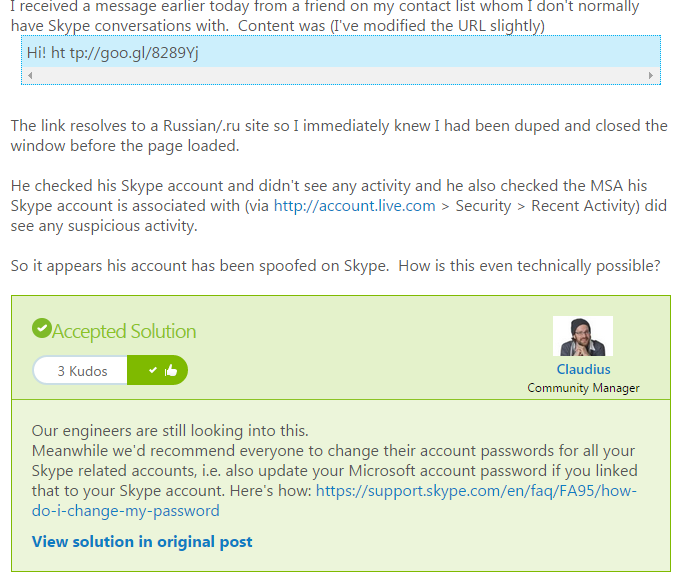
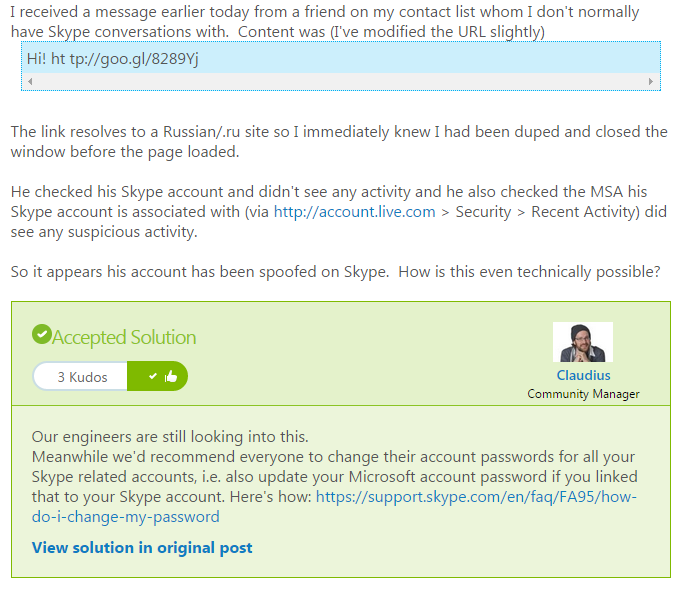
Threat analysts and malware researchers in the Avast Virus Lab detect and neutralize threats as soon as they appear.
The Avast Threat Report provides an overview of global threat activity.
Avast malware researchers and Avast customers work 24/7 to protect each other.
Avast protects 230 million people worldwide in more than 186 different countries — we are present in more countries than McDonalds and protect more people than any other antivirus security provider. We stream 250 micro updates a day that protect our users from attacks. This is made possible by the 230 million devices we protect that simultaneously act as de facto sensors. These sensors provide us with information about suspicious files to help detect and neutralize threats as soon as they appear. Once we identify a suspicious file on a single device, it is reported back to the Avast servers and all Avast users around the world are immediately protected. This is called our Community IQ – it not only lets us better protect our users but also gives us valuable insights into the current security landscape.
Top targeted countries
Romania, Turkey and Vietnam were targeted the most in terms of PC threats in Q1 of 2015, with Romanians having a 54% chance of encountering threats. In France, Germany, Brazil, Great Britain and the United States, the chances were much lower; nonetheless, nearly one out of every three PC users encountered threats in these countries.
Percentage of PC threats encountered by country:
- 41 percent Russia
- 37 percent Spain
- 34 percent Brazil and France
- 29 percent Germany
- 28 percent United States and Great Britain
Within the mobile sphere, Romania also had a high chance of encountering malware, along with China and Malaysia.China was targeted the most, which is most likely due to the fact that the Google Play Store is blocked in the region and, therefore, mobile users download apps from third-party stores.
The number of users accessing the Internet in China via mobile devices has surpassed the number of users accessing the Internet via PC this year, which also makes them an attractive point of access for cybercriminals on the hunt for a widespread target pool.
Percentage of mobile threats encountered by country:
- 21 percent Russia
- 16 percent Spain
- 12 percent United States
- 10 percent Brazil
- 8 percent France and United Kingdom
- 6 percent Germany
Top detections and exploits
Despite Android being fairly secure, mobile malware did grow dramatically with potentially unwanted programs (PUPs – a cute acronym for a not-so-cute threat), including adware, dominating the top ten Android detections.
On the PC side, the majority of the top ten detections included LNK files. LNK files are used to create shortcuts that typically point to an executable file or script and appear on one’s computer desktop as an icon, tricking users into using malicious shortcuts.
In terms of exploits, two of the biggest vulnerabilities that were exploited targeted Javascript and an HTML parser. The first exploit, targeting Javascript, could lead to a remote code execution in Internet Explorer versions 6 to 10 The second, on the other hand, targeted an HTML parser in Internet Explorer 10, and if successful, the attack could lead to remote code execution. Even if the attack was unsuccessful, it could still cause a denial of service.
Malicious ways
We observed a variety of tricks that cybercriminals use and one interesting, less common technique cybercriminals use is domain rotation. This method regularly creates new domains and subdomains and redirects malicious traffic to them. This is done to avoid blacklisting and capitalizes on the fact that it takes time for antivirus software to find and check these new domains, releasing new detections after they’ve been properly examined. Fortunately, Avast uses advanced algorithms to recognize domain rotations and block infected subdomains.
We also watched ransomware targeting PCs and mobile devices evolve. For example, PC ransomware CryptoWall did not originally use anonymization networks in earlier versions. CryptoWall 2.0 began using TOR to communicate with the command and control (C&C) server and now CryptoWall 3.0 uses I2P (Invisible Internet Project) a lesser-known anonymization network to avoid being blocked. Mobile ransomware Simplocker, on the other hand, reappeared in February 2015 using asymmetrical cryptography, making it impossible to recover encrypted data without accessing the C&C server.
Global Wi-Fi experiment
We not only observe malware threats, but we also ventured out of the office to further explore the security risks of public Wi-Fi. Our mobile security experts traveled to nine cities in the United States (San Francisco, Chicago, New York), Europe (Barcelona, London, Berlin), and Asia (Seoul, Hong Kong, Taipei) to observe public Wi-Fi activity.
Our observations revealed major security flaws in Wi-Fi hotspots and showed how easy it is for hackers to view users’ browsing activity, searches, passwords, videos, emails, and other personal information. While security issues were found in all cities, the experiment showed that users in Asia are more prone to attacks than users in both Europe and the U.S. Users in Berlin and San Francisco were most likely to take the necessary steps to protect their browsing.
Our experiment also shed light on the fact that a significant portion of users browse primarily on unsecured HTTP sites while connected to open Wi-Fi networks. HTTP traffic is not encrypted and is therefore unprotected, meaning that our team was able to view all of the users’ browsing activity, including domain name and page history, searches, personal log information, videos, emails, and comments. Taking this a step further, it was even possible for the Avast researchers to see products that a user browsed on eBay while not being logged in to the site as well as articles that people read on Wikipedia.
We have put together a security report for the first quarter of 2015, which includes a list of top targeted countries, threats, exploits, domain detections and much more. Open the full Avast Threat Report here.
Follow Avast on Facebook, Twitter and Google+ where we keep you updated on cybersecurity news every day