Was it 3798 or 7389? This is the typical doubt we all have when standing in front of the point-of-sale terminal and about to pay: you think that’s the right number, though when you go to enter it, you still have a feeling that the screen might laugh at you for keying in the wrong PIN.
At some time or another, credit card PINs will give you a headache: First, it’s hard to memorize them and at some point you’ll probably make a mistake entering the number. And what if it the number itself gets stolen? Luckily, this is a problem that could soon have a solution, as the most secure password is something that you have with you 24 hours a day, 365 days a year: your fingerprint.
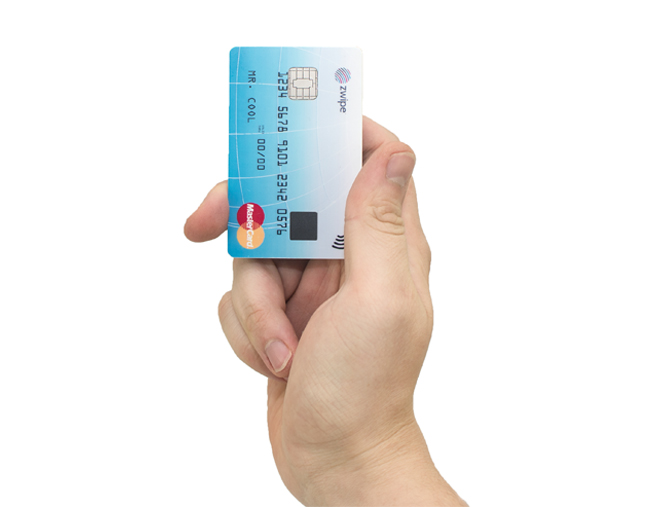
Perhaps even your next credit card won’t ask you to enter a PIN when you go to pay for something, rather just place your finger on the card. MasterCard is already working on it. Along with the Norwegian tech startup Zwipe, the credit card company has come up with the first card with an in-built thumbprint reader to verify the cardholder’s identity.

With this innovation, biometrics have come another step closer to our everyday lives, although this is not the only example. Apple has already introduced biometrics in the Apple Pay digital payment platform, which leverages Touch ID, the fingerprint recognition technology in iPhone 6.
The biometric system used by MasterCard is similar to that employed by Apple: At one end of the card there is the print reader, where the cardholder simply places a thumb to verify their identification. So it could soon be goodbye to all those tedious passwords and PINs.
The cards don’t need batteries to run the technology, instead the fingerprint scanner is powered by energy emitted by the payment terminals, as Zwipe CEO, Kim Humborstad, explains: “All standard contactless terminals dispatch a radio frequency (RF) signal, and we use that RF energy to power the card.”
The card is already a reality, and although there is no specific date, they could be in our wallets by 2015. Everything depends on the banks, who will have to decide whether to commit to biometrics as a secure method of identification.

No one can doubt the usefulness of this innovation, but is it completely secure? It’s probably more secure than having a password that you often forget or that could be stolen if written down on a piece of paper, although it’s still not completely secure.
You don’t need to worry about thieves stealing your card and slicing off your thumb to get your thumbprint, as there are far less gruesome ways of compromising the security of the system. Apple’s Touch ID system has already had its vulnerabilities highlighted, both on the latest iPhone and the previous version.
However, biometric systems such as fingerprint readers developed by Apple or MasterCard, or iris pattern identification are options that are not only being considered for credit card authentication, but also as keys for the smart homes of the future.
Biometrics, however, are not perfect. “If an identity thief or criminal has the necessary resources and motivation, they can make a replica of your thumb from a latent print,” explains Julián Fiérrez, Associate Professor at the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, and an expert in these types of technologies.
Even though the system is not the panacea, it would seem that leading companies now see fingerprint recognition as the future. “Our belief is that we should be able to identify ourselves without having to use passwords or PINs.”, says president of security solutions at Mastercard, Ajay Bhalla. “Biometric authentication can help us achieve this – our challenge is to ensure the technology offers robust security, simplicity of use and convenience for the customer.”
The post Want more security? How about the first credit card that reads your thumbprint? appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.