Researchers at Kaspersky Lab have found two Linux modules connected to the Turla APT campaigns.
Tag Archives: Malware
German phishing scam spreading globally
In recent weeks, we detected another wave of phishing emails, written in German, pretending to be a billing invoice sent from various well-known companies such as Vodafone. Instead of a real invoice, they contain a link to an archive with a malicious code that can infect users’ PCs. The original wave of this malware campaign was already observed earlier this year primarily targeting Germany. This time, it is spreading worldwide. However, they are still in German, which helps identify them as a scam.
In this post, we give a brief technical description of this threat and provide several tips how to not get caught by similar phishing threats.
Phishing Emails
We have found several different versions of these emails that claim to be sent from Vodafone, Telekom Deutschland GmbH, Volksbank, and other companies with a faked sender name (e.g. [email protected]) including the official logos. As we can see in Vodafone’s official statement, these companies are aware of this scam and have already warned their customers. Each version of such email is slightly different and contains the current date, a random customer number and payment amount.
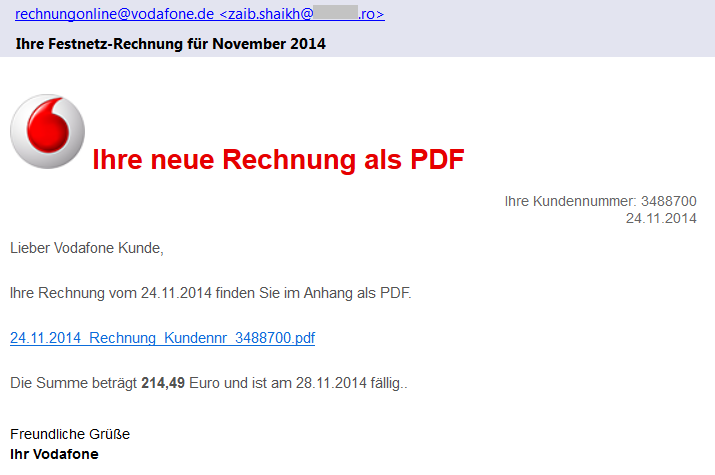

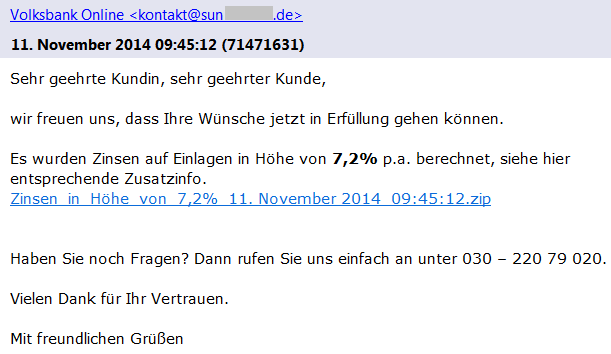
If we look more carefully at the sender’s email address, we can see that the true author did not bother with faking the sender’s email address. This should immediately alert the recipient as an email from German Vodafone would hardly be sent from an unrelated Romanian domain.
In the latest scam, the emails do not contain any attachment, which is different to the other recent phishing campaigns. The proclaimed bill (a PDF file) is available online via a given link (also unique for each version) that actually leads to a ZIP archive stored on one of the hacked sites. These archives contain an exploited/unsecured WordPress instance and they serve as a mule for the distribution of malware to users.
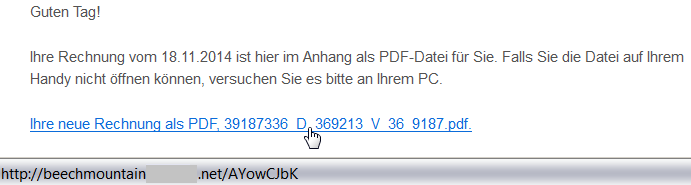
Once again, a user targeted by such an attack should be alerted via a simple inspection of the target location of the link by hovering the cursor over it (but remember to not click on the link). This feature is supported by most browsers and email clients. As we can see from the following figure, the target domain of the link is also very suspicious:
beachmountainXXX.net/AYowCJbK
.
Malicious Content
The downloaded file (e.g.
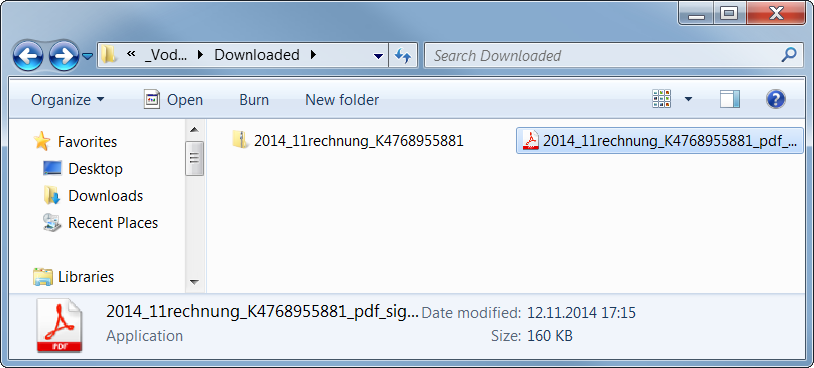
2014_11rechnung_K4768955881.zip
) is a ZIP archive containing an executable file. The user is fooled by the application’s icon (similar to Adobe Reader) to think that it is a PDF file, which is yet another well-known trick used by malware authors.
If you are not sure about the real file type, you can see the file properties.
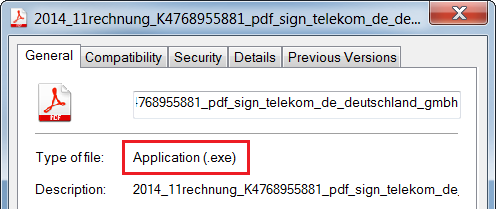
For the following analysis of the malicious content, we use a sample with the MD5 checksum
b0a152fe885a13a6ffb0057f6f21912f
. It is an executable file downloaded from one of these links, likely originally written in C++ by using MFC.
First Stage
The (unwanted) execution of this file starts the first phase of the malicious behavior.
The file itself is 160 kB large, but most of its size is stored within the resource file masked as the following GIF image (109 kB).
The author of this sample used steganography because 99% bytes of the image content represents an encrypted code. This code is decrypted first and the control is passed to this decrypted code.
Furthermore, WinAPI functions are called indirectly (via functions
LoadModule()
and
GetProcAddress()
) and names of these functions are obfuscated and decoded during run-time on the application’s stack in order to make analysis more difficult.
Afterwards, it creates a new process with the same name and fills its sections with the decrypted code from the GIF image (via the
WriteProcessMemory()
function).
This new process copies the original file into
C:Users%USERNAME%AppDataRoamingIdentitiesqwrhwyyy.exe
(as a read-only system file), registers itself to be run at system startup (registry key
HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun
), and deletes the original file by using a generated batch file.
Once the file is executed from this new location, it behaves differently:
It checks whether it is analyzed or virtualized via the following techniques.
- Detection of a loaded Sandboxie module
SbieDll.dll
and detection of running processes
VboxService.exe
(VirtualBox) and
vmtoolsd.exe
(VMware).
- It also uses the
GetTickCount()
function to detect whether it has really started during the startup and also to detect debuggers. - If any of these is detected, the executable file stops its malicious activity.
Afterwards, it extracts and decrypts another executable file on stack from the aforementioned GIF image and injects it into other processes, such as
explorer.exe
,
firefox.exe
. This starts the second stage of infection. Note: some versions of this malware try also to check a working Internet connection via a DnsQuery of www.microsoft.com before starting the second stage.
Second Stage
This extracted file is relatively small (52 kB) because it is packed by the UPX packer (version 3.08).
After its run-time unpacking, it uses the same anti-debugging tricks as the previous sample.
The main body of this file can be described by the following decompiled code:
CreateMutexA(0, 1, mutexName); // "qazwsxedc"
Sleep(1800000); // wait for 30 minutes
WSAStartup(0x202, &WSAData); // initiate Winsock
seconds = getLocalTimeInSeconds(0);
if (GetTickCount() < 1920000 /* 32 minutes after startup */ &&
GetTickCount() > 1000) {
while (1) {
malicious(); // the main functionality
gStateInactive = 1;
Sleep(300000); // wait for 5 minutes
}
}
- For synchronization between the first and second stage, the mutex
qazwsxedc
is used (e.g. another variation of classical
qwert
or
asdfg
names).
- Afterwards, the malware waits for 30 minutes to remain stealthy. After that, it also checks whether no more than 32 minutes have passed since the system startup (i.e. whether it was started during the first two minutes after startup).
- In its main loop, it follows the malicious behavior described in the remaining paragraphs (function
malicious()
). After each iteration, it makes a 5 minutes break before the next action.
In this function, the string
DC85CCC4C4CCC7CED385C6CE919F9F98
is decrypted at first by using the fixed XOR key
0xAB
. The resulting string
w.googlex.me:443
represents a remote address of the command-and-control (C&C) host and its port. The second one is
m.googlex.me:53
. At first, the sample tries to check connection with these servers by using the Winsock functions. The other samples contain different lists of C&C servers:
ahokcjidanptacyu.eu gctrbwqyxxyamcnn.eu ggcrguelfhvtuxdb.eu gkkelsrkypraqhto.eu gunvpvqhnwxxgjsn.eu gvlmoefoqapvrvec.eu mcfpeqbotiwxfxqu.eu ...
Afterwards, it obtains information about the local computer, such as:
- computer name;
- version of operating system;
- processor information and number of cores;
- memory information.
English (United States) // local settings TEST-PC // PC name Windows 7 Professional // Windows version 4096 MB // memory Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-1620 v2 @ 3.70GHz | CORE 8 // CPU 2014-10 // malware version
Afterwards, this information is encrypted and send as a registration to a C&C server from the aforementioned list. The reply from the server is encrypted by the same algorithm. The very first byte of the reply message specifies an action (i.e. a control code) to be performed. To date, we have identified the following codes:
- 18, 19, and 20 – open a specified page in Internet Explorer (with minor differences).
- 16 and 17 – download and execute a file specified within the message. The file is downloaded via the
URLDownloadToFile()
function, stored with a random name, e.g.
%TMP%mibww.exe
and executed via the
WinExec()
function.
- 6 – terminate the process (itself).
- 5 – inactivate itself for a specified time.
- 2, 3, and 4 – these codes imply different types of online communication with other systems (e.g. for downloading other malware modules, communication with other infected systems, attacking specified targets). The communication is executed via a server-specified number of threads running the following built-in functions. Arguments to these functions are also sent within the messages from a C&C server. All of these functions are based on Winsock functions.
- Sending a message to a given IP address (or host name) and port.
- Communication with a remote server on ports 21 and 22.
- Sending multiple types of HTTP GET requests to specified servers.
GET %FILE% HTTP/1.1 Accept: image/gif, image/x-xbitmap, image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/x-shockwave-flash, application/vnd.ms-excel, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint, application/msword, */* Accept-Language: en-us Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate User-Agent:Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE %VERSION%.0; Windows NT %VERSION%.1; SV1) Host: %HOST%:%PORT% Connection: Keep-Alive GET %FILE% HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: text/html Host: %HOST% Accept: text/html, */* User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (X11; U; Linux i686; en-US; re:1.4.0) Gecko/20080808 Firefox/%VERSION%.0 GET %FILE% HTTP/1.1 Referer: http://%ADDR%:80/http://%ADDR% Host: %HOST% Connection: Close Cache-Control : no-cache GET %FILE% HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: text/html Host: %HOST% Accept: text/html, */* User-Agent:Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE %d.00; Windows NT %d.0; MyIE 3.01)
Those actions are constantly executed until the process is terminated by the C&C server (unlikely) or by user (e.g. system shutdown). However, this process is started once again during the system startup.
As we can see, it is up to the attacker to download and execute other malicious modules, such as password stealers, bankers, or to include the infected PC into a botnet.
Conclusion
Although, the analyzed phishing emails are far from perfect (download links and sender addresses are suspicious, the text of email is only available in German, etc.), it is still possible to fool a user into executing the malicious file. This file is powerful enough to infect the user’s machine and turn it into an unsafe place.
Here are some basic tips, that we’ve previously shared about how to detect a phishing email:
- Check the spelling and grammar – it is unlikely that your bank or service provider will send you an email with such mistakes.
- Sender’s name and email address can be spoofed, do not rely on them.
- Look at the target address of the link – different domains than the official ones are highly suspicious.
- Do not panic and do not do any action in haste. The attacker often tries to threaten you and make a time pressure on you.
- Do not open suspicious attachments or links. If you really need to open a file, check its file type before double-clicking it. The file name and icon can be easily crafted to look like a picture or document.
- If you are not sure about the email’s origin, try to contact that company directly (e.g. call official customer care), but do not respond to such email and never ever send your credentials in this way.
- And as always: use AVG to stay protected.
EC3 Head Paints Bleak Cybercrime Picture
Troels Oerting, head of Europol’s EC3, explains the extreme difficulties law enforcement faces when investigating and prosecuting cybercrime at Georgetown Law’s Cybercrime 2020.
DOJ Launches New Cyber Unit, Claims Privacy is Mission Critical
The United States Department of Justice yesterday announced the creation of a new cybercrime unit within its Computer Crime and Intellectual Property Section.
Researcher Releases Database of Known-Good ICS and SCADA Files
A prominent security researcher has put together a new database of hundreds of thousands of known-good files from ICS and SCADA software vendors in an effort to help users and other researchers identify legitimate files and home in on potentially malicious ones. The database, known as WhiteScope, comprises nearly 350,000 files, including executables and DLLs, […]
AirHopper, the malware that infects your corporate network even though you are not connected to the Internet
Seems logical, doesn’t it? If your company has ever warned you that you must tread very carefully when browsing the Internet so that your computer (and sooner or later, every computer in the office) does not get infected with a virus, it would be normal to think that going offline is not a bad (although drastic) alternative.
We are very sorry but you cannot rest easy even if the computer you use at work is not connected to the Internet; it is still vulnerable unless you have an enterprise antivirus solution like Panda Advanced Protection Services.

To start, a pen drive can easily replace the Internet for malicious pursuits. Your work computer’s USB port will thereby become your Internet connection, as far as viruses are concerned, as this would be its entrance.
However, USB ports are not your work computer’s only weak spot if you do not have an Internet connection. There are other vulnerabilities that compromise, and greatly, the security of your computer.
One of these vulnerabilities lies in the radio receivers on smartphones and electromagnetic signals, as proven by AirHopper, a malware that can infect a computer and collect data from it without needing it to be online.
Although it sounds complicated, a group of researchers in Israel have proved it in a study: A computer without an Internet connection is also vulnerable. To start, the cyber-crook needs to install AirHopper on the computer. That is undoubtedly the largest hurdle faced by data thieves because unfortunately, the rest is a breeze.
Once AirHopper is installed on the computer, the malware uses the monitor to emit electromagnetic signals whenever a key is pressed. The cyber-criminal, who must be within seven meters of the computer, will need a smartphone with FM radio to receive the data typed on the computer.
According to the researchers, the data can be transmitted from the computer to the cyber-criminal’s smartphone screen at a rate of 13 to 60 bytes per second.
It might not seem like a fast method that downloads large amounts of data but it is fast enough for a cyber-criminal to steal passwords in just 8 seconds or short texts that you type into your work computer.

Fortunately, it is a type of attack that will probably not go beyond being a proof of concept, as in order to carry it out the cyber-criminal needs physical access to the computer in order to infect it, and then needs to be close by in order to receive the data you type on their smartphone. In addition, not all monitors can emit electromagnetic waves that are strong enough.
So now you know; if you want to keep your company secure from these types of threats, request a free demo of Panda Advanced Protection Services and our team of experts will help you with whatever you need.
The post AirHopper, the malware that infects your corporate network even though you are not connected to the Internet appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.
Gamer PCs – how to keep yours clean and mean
Gamers have become major targets for hackers – from large-scale attacks against gaming companies, to small-scale scams carried out via game chat channels. But a few easy security steps should help keep your precious rig at full speed – and safe.
The post Gamer PCs – how to keep yours clean and mean appeared first on We Live Security.
![]()
Cyber Monday – 12 tips to help you shop safely online
Technology might evolve, but cyber gangs rely on tried-and-tested tactics. With a bit of care and attention, it’s easy to sort the genuine bargains from the too-good-to-be-true fakes.
The post Cyber Monday – 12 tips to help you shop safely online appeared first on We Live Security.
![]()
Do I need to worry about threats like Regin?
Since the discovery of Stuxnet several years ago, there has been a parade of targeted malware that may have been created or sponsored by nation states. Does an average person or business really need to worry about these things?
The post Do I need to worry about threats like Regin? appeared first on We Live Security.
![]()
Rootpipe, WireLurker and Masque Attack, the latest vulnerabilities on Apple devices
You have heard it more than once but it is a myth. It always has been. It does not matter how many times you have been told, Macs do have viruses. It is true that, until not too long ago, Apple computers were not a major target for cyber-crooks, but things are changing.
However, the fact that viruses do affect Macs is nothing new. Back in 1982 malware swarmed the old Apple II. That distant beginning of viruses on Apple machines was just an experiment but it already reflected the harsh reality. Gradually, at a much slower pace than PCs, Macs are also suffering the effects of some infection or other.

The myth that there are no Mac viruses does have a basis, as malware has not roamed freely around Apple computers for various reasons. The main reason is that as Macs were not as widely-used, they were dismissed by cyber-crooks for developing malicious software targeting these machines.
However, the increasing presence of Macs on the market has changed this trend. They are popular and cyber-crooks do not want to miss the opportunity to spread their seeds of evil through these machines.
So, there are a few threats to bear in mind if you have a Mac and the dangers are increasing. In recent months quite a few vulnerabilities have been discovered that put the computers of the company managed by Tim Cook in the firing line.
Rootpipe and WireLurker, Mac vulnerabilities
One of them is Rootpipe. Discovered by a Swedish hacker just a few days ago, it is a critical security hole in OS X Yosemite, the latest version of Apple’s operating system. The flaw, for which a patch is not expected until the beginning of next year, allows cyber-crooks to act as the software administrator on third-party computers. In other words, get into your Mac without your consent.
The vulnerability and Apple’s delay in releasing a patch are very worrying but they are not the only security problem facing Mac users recently. A few days after Rootpipe was discovered, WireLurker came to light, a new malware family affecting Apple devices created in China and which has come to be considered the largest threat to them so far.
In this case, Mac users and the company can rest easier, as the Cupertino firm, which has identified 146 infected apps, has stopped the virus from spreading any further by blocking the apps responsible.
If you want to block Mac OS X malware as well as Windows malware, try the best antivirus for Mac.

Masque Attack, security flaw on iPads and iPhones
The cherry on this cake, which in just a few weeks brought the Apple device security myth crashing down, came with Masque Attack. A security hole in the majority of iPads and iPhones that makes them vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
Masque Attack allows cyber-crooks to access users’ personal data, even managing to get control of their devices. In this case, the Cupertino firm did react rapidly, but not fixing the threat but by releasing a statement down playing the importance of Masque Attack and insisting that iOS and OS X have various measures that warn users against installing potentially malicious software.
In any case, the best thing you can do to make sure that your iPad and iPhone are kept secure is to download apps from trusted sites only, such as the App Store, as the door cyber-crooks use to access your device is no other than making you download a malicious app. So remember, only download things from reliable sites and of course, forget about Apple not having any viruses.
The post Rootpipe, WireLurker and Masque Attack, the latest vulnerabilities on Apple devices appeared first on MediaCenter Panda Security.