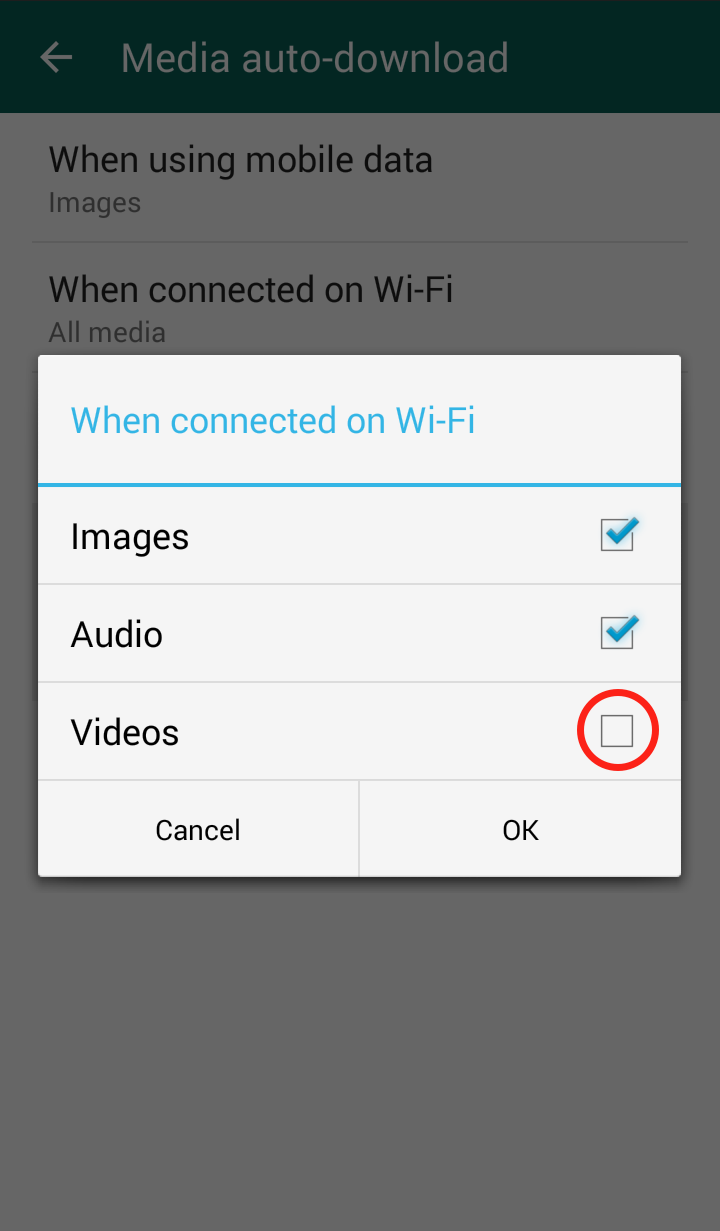
Step 3: Click on “Chat Settings” 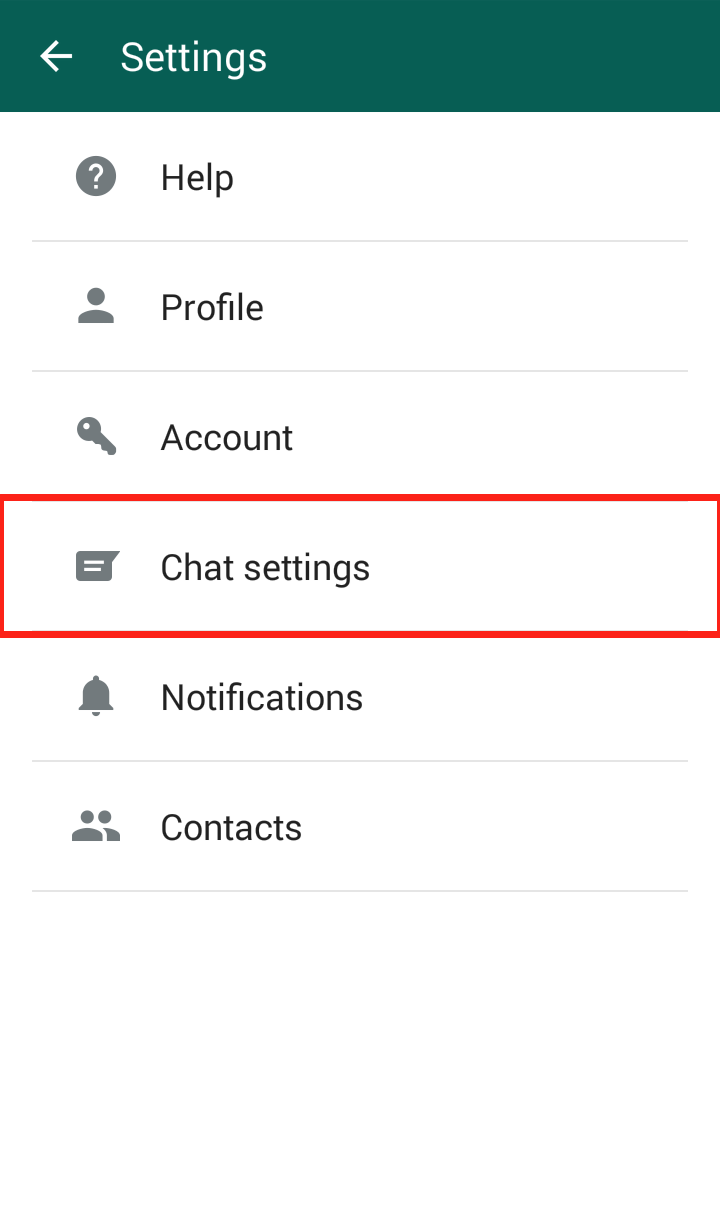 Step 4: Click “Media auto-download”
Step 4: Click “Media auto-download” 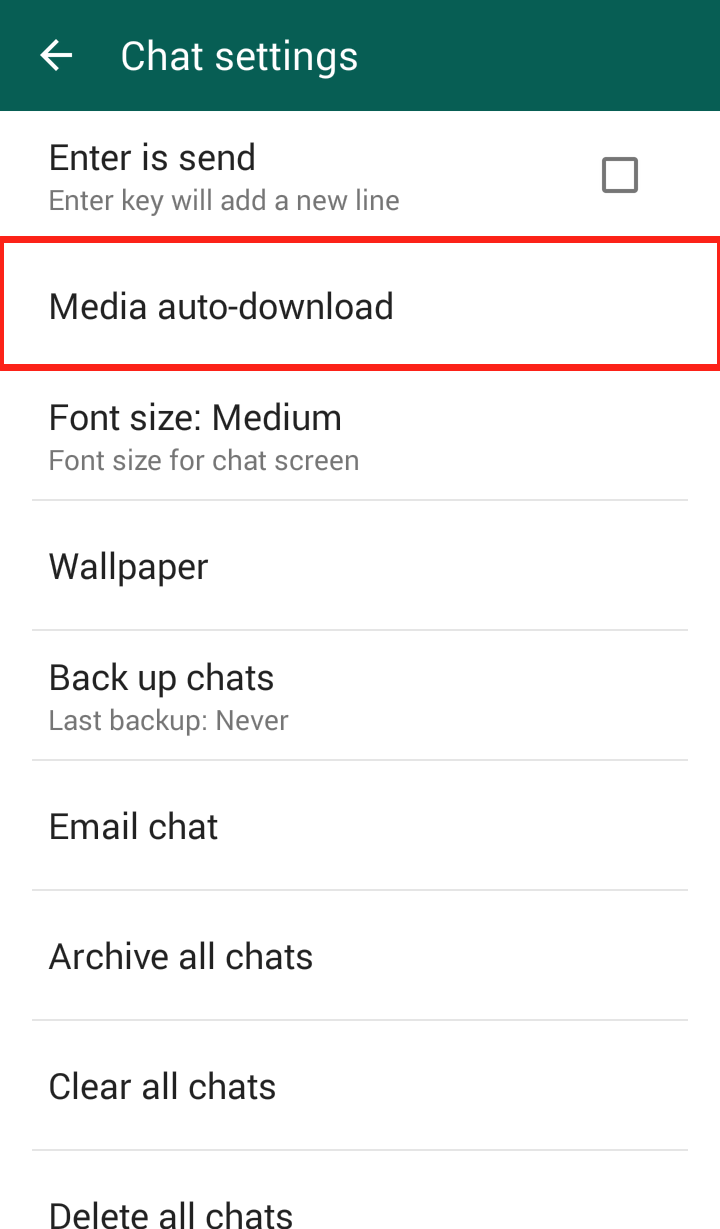 Step 5: Click “When using mobile data” and/or “When connected on Wi-Fi”
Step 5: Click “When using mobile data” and/or “When connected on Wi-Fi” 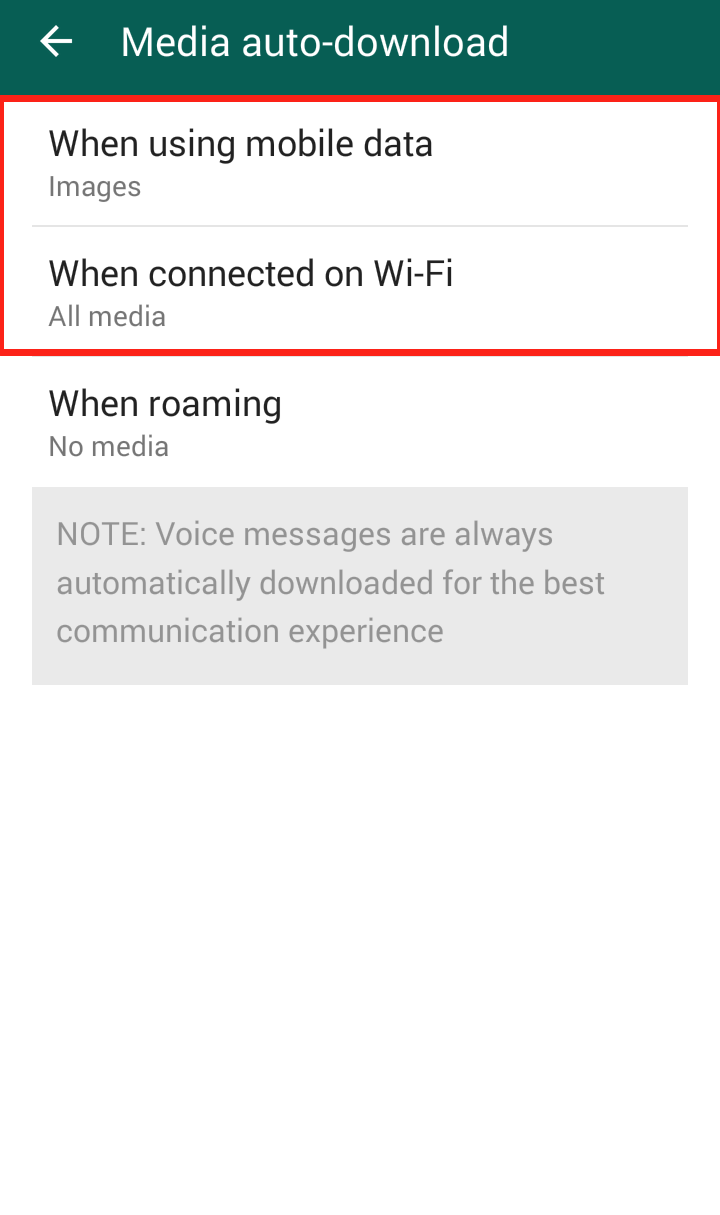 Step 6: The “When connected on Wi-Fi” settings are automatically set to download videos, so it is important to uncheck the checkmark
Step 6: The “When connected on Wi-Fi” settings are automatically set to download videos, so it is important to uncheck the checkmark 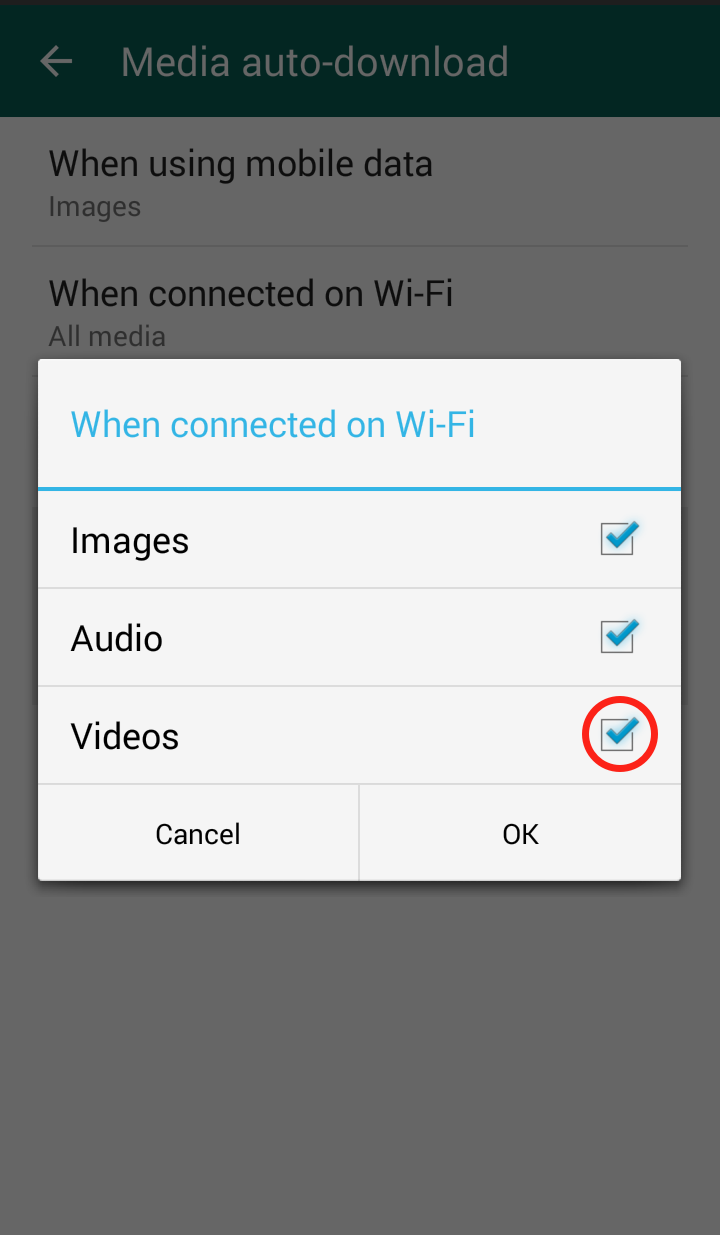 Step 7: The “When connected on mobile data” settings are NOT automatically set to download videos, but in case you did enable it, you should disable it
Step 7: The “When connected on mobile data” settings are NOT automatically set to download videos, but in case you did enable it, you should disable it 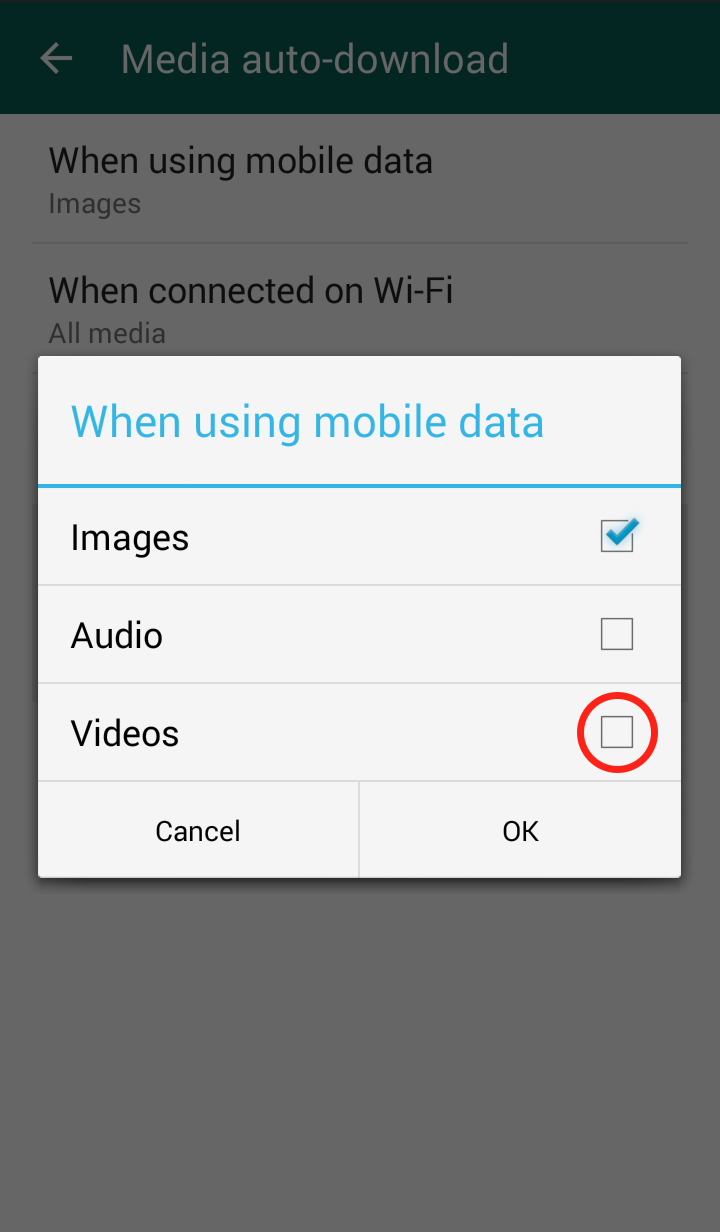 Your WhatsApp “Media auto-download” should now look like this:
Your WhatsApp “Media auto-download” should now look like this: