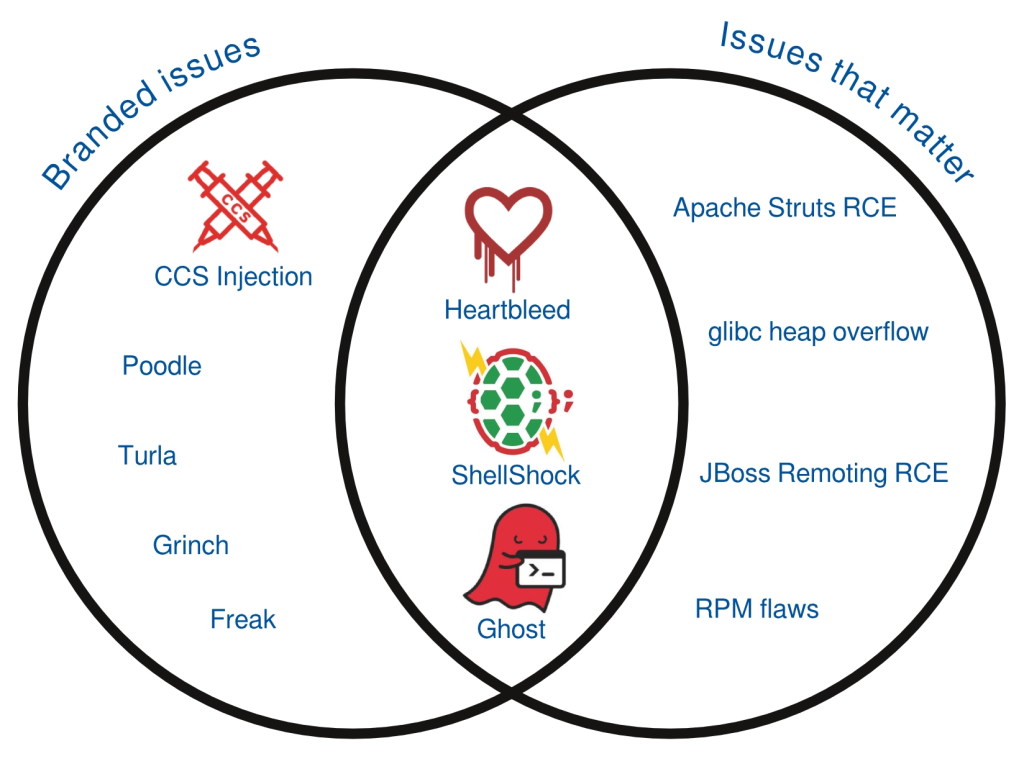
It’s been almost a year since the OpenSSL Heartbleed vulnerability, a flaw which started a trend of the branded vulnerability, changing the way security vulnerabilities affecting open-source software are being reported and perceived. Vulnerabilities are found and fixed all the time, and just because a vulnerability gets a name and a fancy logo doesn’t mean it is of real risk to users.
So let’s take a tour through the last year of vulnerabilities, chronologically, to see what issues got branded and which issues actually mattered for Red Hat customers.
“Heartbleed” (April 2014)CVE-2014-0160
Heartbleed was an issue that affected newer versions of OpenSSL. It was a very easy to exploit flaw, with public exploits released soon after the issue was public. The exploits could be run against vulnerable public web servers resulting in a loss of information from those servers. The type of information that could be recovered varied based on a number of factors, but in some cases could include sensitive information. This flaw was widely exploited against unpatched servers.
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux, only customers running version 6.5 were affected as prior versions shipped earlier versions of OpenSSL that did not contain the flaw.
Apache Struts 1 Class Loader RCE (April 2014) CVE-2014-0114
This flaw allowed attackers to manipulate exposed ClassLoader properties on a vulnerable server, leading to remote code execution. Exploits have been published but they rely on properties that are exposed on Tomcat 8, which is not included in any supported Red Hat products. However, some Red Hat products that ship Struts 1 did expose ClassLoader properties that could potentially be exploited.
Various Red Hat products were affected and updates were made available.
OpenSSL CCS Injection (June 2014) CVE-2014-0224
After Heartbleed, a number of other OpenSSL issues got attention. CCS Injection was a flaw that could allow an attacker to decrypt secure connections. This issue is hard to exploit as it requires a man in the middle attacker who can intercept and alter network traffic in real time, and as such we’re not aware of any active exploitation of this issue.
Most Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions were affected and updates were available.
glibc heap overflow (July 2014) CVE-2014-5119
A flaw was found inside the glibc library where an attacker who is able to make an application call a specific function with a carefully crafted argument could lead to arbitrary code execution. An exploit for 32-bit systems was published (although this exploit would not work as published against Red Hat Enterprise Linux).
Some Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions were affected, in various ways, and updates were available.
JBoss Remoting RCE (July 2014) CVE-2014-3518
A flaw was found in JBoss Remoting where a remote attacker could execute arbitrary code on a vulnerable server. A public exploit is available for this flaw.
Red Hat JBoss products were only affected by this issue if JMX remoting is enabled, which is not the default. Updates were made available.
“Poodle” (October 2014) CVE-2014-3566
Continuing with the interest in OpenSSL vulnerabilities, Poodle was a vulnerability affecting the SSLv3 protocol. Like CCS Injection, this issue is hard to exploit as it requires a man in the middle attack. We’re not aware of active exploitation of this issue.
Most Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions were affected and updates were available.
“ShellShock” (September 2014) CVE-2014-6271
The GNU Bourne Again shell (Bash) is a shell and command language interpreter used as the default shell in Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Flaws were found in Bash that could allow remote code execution in certain situations. The initial patch to correct the issue was not sufficient to block all variants of the flaw, causing distributions to produce more than one update over the course of a few days.
Exploits were written to target particular services. Later, malware circulated to exploit unpatched systems.
Most Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions were affected and updates were available.
RPM flaws (December 2014) CVE-2013-6435, CVE-2014-8118
Two flaws were found in the package manager RPM. Either could allow an attacker to modify signed RPM files in such a way that they would execute code chosen by the attacker during package installation. We know CVE-2013-6435 is exploitable, but we’re not aware of any public exploits for either issue.
Various Red Hat Enterprise Linux releases were affected and updates were available.
“Turla” malware (December 2014)
Reports surfaced of a trojan package targeting Linux, suspected as being part of an “advance persistent threat” campaign. Our analysis showed that the trojan was not sophisticated, was easy to detect, and unlikely part of such a campaign.
The trojan does not use any vulnerability to infect a system, it’s introduction onto a system would be via some other mechanism. Therefore it does not have a CVE name and no updates are applicable for this issue.
“Grinch” (December 2014)
An issue was reported which gained media attention, but was actually not a security vulnerability. No updates were applicable for this issue.
“Ghost” (January 2015) CVE-2015-0235
A bug was found affecting certain function calls in the glibc library. A remote attacker that is able to make an application call to an affected function could execute arbitrary code. While a proof of concept exploit is available, not many applications were found to be vulnerable in a way that would allow remote exploitation.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions were affected and updates were available.
“Freak” (March 2015) CVE-2015-0204
It was found that OpenSSL clients accepted EXPORT-grade (insecure) keys even when the client had not initially asked for them. This could be exploited using a man-in-the-middle attack, which could downgrade to a weak key, factor it, then decrypt communication between the client and the server. Like Poodle and CCS Injection, this issue is hard to exploit as it requires a man in the middle attack. We’re not aware of active exploitation of this issue.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions were affected and updates were available.
Other issues of customer interest
We can also get a rough guide of which issues are getting the most attention by looking at the number of page views on the Red Hat CVE pages. While the top views were for the issues above, also of increased interest was:
- A kernel flaw (May 2014) CVE-2014-0196, allowing local privilege escalation. A public exploit exists for this issue but does not work as published against Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- “BadIRET”, a kernel flaw (December 2014) CVE-2014-9322, allowing local privilege escalation. Details on how to exploit this issue have been discussed, but we’re not aware of any public exploits for this issue.
- A flaw in BIND (December 2014), CVE-2014-8500. A remote attacker could cause a denial of service against a BIND server being used as a recursive resolver. Details that could be used to craft an exploit are available but we’re not aware of any public exploits for this issue.
- Flaws in NTP (December 2014), including CVE-2014-9295. Details that could be used to craft an exploit are available. These serious issues had a reduced impact on Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- A flaw in Samba (February 2015) CVE-2015-0240, where a remote attacker could potentially execute arbitrary code as root. Samba servers are likely to be internal and not exposed to the internet, limiting the attack surface. No exploits that lead to code execution are known to exist, and some analyses have shown that creation of such a working exploit is unlikely.
Conclusion
We’ve shown in this post that for the last year of vulnerabilities affecting Red Hat products the issues that matter and the issues that got branded do have an overlap, but they certainly don’t closely match. Just because an issue gets given a name, logo, and press attention does not mean it’s of increased risk. We’ve also shown there were some vulnerabilities of increased risk that did not get branded.
At Red Hat, our dedicated Product Security team analyse threats and vulnerabilities against all our products every day, and provide relevant advice and updates through the customer portal. Customers can call on this expertise to ensure that they respond quickly to address the issues that matter, while avoiding being caught up in a media whirlwind for those that don’t.